3 scientists were awarded the 2025 Nobel prize in chemistry for locating a brand new type of molecular structure: crystals that comprise massive cavities.
Susumu Kitagawa from Kyoto College, Japan, Richard Robson from the College of Melbourne, Australia, and Omar M. Yaghi from the
College of California, Berkeley, in the USA, will proportion a prize sum of eleven million Swedish kronor (£870,000).
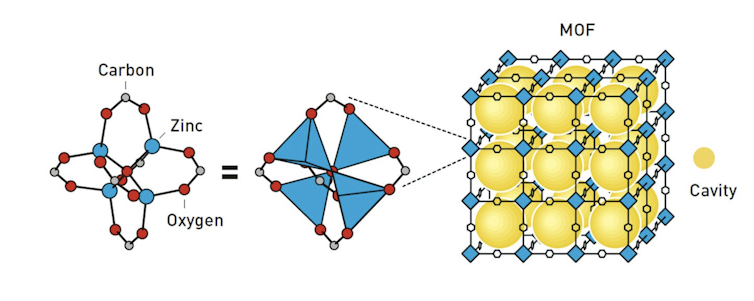
The prize recognises the pioneering contributions of the 3 scientists within the building of one thing referred to as metal-organic frameworks (Mofs). Mofs are a various elegance of crystalline fabrics that experience attracted a lot consideration in chemistry because of the presence of microscopic open cavities of their constructions. They’re serving to to revolutionise inexperienced era, akin to harvesting water from barren region air and shooting CO₂.
The widths of the cavities can vary from a couple of angstroms (an angstrom is a unit of duration equivalent to at least one hundred-millionth of a centimetre) to a number of nanometres (a millionth of a millimetre). That suggests they’re some distance too small to look with the bare eye and even with maximum sorts of microscopes. However they’re the easiest dimension for housing quite a lot of molecules.
The improvement of Mofs may also be traced again to the past due Fifties when researchers began to find “coordination polymers”. Those are fabrics made up of related chains of metallic ions (atoms that experience misplaced or won electrons) and carbon-based bridging molecules referred to as linkers. Those fabrics didn’t comprise cavities, however they had been in line with the similar metal-organic chemistry that will later give upward push to Mofs.
Within the past due Nineteen Eighties, Robson’s analysis staff reported that some coordination polymers might be ready as framework-like constructions the place, crucially, the carbon-based linkers shaped third-dimensional preparations round clusters of liquid solvent molecules. As discussed in Robson’s analysis article, this printed “an unusual situation in which approximately two-thirds of the contents of what is undoubtedly a crystal are effectively liquid”.
Screenshot at.
Nobelprize outreach, CC BY-SA
Within the mid-late Nineties, Yaghi’s staff demonstrated that it used to be imaginable to arrange coordination polymers that retained their constructions even after the solvent molecules had been got rid of from the cavities. This used to be a shocking outcome, which dispelled the existing assumption that such frameworks are fragile and would cave in if the solvent used to be got rid of.
In 1997, Kitigawa’s analysis staff confirmed that the open cavities might be used to take in gasoline molecules. He additionally confirmed that, in lots of circumstances, the framework itself expands as gasoline molecules are absorbed into it and contracts as they’re launched. Those coordination polymers with everlasting, open cavities got here to be referred to as Mofs.
In 1999, Yaghi built an excessively solid subject material, MOF-5, which has cubic areas. Simply a few grams can hang a space as giant as a soccer pitch.
Nobel prize outreach
The discoveries by means of the 3 scientists successfully marked the beginning of contemporary Mof chemistry, with many hundreds of study articles printed on them since.
Wide selection of packages
Why are Mofs so fascinating for chemists? The microscopic cavities inside of Mofs supply a singular and controllable location for chemistry to happen. A key utility of Mofs is gasoline garage. In lots of circumstances, those fabrics can hang gases at a lot upper densities than of their unfastened gaseous state.
This gives vital benefits for inexperienced applied sciences akin to fuel-cell-powered automobiles, by which hydrogen gas must be transported as successfully as imaginable. Many Mofs paintings specifically smartly for particular gases, because of this they are able to additionally lend a hand separate gasoline combinations in exhaust streams, or seize CO₂ from the air to mitigate the results of world warming.
Mofs too can act as efficient catalysts for chemical reactions happening within the cavities. Some of the key benefits of Mofs as catalysts is that it’s quite easy for chemists to modify and switch the metals and carbon-based linkers as a way to music the houses for a specific goal.
In addition to gasoline molecules, Mofs too can accommodate different small molecules, akin to prescribed drugs. This implies they are able to be used to retailer and ship medication to a specific goal, the place their porous nature lets in for managed unlock of healing chemical substances.
In recent times, Mofs have proven promise for lots of different packages, together with batteries, thermal power garage and chemical sensors (gadgets that may observe and hit upon chemical substances akin to contaminants). Excitingly, there stay many different packages that experience but to be explored.
Regardless of having been found out over 3 a long time in the past, Mofs stay considered one of the most up to date analysis spaces in fabrics chemistry and can certainly achieve this for many years yet to come.





