When any person opens the door and enters a health center room, dressed in a stethoscope is a telltale signal that they’re a clinician. This clinical software has been round for over 200 years and stays a staple within the hospital regardless of vital advances in clinical diagnostics and applied sciences.
The stethoscope is a clinical device used to hear and enlarge the inner sounds produced via the frame. Physicians nonetheless use the sounds they listen thru stethoscopes as preliminary signs of middle or lung illnesses. As an example, a middle murmur or crackling lungs frequently represent a topic is provide. Despite the fact that there were vital advances in imaging and tracking applied sciences, the stethoscope stays a handy guide a rough, out there and cost-effective instrument for assessing a affected person’s well being.
Regardless that stethoscopes stay helpful these days, audible signs of illness frequently seem best at later phases of sickness. At that time, therapies are much less more likely to paintings and results are frequently deficient. That is particularly the case for middle illness, the place adjustments in middle sounds don’t seem to be all the time obviously outlined and could also be tricky to listen to.
We’re scientists and engineers who’re exploring tactics to make use of middle sounds to discover illness previous and extra appropriately. Our analysis means that combining stethoscopes with synthetic intelligence may just assist medical doctors be much less reliant at the human ear to diagnose middle illness, resulting in extra well timed and superb remedy.
Historical past of the stethoscope
The discovery of the stethoscope is extensively credited to the Nineteenth-century French doctor René Theophile Hyacinthe Laënnec. Earlier than the stethoscope, physicians frequently positioned their ear immediately on a affected person’s chest to pay attention for abnormalities in respiring and middle sounds.
In 1816, a tender lady appearing signs of middle illness sought session with Laënnec. Hanging his ear on her chest, alternatively, used to be regarded as socially irrelevant. Impressed via kids transmitting sounds thru a protracted picket stick, he as a substitute rolled a sheet of paper to hear her middle. He used to be shocked via the unexpected readability of the center sounds, and the primary stethoscope used to be born.
One in all René Laënnec’s unique picket stethoscopes.
Science Museum London/Science and Society Image Library, CC BY-NC-SA
Over the following couple of many years, researchers changed the form of this early stethoscope to enhance its convenience, portability and sound transmission. This contains the addition of a skinny, flat membrane known as a diaphragm that vibrates and amplifies sound.
The following primary step forward befell within the mid-1850s, when Irish doctor Arthur Leared and American doctor George Philip Cammann evolved stethoscopes that might transmit sounds to each ears. Those binaural stethoscopes use two versatile tubes attached to split earpieces, permitting clearer and extra balanced sound via decreasing out of doors noise.
Those early fashions are remarkably very similar to the stethoscopes clinical medical doctors use these days, with best slight changes principally designed for consumer convenience.
Being attentive to the center
Clinical colleges proceed to show the artwork of auscultation – the usage of sound to evaluate the serve as of the center, lungs and different organs. Virtual fashions of stethoscopes, that have been commercially to be had for the reason that early 2000s, be offering new gear like sound amplification and recording – but the fundamental concept that Laënnec presented endures.
When taking note of the center, medical doctors pay shut consideration to the acquainted “lub-dub” rhythm of every heartbeat. The primary sound – the lub – occurs when the valves between the higher and decrease chambers of the center shut because it contracts and pushes blood out to the frame. The second one sound – the dub – happens when the valves main out of the center shut as the center relaxes and refills with blood.
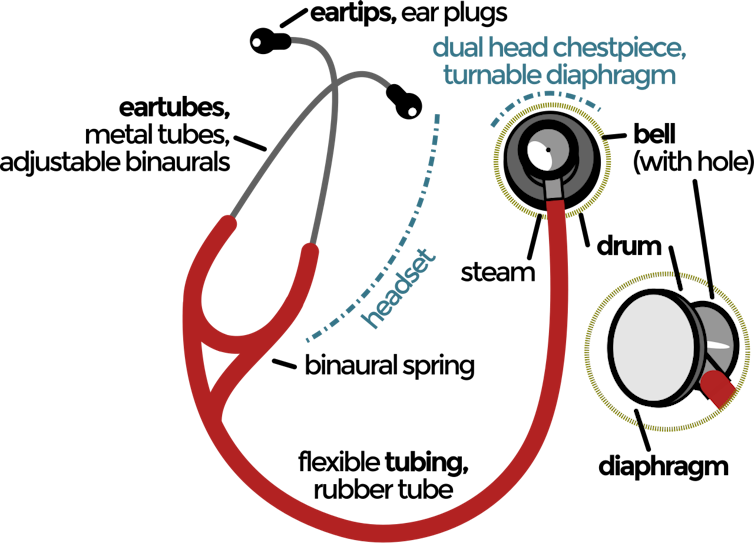
The diaphragm and bell of a stethoscope transmit other sound frequencies to the listener.
Jarould/Wikimedia Commons, CC BY-SA
Together with those two commonplace sounds, medical doctors additionally pay attention for extraordinary noises – reminiscent of murmurs, additional beats or clicks – that may level to issues of how blood is flowing or whether or not the center valves are running correctly.
Center sounds can range very much relying on the kind of middle illness provide. Every now and then, other illnesses produce the similar unusual sound. As an example, a systolic murmur – an additional sound between first and 2nd middle sounds – could also be heard with narrowing of both the aortic or pulmonary valve. But the exact same murmur too can seem when the center is structurally commonplace and wholesome. This overlap makes it difficult to diagnose illness founded only at the presence of murmurs.
Instructing AI to listen to what other folks can’t
AI generation can determine the hidden variations within the sounds of wholesome and broken hearts and use them to diagnose illness earlier than conventional acoustic adjustments like murmurs even seem. As a substitute of depending at the presence of additional or unusual sounds to diagnose illness, AI can discover variations in sound which can be too faint or delicate for the human ear to discover.
To construct those algorithms, researchers document middle sounds the use of virtual stethoscopes. Those stethoscopes convert sound into digital indicators that may be amplified, saved and analyzed the use of computer systems. Researchers can then label which sounds are commonplace or unusual to coach an set of rules to acknowledge patterns within the sounds it will probably then use to expect whether or not new sounds are commonplace or unusual.
Stethoscopes can seize diagnostic data the human ear on my own can’t listen.
Drs Producoes/E+ by means of Getty Photographs
Researchers are creating algorithms that may analyze digitally recorded middle sounds together with virtual stethoscopes as a cheap, noninvasive and out there instrument to display screen for middle illness. On the other hand, a large number of those algorithms are constructed on datasets of moderate-to-severe middle illness. As a result of it’s tricky to seek out sufferers at early phases of illness, previous to when signs start to display, the algorithms don’t have a lot data on what hearts within the earliest phases of illness sound like.
To bridge this hole, our staff is the use of animal fashions to show the algorithms to research middle sounds to seek out early indicators of illness. After coaching the algorithms on those sounds, we assess its accuracy via evaluating it with symbol scans of calcium buildup within the middle. Our analysis means that an AI-based set of rules can classify wholesome middle sounds accurately over 95% of the time and may also differentiate between kinds of middle illness with just about 85% accuracy. Most significantly, our set of rules is in a position to discover early phases of illness, earlier than cardiac murmurs or structural adjustments seem.
We consider educating AI to listen to what people can’t may just develop into how medical doctors diagnose and reply to middle illness.







