Consider a wholesome wooded area, house to a lot of species: Birds are flitting between tree branches, salamanders are sliding via leaf muddle, and wolves are monitoring the smell of deer during the understory. Each and every of those animals has a job within the wooded area, and maximum ecologists would argue that dropping any this type of species can be dangerous for the ecosystem as a complete.
As an ecologist, I’m fascinated with what those adjustments imply for ecosystems – can those newly arrived species functionally exchange the species that was there? I studied this procedure in japanese North The usa, the place some best predators have disappeared and a brand new predator has arrived.
A primer on predators
Wolves used to roam throughout each state east of the Mississippi River. However because the land was once evolved, many of us considered wolves as threats and wiped maximum of them out. At the moment, a mixture of grey wolves and japanese wolves persist in Canada and across the Nice Lakes, which I jointly confer with as northeastern wolves. There’s additionally a small inhabitants of crimson wolves – a definite and smaller species of wolf – at the coast of North Carolina.
The disappearance of wolves can have given coyotes the chance they wanted. Beginning round 1900, coyotes started increasing their vary east and feature now colonized the majority of japanese North The usa.
Coyotes colonized maximum of japanese North The usa within the wake of wolf extirpation.
Jensen 2025, CC BY
So are coyotes the brand new wolf? Can they fill the similar ecological position that wolves used to? Those are the questions I set out to reply to in my paper printed in August 2025 within the Stacks Magazine. I taken with their position as predators – what they devour and the way incessantly they kill giant herbivores, akin to deer and moose.
What’s at the menu?
I began by way of reviewing each paper I may just to find on wolf or coyote diets, recording what % of scat or abdomen samples contained not unusual meals pieces akin to deer, rabbits, small rodents or fruit. I when put next northeastern wolf diets to northeastern coyote diets and crimson wolf diets to southeastern coyote diets.
I discovered two placing variations between wolf and coyote diets. First, wolves ate extra medium-sized herbivores. Particularly, they ate extra beavers within the northeast and extra nutria within the southeast. Either one of those species are massive aquatic rodents that affect ecosystems – beaver dam construction adjustments how water strikes, infrequently undesirably for land homeowners, whilst nutria are non-native and destructive to wetlands.
2d, wolves have narrower diets general. They devour much less fruit and less omnivores akin to birds, raccoons and foxes, in comparison to coyotes. Because of this coyotes are most probably doing a little ecological roles that wolves by no means did, akin to dispersing fruit seeds of their poop and suppressing populations of smaller predators.
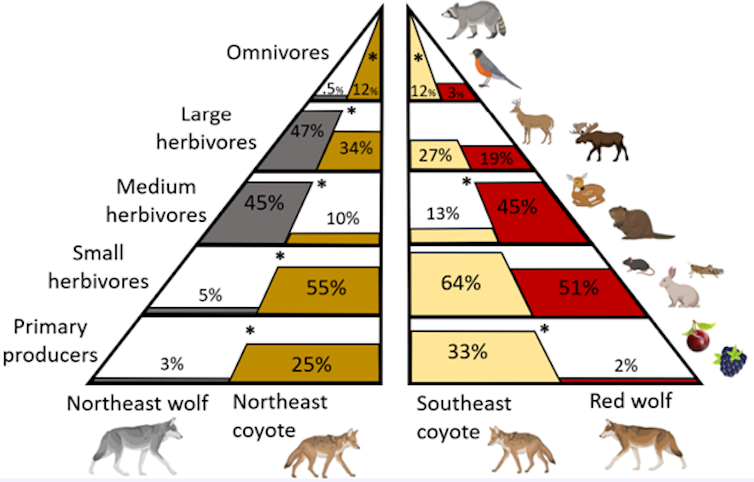
Grouping meals pieces by way of dimension and trophic stage printed some transparent variations between wolf and coyote diets. Percents are the % of samples containing every stage, and stars point out a statistically important distinction.
Alex Jensen, CC BY
Killing deer and moose
However vitamin research on my own can’t inform the entire tale – it’s generally not possible to inform whether or not coyotes killed or scavenged the deer they ate, as an example. So I additionally reviewed each learn about I may just to find on ungulate mortality – those are research that tag deer or moose, observe their survival, and characteristic a reason for demise in the event that they die.
Those research printed different necessary variations between wolves and coyotes. For instance, wolves had been accountable for a considerable proportion of moose deaths – 19% of adults and 40% of calves – whilst not one of the research documented coyotes killing moose. Because of this all, or just about all, of moose in coyote diets is scavenged.
Coyotes are adept predators of deer, alternatively. Within the northeast, they killed extra white-tailed deer fawns than wolves did, 28% in comparison to 15%, and a an identical proportion of grownup deer, 18% in comparison to 22%. Within the southeast, coyotes killed 40% of fawns however most effective 6% of adults.
Infrequently killing grownup deer within the southeast can have implications for different participants of the ecological group. For instance, after killing an grownup ungulate, many massive predators depart one of the crucial carcass at the back of, which will also be crucial supply of meals for scavengers. Even if there’s no information on how incessantly crimson wolves kill grownup deer, it’s most probably that coyotes aren’t supplying meals to scavengers to the similar extent that crimson wolves do.

Wolves and coyotes each kill a considerable share of deer, however they focal point on other age categories.
imageBROKER/Raimund Linke by way of Getty Photographs
Are coyotes the brand new wolves?
So what does this all imply? It implies that even supposing coyotes devour one of the crucial identical meals, they can’t absolutely exchange wolves. Variations between wolves and coyotes had been specifically pronounced within the northeast, the place coyotes hardly ever killed moose or beavers. Coyotes within the southeast had been extra very similar to crimson wolves, however coyotes most probably killed fewer nutria and grownup deer.
The go back of wolves is usually a herbal resolution for areas the place natural world managers need a aid in moose, beaver, nutria or deer populations.
But even with assistance from reintroductions, wolves will most probably by no means absolutely get well their former vary in japanese North The usa – there are too many of us. Coyotes, then again, do rather smartly round other people. So even though wolves by no means absolutely get well, a minimum of coyotes will likely be in the ones puts in part filling the position that wolves as soon as had.
Certainly, people have modified the arena such a lot that it can be not possible to go back to the best way issues had been ahead of other people considerably modified the planet. Whilst some recovery will indubitably be imaginable, researchers can proceed to guage the level to which new species can functionally exchange lacking species.






