A longstanding medical trust a couple of hyperlink between most cancers incidence and animal frame measurement has examined for the primary time in our new learn about ranging throughout masses of animal species.
If better animals have extra cells, and most cancers comes from cells going rogue, then the most important animals on earth – like elephants and whales – will have to be riddled with tumours. But, for many years, there was little proof to reinforce this concept.
Many species appear to defy this expectation fully. For instance, budgies are infamous amongst puppy homeowners for being liable to renal most cancers regardless of weighing handiest 35g. But most cancers handiest accounts for round 2% of mortality amongst roe deer (as much as 35kg).
Peto’s paradox is that larger, longer-lived species will have to have upper most cancers incidence, but they don’t appear to. Again in 1977, Professor Sir Richard Peto famous that, on a cell-by-cell foundation, mice appear to have a lot upper susceptibility to most cancers than people. This has ended in hypothesis that better species should have advanced herbal most cancers defences.
A number of examples of those most cancers defences have since been recognized. For instance, Asian elephants, a species with significantly low most cancers incidence, have over 20 copies of a tumour suppressor gene (TP53) in comparison to our personal lone reproduction. Then again, scientists are but to seek out broader proof throughout a variety of animal species.
Our new learn about demanding situations Peto’s paradox. We used a lately compiled dataset of most cancers incidence in over 260 species of amphibians, birds, mammals and reptiles from flora and fauna establishments. Then, the usage of robust fashionable statistical tactics, we in comparison most cancers incidence between the animals.
Huge species have a miles better possibility of having most cancers (cast line), however quicker evolution charges scale back that possibility (dashed line).
Jo Baker and George Butler, CC BY-NC-ND
We discovered that better species do, in truth, have extra most cancers in comparison to smaller ones. This holds throughout all 4 primary vertebrate teams, which means that the normal interpretation of Peto’s paradox doesn’t hang up. However the tale doesn’t finish there.
To start with glance, our findings looked to be at odds with every other long-standing medical thought. Cope’s rule is that evolution has many times favoured better frame sizes, as a result of benefits like advanced predation and resilience. However why would herbal variety power species against a trait that carries an inherent possibility of most cancers?
The solution lies in how briefly frame measurement evolves. We discovered that birds and mammals which reached massive sizes extra all of a sudden have lowered most cancers incidence. For instance, the typical dolphin, Delphinus delphis advanced to succeed in its massive frame measurement – together with maximum different whales and dolphins (known as cetaceans) about 3 times quicker than different mammals. Then again, cetaceans have a tendency to have much less most cancers than anticipated.
Greater species face upper most cancers dangers however those who reached that measurement all of a sudden advanced mechanisms for mitigating it, similar to decrease mutation charges or enhanced DNA restore mechanisms. So somewhat than contradicting Cope’s rule, our findings refine it.
Greater our bodies regularly evolve, however no longer as briefly in teams the place the weight of most cancers is upper. This implies that the specter of most cancers will have formed the tempo of evolution.
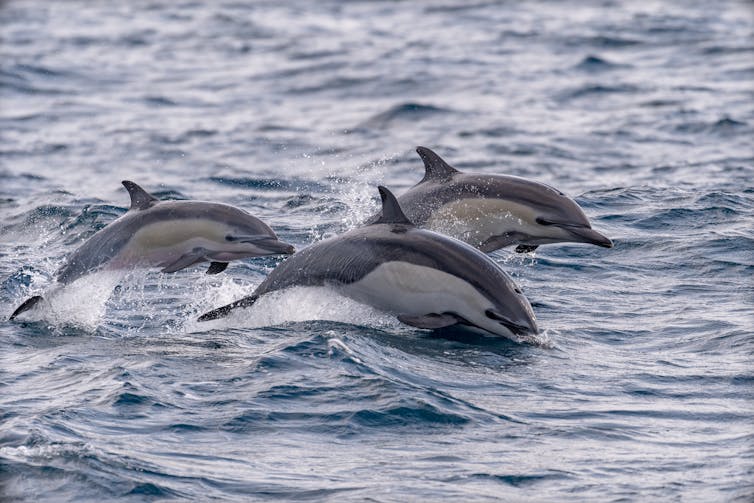
Not unusual dolphins advanced all of a sudden.
DesiDrewPhotography/Shutterstock
People advanced to our present frame measurement reasonably all of a sudden. According to this, we might be expecting people and bats to have identical most cancers incidence, as a result of we advanced at a miles, a lot quicker fee. Then again, it is very important notice that our effects can’t give an explanation for the real incidence of most cancers in people. Neither is that a very easy statistic to estimate.
Human most cancers is a sophisticated tale to resolve, with a plethora of varieties and plenty of components affecting its incidence. For instance, many people no longer handiest have get entry to to trendy drugs but in addition numerous life that impact most cancers possibility. Because of this, we didn’t come with people in our research.
Preventing most cancers
Figuring out how species naturally evolve most cancers defences has necessary implications for human drugs. The bare mole rat, for instance, is studied for its exceptionally low most cancers incidence within the hopes of uncovering new techniques to forestall or deal with most cancers in people. Only some most cancers instances have ever been noticed in captive mole rats so, the precise mechanisms in their most cancers resistance stay most commonly a thriller.
On the identical time, our findings lift new questions. Even though birds and mammals that advanced briefly appear to have more potent anti-cancer mechanisms, amphibians and reptiles didn’t display the similar development. Greater species had upper most cancers incidence irrespective of how briefly they advanced. This may well be because of variations of their regenerative skills. Some amphibians, like salamanders, can regenerate whole limbs – a procedure that comes to numerous cellular department, which most cancers may exploit.
Striking most cancers into an evolutionary context allowed us to expose that its incidence does building up with frame measurement. Learning this evolutionary hands race might unencumber new insights into how nature fights most cancers – and the way we may do the similar.

