With the arena at the threshold of one.5°C of warming, one urgent query is: how dangerous can it get? The solution would possibly lie underneath our toes.
Buried underground are rocks, many rocks, and they’re previous. For palaeontologists like us, they’re an infinite archive of previous lifestyles on Earth. Specifically, they may be able to let us know how lifestyles on land fared all through instances when the local weather warmed all of sudden. Our new learn about confirmed that crops had been significantly affected and forests took tens of millions of years to get well.
About 252 million years in the past greater than 80% of marine species turned into extinct. That is referred to as the end-Permian mass extinction, arguably essentially the most important climatic disaster because the earliest look of animals, greater than 555 million years in the past. It sort of feels that the high wrongdoer used to be the large quantity of warming-inducing greenhouse gasoline launched by way of volcanoes in a area referred to as the Siberian Traps in Russia.
Carbonised influence of a plant fossil at the shores of Lengthy Reef, Sydney, Australia.
Marcos Amores
Proof means that crops would possibly not have suffered a mass extinction, however their communities had been closely affected, if now not destroyed outright. Whilst the extraordinary warmth would have driven crops and animals previous their tolerance limits, they almost definitely additionally confronted fatal droughts, ozone depletion, in style wildfires and poisonous heavy steel contamination.
Knowledge on how crops fared following the end-Permian extinction are considerable, however little is understood about the ones positioned at upper latitudes, the place it used to be cooler. Thriving ecosystems existed at polar latitudes again then, aided by way of a most commonly ice-free polar area. On the end-Permian match, then again, this ecosystem used to be totally burnt up.
Our paintings tested the rocks and fossils of the Sydney area of Australia, which used to be positioned close to the south pole for no less than 8 million years following the worst mass extinction in Earth’s historical past. Those well-preserved, long-term data supply a window into the restoration of plant communities furthest clear of the supply of hassle.
The lengthy, unsteady trail to restoration
The plant fossils from those Australian rocks confirmed that conifers, like trendy pines or cypresses, had been probably the most earliest to colonise the land straight away following the calamity. The restoration to flourishing forests, then again, used to be now not clean crusing.
We came upon that even upper temperatures 2 million years after the end-Permian match brought about the cave in of those conifer survivors. In flip, they had been changed by way of tricky, shrubby crops reminiscent of trendy clubmosses (like Isoetes). How sizzling it were given in Sydney isn’t recognized, however this sizzling duration lasted for approximately 700,000 years and made lifestyles difficult for timber and different massive crops.
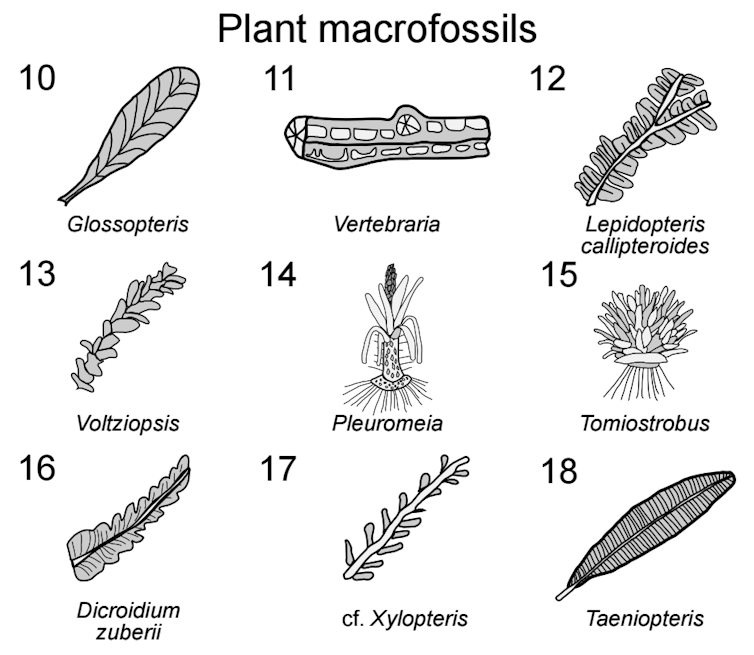
The primary plant sorts provide round 250 million years in the past within the Sydney area, Australia, together with clubmosses (numbers 14 and 15).
Amores et al. 2025, GSA Bulletin
When cooling stipulations in the end manifested, massive however strange crops that gave the look of ferns however bore seeds like conifers flourished and established extra strong forests in Sydney. This restoration took lower than 100,000 years to occur. Those crops ultimately ruled the panorama for tens of millions of years, paving the best way for the plush forests all through the Mesozoic age of the dinosaurs.
So, after million of years, the wooded area ecosystems of the Mesozoic got here to seem like the ones from sooner than the end-Permian match. However crucially, the plant species that made up the brand new forests had been utterly other.
The time period “recovery” may also be deceptive. Forests get well ultimately, however extinction of particular person species is without end.
Via figuring out how historic plant ecosystems weathered excessive local weather swings, we, as researchers, hope to be told treasured courses about how trendy crops and ecosystems would possibly cope (or now not) with nowadays’s local weather disaster. With this information, we will be able to tell policymakers of what’s but to come back, and lend a hand steer a route that may steer clear of the worst local weather results over the longest conceivable timeframes.
So, fossil data upload a data-driven long-term standpoint to the local weather possible choices we make nowadays. Ecosystems rely on a delicate steadiness, with crops because the spine of meals webs on land and local weather regulators.
The fossils have spoken: the disruption of those programs may have penalties that closing loads of hundreds of years, so protective nowadays’s ecosystems is extra essential than ever.







