These days the arena of Egyptology faces a silent disaster – now not of looting, despite the fact that that performs an element, however of disconnection. Stroll into any primary museum, from Copenhagen to California, and you notice glass circumstances full of what may well be known as orphaned artifacts: exceptional gadgets, incessantly got within the nineteenth and early twentieth century, which were totally stripped in their histories. You’ll be able to see what they’re – a mummy’s painted foot case, a golden masks – however we haven’t any thought the place they got here from. They’re stunning, however traditionally they’re mute.
Every now and then an object can also be most commonly intact in a museum assortment, however with few info identified about its starting place.
Carlo Rindi Nuzzolo
Many gadgets entered museum collections every now and then when excavation and amassing practices have been very other from nowadays. Previously, excavated gadgets have been incessantly divided between establishments world wide, and show was once prioritized over documentation. Over the years, connections between items have been misplaced. Because of this, museums world wide hang exceptional artifacts whose backstories are skinny, fragmentary or lacking altogether.
Archaeologists like me operating within the box nowadays incessantly discover fragments: damaged items of gadgets that after shaped a part of one thing better. In some circumstances, the ones fragments would possibly proportion the similar underlying geometry with gadgets already held in museums. For instance, a mummy’s foot case and a newly discovered shard will have been produced the use of the similar mildew, so that they proportion a constant 3-dimensional shape even supposing they’re now separated through time, distance and lack of documentation.
Historically, comparing whether or not a fraction suits up with a selected museum object has depended on visible judgment and incomplete data, fairly than a quantitative comparability of form.
This hole between excavation archaeology and museum collections is likely one of the maximum chronic demanding situations within the box. My analysis asks a easy query: Are we able to use virtual equipment to check whether or not fragments and museum gadgets may well be similar and, in doing so, get better portions in their histories that have been up to now inaccessible?
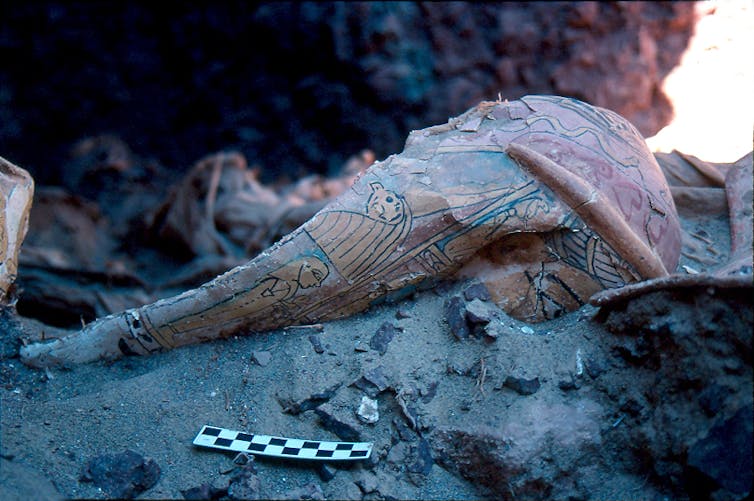

Reuse through the years and looting shifted and broken the contents of an historical Egyptian tomb. This displaced mummy masks may have a courting to different artifacts already in museums world wide.
Carlo Rindi Nuzzolo
A protracted-standing downside in archaeology
Archaeology is, through nature, fragmentary. Items wreck, decay or are disturbed over centuries. Historically, archaeologists have depended on visible inspection, stylistic comparability and written data to suggest connections between fragments and gadgets. Those approaches are nonetheless very important, however in addition they have limits. Visible judgments can also be subjective, and archival documentation is incessantly incomplete or inconsistent.
Because of this, many attainable hyperlinks between excavated subject material and museum artifacts have remained speculative or have by no means been proposed in any respect. An object in a museum would possibly seem whole but nonetheless have a fragmented historical past. And not using a approach to take a look at relationships systematically, fragments incessantly stay sidelined as secondary or uninformative.
Greater than a century in the past, the archaeologist Flinders Petrie argued that an object’s price lies now not in its attractiveness however within the knowledge it carries. An unremarkable fragment with a identified historical past, he believed, may well be extra necessary than a finely made object with out one. These days, virtual equipment are giving archaeologists new techniques to place that concept into apply.
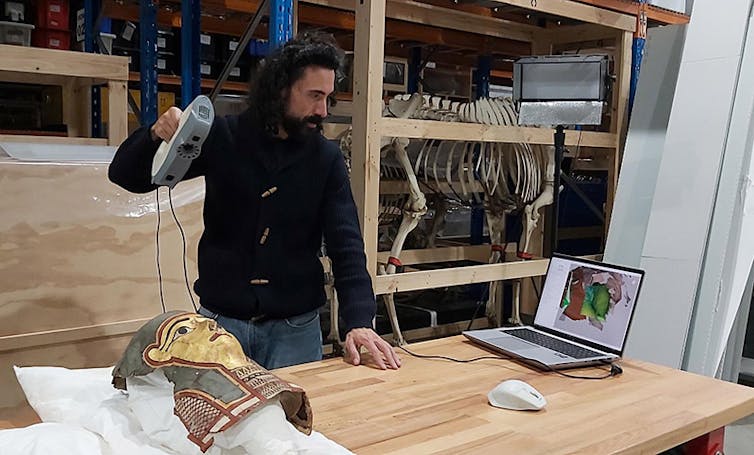

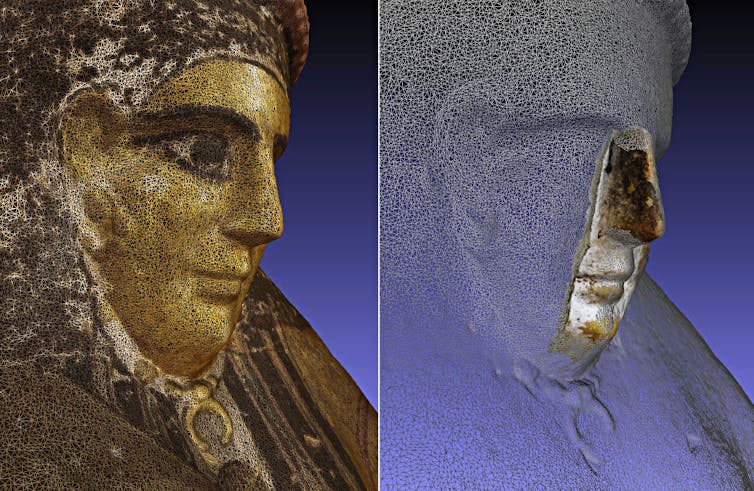
Archaeologists can use hand-held three-D scanners to noninvasively map gadgets in very nice element.
Carlo Rindi Nuzzolo
Turning gadgets into information that may be when put next
A type of equipment is three-D scanning. The usage of moveable scanners, it’s now conceivable to seize the entire floor geometry of an object with excessive precision, with out touching or harmful it. Each curve, contour and variation in thickness can also be recorded digitally.
As soon as scanned, an artifact turns into greater than a picture. It turns into information: an in depth virtual style that may be turned around, measured, when put next and analyzed. Importantly, this procedure is noninvasive. Fragile gadgets don’t wish to be moved, dismantled or bodily examined.
For archaeologists and museum curators, this procedure opens up new probabilities. Items held in several establishments, or fragments saved in excavation archives, can also be when put next digitally, even supposing the originals by no means depart their places.
Scanning is best step one. The actual problem lies compared. Reasonably than asking whether or not two items glance an identical, computational form research lets in researchers to invite a extra exact query: How an identical are their shapes?
In easy phrases, the pc compares the geometry of 2 surfaces. It seems to be at curvature, thickness and spatial relationships, measuring how carefully one floor suits some other. It’s like evaluating a type of geometric fingerprint.
This manner doesn’t exchange skilled judgment. As an alternative, it helps it through offering measurable proof that may verify, refine or problem visible impressions. It lets in archaeologists to transport from instinct to checking out.
When a fraction meets a museum object
In a up to date find out about revealed within the magazine Heritage Science, I carried out those the way to Graeco-Roman Egyptian funerary artifacts product of cartonnage, a composite subject material of linen, plaster and paint.
I created high-resolution three-D scans of excavated cartonnage fragments and when put next them with an intact funerary masks held in a museum assortment. The purpose was once to not reconstruct the thing bodily however to check whether or not their shapes have been appropriate in significant techniques.
The comparability interested in 3-dimensional geometry fairly than ornament. This issues as a result of cartonnage mask have been incessantly formed in molds: If two gadgets have been shaped in the similar mildew, they may be able to proportion extremely constant curvature and thickness patterns even if their painted surfaces fluctuate.
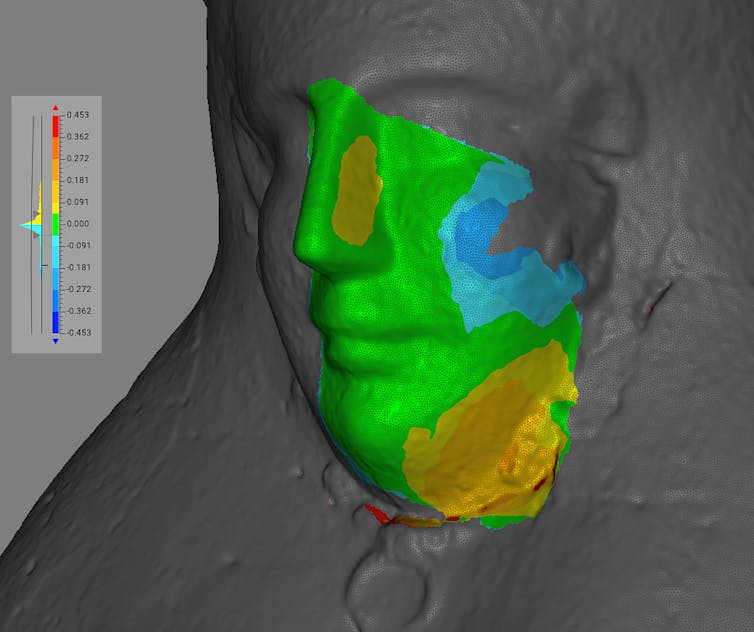
The masks reference floor is proven in grey, whilst the aligned fragment is coloured in response to the surface-to-surface distance at each and every level. Inexperienced signifies a excellent fit with nearly no distance. Cooler colours display spaces the place the fragment lies beneath the reference masks, and hotter colours display the place it lies above.
Carlo Rindi Nuzzolo
I used a distance-mapping manner known as deviation mapping. After aligning the three-D style of an excavated fragment to the corresponding area of the intact museum object, the set of rules calculates the distances between the 2 surfaces at hundreds of issues. Spaces the place the distances have been persistently small are geometrically very an identical. Spaces with persistently better distances point out that the fragment’s form diverges from the reference floor.
On this case, the surfaces corresponded carefully, with variations typically of lower than a millimeter – a degree of settlement in step with manufacturing in the similar mildew fairly than a coincidental visible resemblance.
What mattered maximum was once now not a unmarried “match” however the skill to judge relationships transparently and reproducibly, the use of shared virtual proof.
One of the vital robust sides of this manner is that it really works throughout distance. Researchers can simply proportion virtual fashions, permitting them to examine fragments and gadgets held in several establishments, with out transporting fragile artifacts. Excavation archives, museum collections and analysis establishments can start to talk the similar virtual language, reconnecting proof that has lengthy been separated through geography and historical past.
The masks fragment was once an overly shut fit to a whole masks, suggesting they have been made in the similar mildew.
Carlo Rindi Nuzzolo
Virtual equipment are reshaping collections analysis
The paintings I describe right here, a part of my contemporary CRAFT Challenge, does now not use synthetic intelligence or system studying. It will depend on computer-based form comparability and cautious interpretation of metrological effects. However it sits inside of a broader motion in heritage analysis.
The world over, researchers and establishments are starting to mix three-D scanning with system studying to discover collections in several techniques. For instance, the EU-funded RePAIR undertaking makes use of AI and robotics to assist reassemble fragmented archaeological artifacts, whilst primary establishments such because the Smithsonian are experimenting with AI-driven research of huge three-D collections.
In combination, those tasks level to a long term by which virtual equipment play an increasingly more energetic position in how museums and archaeologists perceive the previous.
Virtual archaeology is now and again related to flashy reconstructions or digital presentations. However its deeper price lies somewhere else. Via giving fragments a brand new analytical position, virtual strategies permit archaeologists to get better relationships that have been lengthy idea irretrievably misplaced.
New virtual methodologies are respiring new existence right into a long-standing archaeological theory: Modest fragments can raise oversized importance after they explain an object’s origins and its misplaced context, after all permitting it to search out its long ago house.