In contemporary weeks, tough atmospheric river storms have swept throughout Washington, Oregon and California, unloading monumental quantities of rain. As rivers surged, they overtopped or breached a couple of levees – the ones lengthy, regularly left out boundaries conserving floodwaters again from properties and cities.
More often than not, levees don’t call for consideration. They quietly do their process, 12 months after 12 months. But if storms accentuate, levees abruptly subject in an excessively private means. They may be able to decide whether or not an area remains dry or finally ends up underwater.
The wear within the West displays a national drawback that has been construction for many years. Around the U.S., levees are ageing whilst climate is getting extra excessive. Many of those constructions have been by no means designed for the large duty they now raise.
Crews check up on harm to a Inexperienced River levee within the Seattle suburbs on Dec. 15, 2025. Hundreds of other folks have been advised to evacuate all through a chain of atmospheric river storms, and the Nationwide Guard was once despatched to observe and give a boost to a number of levees regarded as in danger.
AP Picture/Manuel Valdes
As a civil engineer at Tufts College, I find out about water infrastructure, together with the vulnerability of levees and methods for making them extra resilient. My analysis additionally displays that once levees fail, the effects don’t fall flippantly at the inhabitants.
Levees was essential infrastructure nearly accidentally
Many of us suppose levees have been constructed as a part of trendy, moderately engineered flood-control techniques. If truth be told, lots of the levees nonetheless in use as of late started a lot more humbly.
Many years in the past, farmers constructed easy earthen embankments to give protection to their fields and cattle from seasonal flooding. Those early levees have been sensible answers, formed by way of enjoy quite than formal engineering. They weren’t built the use of rigorous design requirements, and they didn’t practice constant building or repairs tips.
Through the years, the panorama round those levees modified. Farmland gave strategy to neighborhoods. Roads, railways, factories and ports expanded into floodplains. Populations grew. What have been as soon as modest, native constructions protective farms progressively was the primary defensive line for hundreds of thousands of other folks in properties and offices.
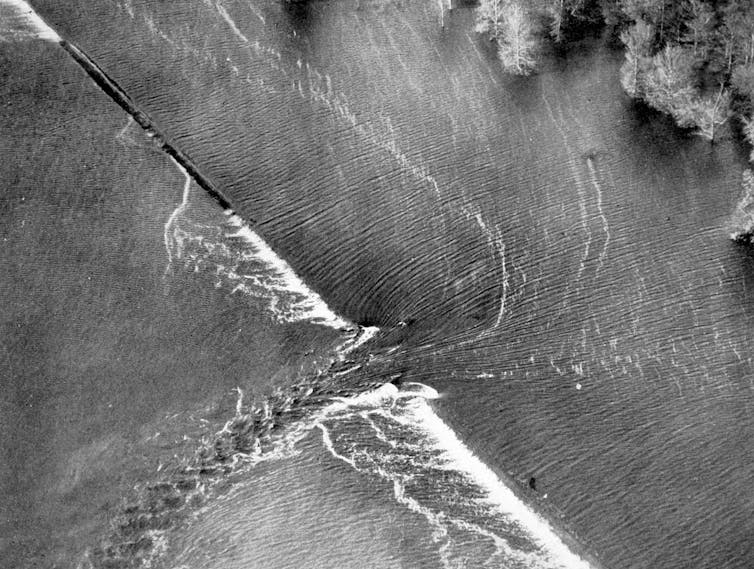

All over the Nice Mississippi Flood of 1927, the river poured over and broke via levees, flooding hundreds of sq. miles of land. Each overtopping and a breach are visual on this photograph.
Nationwide Climate Provider Archival Pictures by way of Steve Nicklas, NOS, NGS
With out a lot public debate or making plans, those semi-engineered levees took on a essential and unintentional position. The query that also lingers is whether or not they have been ever ready for it.
Huge, ageing levee machine now protective hundreds of thousands
Nowadays, the Nationwide Levee Database counts greater than 24,000 miles (38,600 kilometers) of levees within the U.S., with a median age of about 61 years and lots of of them a lot older. In combination, they offer protection to over 23 million other folks, round 7 million structures and just about US$2 trillion in assets price.
That’s an ordinary degree of duty for a machine this is erratically maintained with various oversight. Some levees are inspected incessantly. Others are owned by way of small native companies or non-public entities with restricted investment. In some instances, duty is unclear or fragmented.
One levee that was once breached alongside the Inexperienced River in Washington state all through storms in mid-December 2025 were due for upkeep for a number of years, however disagreements amongst governments had lately held up wanted paintings, The Seattle Occasions reported. The breach pressured hundreds of other folks to evacuate
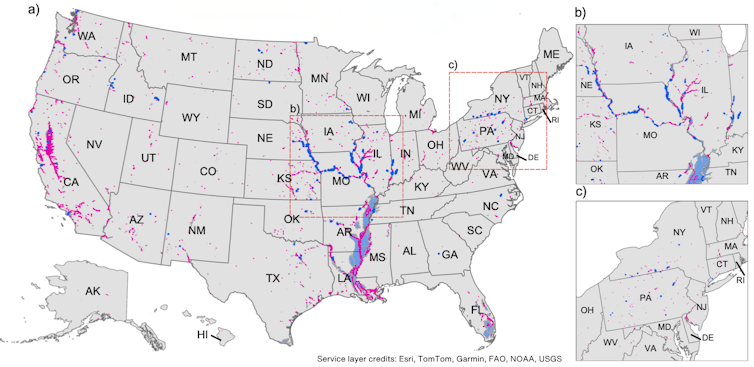
Many states have at-risk levees. The map displays all levees within the U.S. Nationwide Levee Database (in purple) and 478 levee segments the place overtopping is understood to have took place within the earlier 15 years (in blue).
S. Flynn, et al., 2025
The American Society of Civil Engineers’ 2025 Document Card for American Infrastructure, which I contributed to, gave the country’s levees a D-plus grade, bringing up ageing infrastructure, inconsistent tracking and long-term underinvestment. A brand new dataset that colleagues and I created of levee harm contains 487 instances the place rivers poured over levees, referred to as overtopping, previously 15 years. That doesn’t imply levees are failing all over; it signifies that many are working with little margin for error.
How levees fail
Levee screw ups are hardly ever surprising collapses. Extra regularly, they begin quietly.
The most typical reason why levees fail is overtopping, when water from a river, circulate or lake in the back of the levee flows excessive. As soon as that occurs, erosion can start at the landward aspect, weakening the construction from in the back of. What begins as a gradual trickle can briefly develop right into a breach, growing a big hole within the levee the place water can pour in.
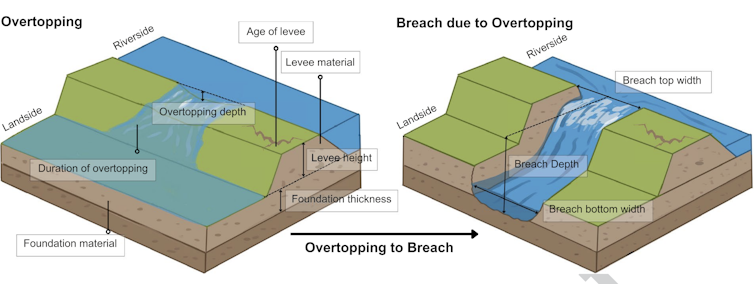
A demonstration displays the variation between overtopping and a breach, and one of the vital causes a levee can fail.
S. Flynn et al., 2025
Atmospheric river storms make the danger of overtopping and breaches a lot upper. Those storms ship monumental quantities of rainfall throughout vast spaces in a question of hours, regularly mixed with snowmelt. Rivers upward push quicker and keep top longer. Many levees have been by no means designed for that more or less sustained drive.
When a levee breaches, flooding will also be speedy and deep, leaving little time for evacuation and inflicting harm that spreads a long way past the floodplain.
Who depends on levees as of late?
Hundreds of thousands of American citizens reside and paintings in space secure by way of levees, regularly with out knowing it. Properties, colleges, highways, rail corridors, ports and gear amenities rely at the integrity of those constructions.
A up to date nationwide find out about discovered that around the contiguous U.S., city enlargement into floodplains took place greater than two times as speedy after levee building because it did in surrounding counties, highlighting how levees can impact communities’ belief of threat.
In truth, when levees fail, flooding will also be worse than in spaces with out levees, as a result of water rushes in briefly and drains slowly.
The hazards also are asymmetric, formed by way of historical past, economics and coverage selections.
That fact was painfully transparent all through an atmospheric river hurricane in March 2023 when a levee alongside California’s Pajaro River failed, flooding the city of Pajaro. Pajaro is house to many low-income farmworkers. Floodwaters pressured loads of citizens to evacuate, and a few other folks have been trapped as water ranges rose.
How the Pajaro Valley flooded after intense rainfall from an atmospheric river in March 2023, breaching a levee protective a small California the town.
What made the crisis particularly troubling was once what emerged later on. Officers and engineers had recognized for many years that the Pajaro River levee was once inclined. Studies documented its weaknesses, however upkeep have been time and again not on time.
Interviews by way of The Los Angeles Occasions and public information confirmed that a part of the explanation was once monetary. Determination-makers didn’t prioritize making an investment in a levee machine protective the low-income group. The danger was once recognized, however the coverage was once deferred.
Pajaro isn’t an remoted case. Around the nation, deprived communities and communities of colour are much more likely to depend on older levees or levees that aren’t a part of primary federal methods. Rural cities regularly rely on agricultural levees. City neighborhoods would possibly depend on constructions constructed for a way smaller inhabitants.
When levees fail, the affects cascade, remaining roads, knocking out energy, contaminating water provides and disrupting lives for years.
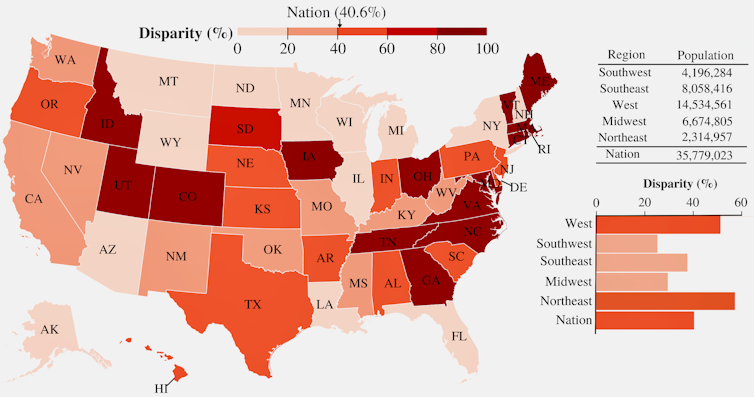
Disparity refers back to the proportion of every state’s citizens secure by way of levees who’re regarded as deprived, in accordance with the U.S. Council on Environmental High quality’s Local weather and Financial Justice Screening Software. All levees within the Nationwide Levee Database are counted.
F. Vahedifard et al., 2023
Why this second issues
Advances in engineering, tracking and menace evaluate have progressed how levees are evaluated and designed.
Typhoon Katrina marked a turning level in 2005 when its hurricane surge broke via levees protective New Orleans. Masses of other folks died within the flooding. The crisis uncovered the effects of forget and fragmented duty for levee repairs.
On the identical time, there was actual development. During the last 20 years, vital federal investments have reinforced the situation and control of lots of the country’s levees, in particular throughout the paintings of federal companies such because the U.S. Military Corps of Engineers.
Nonetheless, the legacy of choices made a long time in the past stays, and local weather exchange is elevating the hazards. Heavier rainfall, speedy snowmelt and emerging seas are pushing water management techniques past what many levees have been designed to maintain. Occasions as soon as regarded as uncommon are changing into extra common.
As atmospheric rivers check levees within the West and flood dangers develop national, the problem is not simply technical. It’s about how society values coverage, communicates menace and makes a decision whose protection is prioritized.
Levees will proceed to play a very important position in protective communities. Figuring out their historical past, and their limits, is very important because the storms of the longer term arrive.





