While you put your hand out the window of a transferring automotive, you are feeling a power pushing towards you referred to as drag. This power opposes a transferring car, and it’s a part of the explanation why your automotive naturally slows to a prevent if you’re taking your foot off the gasoline pedal. However drag doesn’t simply decelerate automobiles.
Aerospace engineers are operating on the use of the drag power in house to expand extra fuel-efficient spacecraft and missions, deorbit spacecraft with out growing as a lot house junk, or even position probes in orbit round different planets.
Area isn’t an entire vacuum − a minimum of now not it all. Earth’s environment will get thinner with altitude, but it surely has sufficient air to impart a power of drag on orbiting spacecraft, even as much as about 620 miles (1,000 kilometers).
As an aerospace engineering professor, I learn about how drag impacts the motion of spacecraft in orbit. Aerobraking, because the title suggests, is one of those maneuver that makes use of the skinny air in house to use a drag power within the route reverse to a spacecraft’s movement, similar to braking in a automotive.
Converting an orbit
In house, aerobraking can trade the orbit of a spacecraft whilst minimizing using its propulsion gadget and gasoline.
Spacecraft that orbit round Earth achieve this in two kinds of orbits: round and elliptical. In a round orbit, the spacecraft is at all times on the similar distance from the middle of the Earth. Because of this, it’s at all times transferring on the similar pace. An elliptical orbit is stretched, so the space from Earth − and the rate the craft strikes at − adjustments because the spacecraft travels alongside the orbit.
The nearest level in an elliptical orbit round Earth, the place the satellite tv for pc or spacecraft is transferring quickest, is named the perigee. The farthest level, the place it’s transferring slowest, is named the apogee.
The apogee is the purpose farthest from Earth in an elliptical orbit, whilst the perigee is the purpose closest to Earth.
Iketsi/Wikimedia Commons, CC BY-SA
The overall concept at the back of aerobraking is to start out in a big round orbit and maneuver the spacecraft right into a extremely elliptical orbit, in order that the bottom level within the orbit − the perigree − lies within the denser a part of the higher environment. For Earth, that’s between about 62 and 310 miles (100 and 500 kilometers), with the selection relying on time required to finish the orbit trade.
Because the spacecraft passes via this lowest level, the air exerts a drag power on it, which reduces the stretch of the orbit over the years. This power pulls the craft towards a round orbit smaller than the unique orbit.
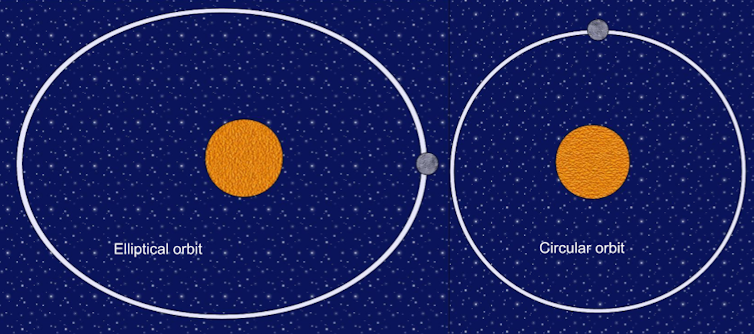
Aerobraking brings a spacecraft from a big, round orbit right into a extremely elliptical orbit, right into a smaller, extra round one.
Moneya/Wikimedia Commons, CC BY-SA
The primary maneuver to place the spacecraft in an elliptical orbit in order that drag can take impact does require the use of a propulsion gadget and a few gasoline. However as soon as it’s within the elliptical orbit, drag from the ambience slows the craft, and it doesn’t want to use a lot, if any, gasoline.
Aerobraking brings a craft from a big orbit to a small orbit and isn’t reversible − it may well’t building up the dimensions of an orbit. Expanding the dimensions of an orbit or elevating the spacecraft to a better orbit calls for propulsion and gasoline.
Aerobraking makes use of
A not unusual case the place spacecraft controllers use aerobraking is when converting the craft’s orbit from a geostationary orbit − GEO − to a low Earth orbit, LEO. A GEO orbit is a round orbit with an altitude of kind of 22,236 miles (35,786 km). In GEO, the spacecraft makes one orbit round Earth in 24 hours, so the spacecraft at all times remains above the similar level on Earth’s floor.
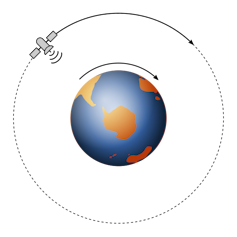
In GEO orbit, a spacecraft orbits with Earth and remains above the similar level at the floor the entire time.
MikeRun/Wikimedia Commons, CC BY-SA
Earlier than aerobraking, the spacecraft’s onboard propulsion gadget thrusts in the wrong way of the GEO orbit’s movement. This thrust places it into an elliptical orbit. The craft passes throughout the environment more than one occasions, which in the end circularizes the orbit.
As soon as it makes it to LEO, the spacecraft might want to use slightly little bit of gasoline to propel itself up into its goal orbit. Normally, the bottom level of the unique elliptical orbit is less than the general goal round orbit.
This procedure is conceptually very similar to how the U.S. Area Power’s X-37B used aerobraking in early 2025.
The U.S. Area Power reported that its unmanned spaceplane, X-37B, used aerobraking. This take a look at demonstrated the craft’s agility and maneuverability.
Every other utility for aerobraking is to make a spacecraft deorbit − or reenter the ambience − after it has stopped operating. This manner, the corporate or company can get rid of the spacecraft and steer clear of growing house junk, since it’ll deplete within the decrease environment.

NASA’s Mars reconnaissance orbiter used aerobraking to orbit round Mars.
NASA/JPL
Aerobraking for interplanetary missions
A couple of Mars missions, together with the Mars reconnaissance orbiter and the Mars Odyssey orbiter, have used aerobraking to achieve their goal orbits across the crimson planet.
For interplanetary missions like those, scientists use aerobraking along side the craft’s onboard propulsion gadget. When a spacecraft arrives at Mars, it does so in a hyperbolic orbit.
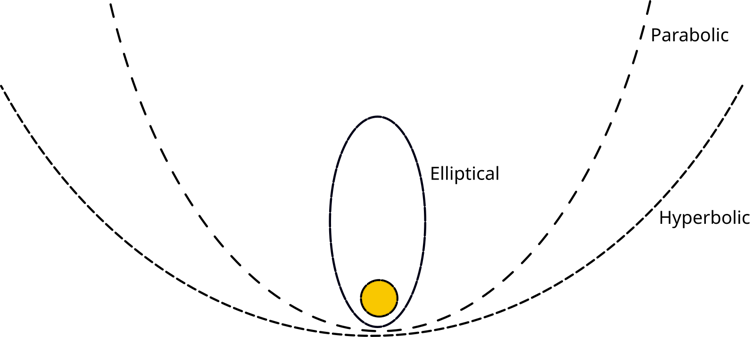
Whilst an elliptical orbit is closed, a hyperbolic orbit doesn’t cross the entire method round a planet.
Maxmath12/Wikimedia Commons
In contrast to a round or an elliptical orbit, the spacecraft’s trail in hyperbolic orbit gained’t stay it orbiting round Mars. As an alternative, it will fly via and leave Mars − until it makes use of thrust from its propulsion gadget to get “captured” right into a closed elliptical orbit.
Because the spacecraft arrives at Mars, the onboard propulsion gadget fires to give you the power important to seize the spacecraft right into a extremely elliptical orbit round Mars. As soon as captured, scientists use aerobraking over a number of orbital passes throughout the environment to reach the general orbit, in most cases a round one.
Aerobraking maneuvers may end up in important gasoline financial savings. As people get nearer to touchdown at the floor of the crimson planet, the gasoline financial savings enabled through aerobraking may just save mass and make allowance each and every spacecraft headed to Mars to take extra provides.
Within the grand arc of house exploration, aerobraking isn’t just a maneuver. It has a the most important function to play someday of house operations and planetary missions and colonization.




