The western US is a geologists’ dream, house to the Rocky Mountains, the Grand Canyon, lively volcanoes and hanging sandstone arches. However one landform merely doesn’t make sense.
Rivers most often glide round limitations. The Danube river, as an example, flows between the Alps and the Carpathians, twisting and turning to keep away from the mountains.
However in north-western Colorado, one river does the other.
The intimidatingly named Gates of Lodore marks the doorway to the 700-metre deep Canyon of Lodore that slices directly in the course of the Uinta Mountains as though the variability wasn’t there in any respect. It used to be created through the Inexperienced River, the most important tributary of the Colorado River (of Grand Canyon reputation).
For greater than 150 years, geologists have debated why the Inexperienced River selected such an peculiar trail, making a impressive canyon within the procedure.
The Inexperienced River carves its means in the course of the Uintas in Dinosaur Nationwide Monument, at the border of Colorado and Utah.
Eric Poulin / shutterstock
In 1876, John Wesley Powell, a mythical explorer and geologist pondered this query. Powell hypothesised that the river didn’t reduce in the course of the mountain, however as an alternative flowed over this course earlier than the variability existed. The river will have to have merely maintained its route because the mountains grew, carving the canyon within the procedure.
Sadly, geological proof presentations this can’t be the case. The Uinta Mountains shaped round 50 million years in the past, however we all know that the Inexperienced River has best been following this course for not up to 8 million years. Consequently, geologists had been compelled to hunt selection explanations.
And it sort of feels the solution lies a ways under the skin.
Drip drip
Colleagues and I’ve discovered proof for a procedure during which a part of the Earth’s crust turns into so dense that it starts to sink into the mantle underneath it. This phenomenon, referred to as a “lithospheric drip”, happens deep within the Earth, however may have profound results at the floor.
Drips ceaselessly shape underneath mountain levels. The sheer weight of the mountains carry temperatures and pressures on the base of the crust, inflicting dense minerals to shape. As those minerals gather, the decrease crust can change into heavier than the mantle it “floats” on. At this level, the crust starts to detach, or “drip”, into the mantle.
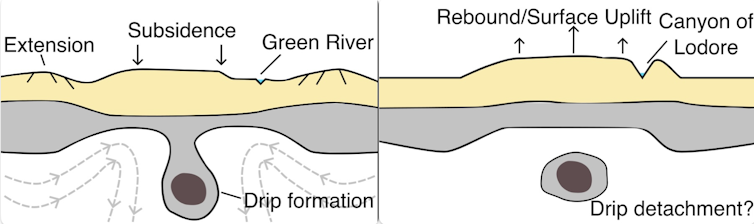
Dripping (left) then rebounding (proper).
Smith et al (2026)
On the floor, this reasons two issues. To begin with because the drip bureaucracy, it pulls the crust down, decreasing the peak of the mountain vary above. Then because the drip detaches, the crust springs or rebounds again. The entire procedure is like pulling a trampoline down after which letting it move once more.
For the Inexperienced River, this transient decreasing of the Uinta Mountains seems to have got rid of a essential barrier. The river used to be ready to pass the variability all through this low length, after which, as the variability rebounded, it carved the Canyon of Lodore because it endured on its new route.
A geological bullseye
Our proof for the lithospheric drip comes from the river networks across the Uinta Mountains. Rivers file a file of previous adjustments to landscapes, which geomorphologists can use to evaluate how the elevation of a mountain vary could have modified within the far away previous. The rivers across the Uintas display that the variability had lately (in geological phrases) gone through a segment of renewed uplift.
Via modelling those river networks, we have been ready to map out the uplift. The end result used to be hanging: a bullseye-shaped trend, with the best uplift on the centre of the mountain vary, with issues reducing farther from the centre. All over the world, this similar trend represents the telltale signal of a lithospheric drip. Equivalent indicators had been recognized in puts such because the Central Anatolian Plateau in Turkey, in addition to nearer to the Uinta Mountains at the Colorado Plateau or the Sierra Nevada of California.

An artists influence of a identical drip in Borneo.
Simone Pilia (symbol: Claudio Pilia)
To check whether or not this type of procedure used to be going on underneath the Uintas, we became to seismic tomography. This method is very similar to a scientific CT (computerised tomography) scan: as an alternative of the usage of X-rays, geophysicists analyse seismic waves from earthquakes to deduce the construction of the deep earth.
Present seismic imaging unearths a chilly, spherical anomaly greater than 100 miles under the skin of the Uintas. We interpreted this massive function, some 30-60 miles throughout, as our broken-off phase of the drip.
Via estimating the rate of the sinking drip, we calculated it had indifferent between 2 and 5 million years in the past. This timing fits the uplift inferred from within reach rivers and, crucially, completely fits separate geological estimates for when the Inexperienced River crossed the Uinta Mountains and joined the Colorado River.
Taken in combination, those other bits of proof level in opposition to a lithospheric drip being the cause that allowed the Inexperienced River to glide over the Uintas, resolving a 150-year-old debate.
A pivotal second within the historical past of North The united states
When the Inexperienced River carved in the course of the Uinta Mountains, it basically modified the panorama of North The united states. Reasonably than flowing eastwards into the Mississippi, it turned into a tributary of the Colorado River, and its waters have been redirected to the Pacific.
This rerouting altered the continental divide, the road that divides North American river methods that glide into the Atlantic from those who glide into the Pacific. In doing so, it created new obstacles and connections for natural world and ecosystems.
The tale of the Inexperienced River presentations that processes deep throughout the Earth may have profound affects for lifestyles at the floor. Over geological timescales, actions of country-sized lumps of minerals many miles under the skin can reshape mountains, redirect rivers and in the end affect lifestyles itself.






