Oceans play a significant function in carbon garage, in particular during the biomass they comprise. The lifestyles cycle of fish thus contributes to the sustainable sequestration of CO2 in sinks, however business fishing has weakened this very important mechanism, additionally threatened by means of local weather trade. Restoring marine populations within the excessive seas may just fortify this herbal carbon sink whilst proscribing meals safety conflicts.
Once we speak about herbal carbon sinks, the ones herbal techniques that entice extra carbon than they emit, we in most cases recall to mind forests and soils, now not oceans. Alternatively, the oceans constitute the second one greatest herbal carbon sink.
The have an effect on of human actions (particularly fishing) on ocean carbon garage has up to now been little studied, even though marine macrofauna (particularly fish) account for approximately a 3rd of the natural carbon saved within the oceans. Our analysis, lately printed within the journals Nature Communications and One Earth, sought to right kind this.
Our effects display that fishing has already diminished carbon sequestration in fish by means of nearly part since 1950. Via the top of the century, this aid is predicted to achieve 56% beneath the mixed impact of fishing and local weather trade. Sufficient to suggest for extra sustainable ocean control, which might be mindful the have an effect on of fishing on carbon sequestration.
Why are we all in favour of carbon sequestration within the oceans?
The Intergovernmental Panel on Local weather Trade (IPCC) states this explicitly in its reviews: to succeed in local weather objectives, we will have to first enormously and right away scale back our greenhouse gasoline emissions (human actions emit about 40 billion lots of CO₂ an identical every 12 months), after which increase nature-based local weather answers.
They combine all measures to revive, offer protection to and higher set up carbon-storing ecosystems comparable to forests. Those measures may just quilt 10 billion tonnes of CO₂ an identical consistent with 12 months and will have to be applied along emission aid insurance policies.
Alternatively, the carbon saved in those ecosystems is increasingly more threatened by means of local weather trade. For instance, wooded area fires in Canada emitted 2.5 billion lots of CO₂ an identical in 2023: the wooded area is then now not a carbon sink, however turns into a supply of emissions.
Confronted with this remark, the clinical neighborhood is now turning to the oceans, in search of new answers that may permit extra carbon to be sequestered there.
However for this to be conceivable, we will have to first know the way lifestyles secure by means of the oceans impacts the carbon cycle, in addition to the have an effect on of local weather trade, at the one hand, and fishing, at the different.
What function do fish play on this procedure?
Nearly all of the 38,000 billion lots of carbon saved within the ocean is saved via bodily phenomena. However ocean biomass additionally contributes about 1,300 billion lots of natural carbon. Fish constitute about 30% of this carbon inventory.
That is made conceivable by means of their contribution to what’s known as the organic carbon pump, this is, a sequence of organic processes that permit the shipping of carbon from floor waters to the seabed. This is a primary component of the carbon cycle.
This organic pump begins with phytoplankton, in a position to remodeling CO2 into carbonaceous natural subject. When it dies, a few of this carbon will sink to the depths of the sea the place it’s going to be completely sequestered, whilst the remainder will likely be ate up by means of predators. Once more, when this carbon sinks to the depths (faecal pellets, carcasses of lifeless predators, and many others.) it’s going to be completely sequestered.
Fish play a key function on this procedure: their denser carcasses and faecal pellets sink a lot quicker than plankton. Alternatively, the speedier the carbon sinks to the depths – and clear of the ambience – the longer it’s going to take to go back to the ambience: the carbon will thus be saved in a extra sustainable means.
The organic carbon pump and the contribution of various organisms are the results of a mixture of processes: (1) conversion of CO₂ to natural carbon by means of phytoplankton sporting out photosynthesis; (2) phytoplankton give a contribution to carbon sequestration during the gravitational fall of lifeless phytoplankton cells; (3) zooplankton devour phytoplankton and the carbon they comprise. Zooplankton give a contribution to carbon sequestration via (4) the gravitational fall in their faecal pellets or (5) their carcasses, either one of which comprise ingested carbon. (6) Zooplankton and the carbon they comprise are eaten by means of fish. Fish give a contribution to carbon sequestration via (4) the gravitational fall in their faecal pellets, or (5) their carcasses, either one of which comprise ingested carbon. Equipped by means of the writer
Our find out about, which targeted in particular on fish species of business passion (ie, centered by means of fisheries), estimates that the latter have been in a position to sequester 0.23 billion lots of carbon consistent with 12 months in 1950 (ie, 0.85 lots of CO2 consistent with 12 months).
A vicious cycle because of local weather trade
However since 1950, issues have modified. First, because of local weather trade: because of the shortage of meals assets (much less phytoplankton) and adjustments in environmental stipulations (temperature, oxygen, and many others.), the more potent the local weather trade, the extra the biomass of species of business passion will lower – and thus their capability to sequester carbon.
In a situation the place the common building up in temperature can be restricted to at least one.5°C (a situation of compliance with the Paris Settlement), biomass would lower by means of round 9% by means of the top of the century, i.e. a discount in carbon sequestration by means of round 4%.
On the subject of a established order situation the place temperatures building up by means of 4.3°C, this aid would succeed in about 24% for biomass and nearly 14% for carbon sequestration.
So we are coping with what is known as a favorable comments loop – in different phrases, a vicious cycle: the larger the local weather trade, the fewer carbon the fish will sequester, which can enlarge the local weather trade itself. This is a snake biting its personal tail.
Carbon sequestration is already halved by means of fishing
The have an effect on of local weather trade within the 1.5°C warming situation (which we’re at the verge of exceeding) is subsequently low, however the results of fishing are already visual.
These days, industrial fish species already sequester most effective 0.12 billion lots of CO2 consistent with 12 months (in comparison to 0.23 billion lots of carbon consistent with 12 months in 1950), a discount of virtually part.
Particularly because the results of fishing don’t seem to be the similar relying at the sequestration direction thought to be. Since 1950, fishing has diminished carbon sequestration by the use of faecal pellets by means of roughly 47%. For the direction during the hulls, this aid is roughly 63%.
That is related to the truth that fishing objectives the biggest organisms, the ones with the fewest predators – and subsequently the ones in all probability to die of outdated age and spot their carcasses sink into the abyss.
This aid may be synonymous with a discount within the arrival of meals into the sink, as carcasses are a in particular nutritious useful resource for the organisms that reside there.
Alternatively, we all know little or no about those abyssal ecosystems, with thousands and thousands of species but to be came upon. To this point, now we have seen most effective 0.001% of the full space of those ecosystems. So we could also be ravenous a mess of deep-sea organisms we slightly learn about.
To maintain the local weather, repair fish populations?
Our find out about displays that if fish populations have been to go back to ancient 1950 ranges, this could permit sequestration of an extra 0.4 billion lots of CO2 consistent with 12 months, a possible related to mangroves. With a bonus: this carbon can be sequestered for approximately 600 years, longer than in mangroves, the place most effective 9% of the trapped carbon continues to be sequestered after 100 years.
Alternatively, regardless of this important attainable, local weather answers in response to the recovery of marine macrofauna, if applied on my own, would have just a small have an effect on at the local weather, in comparison to the 40 billion lots of CO₂ emitted every 12 months.
Particularly since this space of analysis is fresh, a number of uncertainties stay. For instance, our research don’t be mindful trophic relationships (i.e., associated with the meals chain) between predators and their prey, which additionally give a contribution to carbon sequestration. Alternatively, if we building up the biomass of the predator, the biomass of the prey will routinely lower. Thus, if carbon sequestration by means of predators will increase, so does prey, which would possibly neutralize the have an effect on of measures aimed toward returning fish populations to sequester carbon.
Subsequently, our effects must now not be observed as enough proof to believe such measures as a viable resolution. They however illustrate the significance of learning the have an effect on of fishing on carbon sequestration and the desire to offer protection to the sea to restrict the hazards of depleting this carbon sink, allowing for the services and products the sea supplies to our societies (meals safety, jobs, and many others.).
Conflicts between fishing and carbon sequestration, particularly within the excessive seas
Certainly, marine organisms immediately take part in carbon sequestration, whilst additionally reaping benefits the fisheries sector. Alternatively, this sector is a supply of employment and a big financial revenue for the coastal inhabitants, immediately contributing to the upkeep and success of meals safety in sure areas.
Subsequently, conflicts between carbon sequestration and socio-economic advantages from fishing can theoretically get up. If fishing will increase, fish populations and their skill to sequester carbon will lower, and vice versa.
Alternatively, now we have proven that most effective 11% of the sea floor is doubtlessly uncovered to such conflicts. Those are spaces the place fishing effort and carbon sequestration are excessive.
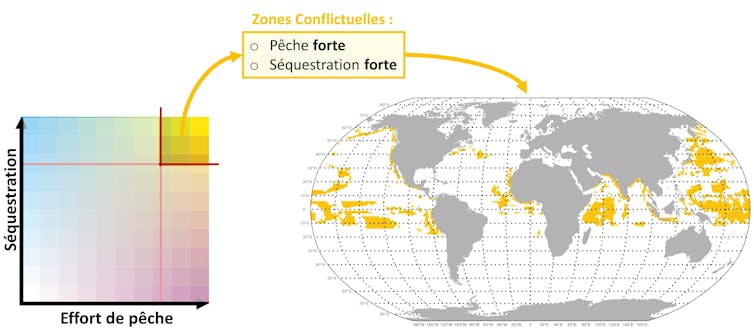
Possible spaces of struggle between fishing and carbon sequestration by means of fish correspond to spaces the place (1) fishing effort is excessive and (2) fish give a contribution strongly to carbon sequestration. These types of spaces (about 60%) are positioned within the open sea, ie greater than 370 kilometers from the coast, outdoor any nationwide jurisdiction. Equipped by means of the writer
As well as, maximum (about 60%) of those doubtlessly struggle zones are positioned within the open sea, the place catches give a contribution negligible to general meals safety. Additionally, excessive seas fishing is understood for its low profitability and large subsidization by means of governments (to the song of one.5 billion greenbacks, or greater than 1.2 billion euros, in 2018).
Those govt subsidies had been closely criticized as threatening the sustainability of artisanal coastal fisheries, selling gas intake and extending inequalities between low- and high-income nations.
Thus, our effects supply an extra argument in prefer of defending the excessive seas. Along with keeping off more than one damaging socio-economic results, this could additionally offer protection to biodiversity and, on the identical time, maintain the sea’s capability to sequester natural carbon.






