When Apollo 13 looped across the Moon in April 1970, greater than 40 million other people all over the world watched the USA recuperate from a possible disaster. An oxygen tank explosion grew to become a deliberate touchdown into an pressing workout in problem-solving, and the 3 astronauts on board used the Moon’s gravity to sling themselves safely house. It used to be a second of unusual human drama, and a revealing geopolitical one.
The Chilly Struggle area race used to be a two-player contest. The Soviet Union and the USA operated in parallel, hardly cooperating, however obviously measuring themselves in opposition to one every other. By means of 1970, the USA had already landed at the Moon, and festival targeted on demonstrating technological capacity, political and financial superiority and nationwide status. As Apollo 13 confirmed, even missions that didn’t cross as deliberate may fortify a rustic’s management in the event that they had been controlled successfully.
Greater than part a century later, NASA’s Artemis II project will ship people across the Moon once more in early 2026, this time intentionally. However the technique going into Artemis II appears very other from that of 1970. America is not competing in opposition to a unmarried rival in a in large part symbolic race.
The staff will make a unmarried flyby of the Moon in an Orion tablet, proven on this representation.
NASA, CC BY-NC
As a professor of air and area regulation, I analysis questions of governance and battle avoidance past Earth. From an area regulation point of view, sustained human process at the Moon and past relies on shared expectancies about protection and accountable habits. In follow, the international locations that display up, perform time and again and display how process at the lunar floor and in outer area may also be performed through the years form those expectancies.
Artemis II issues no longer as nostalgia or simply a technical take a look at flight. This can be a strategic sign that the USA intends to compete in a distinct more or less Moon race, one outlined much less by way of singular achievements and extra by way of sustained presence, partnerships and the facility to form how process at the Moon is performed.
From a 2-player race to a crowded box
As of late, extra international locations are competing to land at the Moon than ever earlier than, with China rising as a pacing competitor. Whilst nationwide status stays an element, the stakes now lengthen well past flags and firsts.
Governments stay central actors within the race to the Moon, however they not perform on my own. Business corporations design and perform spacecraft, and global partnerships form missions from the beginning.
China, specifically, has advanced a lunar program this is planned, well-resourced and fascinated about setting up a long-term presence, together with plans for a analysis station. Its robot missions have landed at the Moon’s a long way aspect and returned samples to Earth, and Beijing has introduced plans for a crewed touchdown by way of 2030. In combination, those steps replicate a program constructed on incremental capacity fairly than symbolic milestones.
Why Artemis II issues with out touchdown
Artemis II, scheduled to release in February 2026, won’t land at the Moon. Its four-person staff will loop across the Moon’s a long way aspect, take a look at life-support and navigation techniques, and go back to Earth. This project would possibly seem modest. Strategically, then again, crewed missions elevate a distinct weight than robot missions.
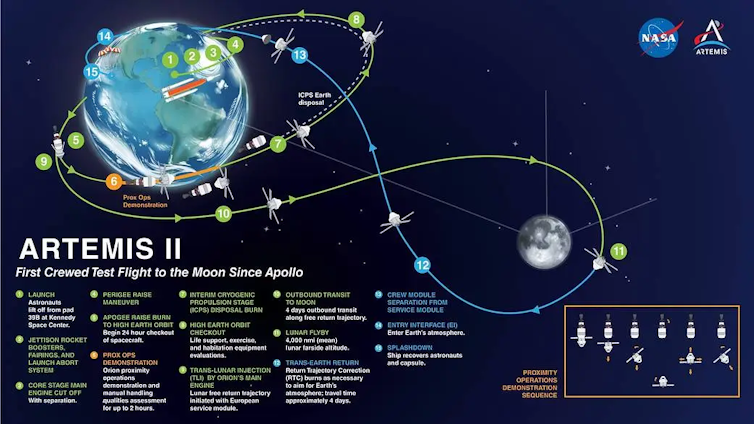
Artemis II’s four-person staff will circle across the Earth and the Moon.
NASA
Sending other people past low Earth orbit calls for sustained political dedication to spaceflight, investment steadiness and techniques dependable sufficient that sovereign and industrial companions can align their very own plans round them.
Artemis II additionally serves as a bridge to Artemis III, the project the place NASA plans to land astronauts close to the Moon’s south pole, these days focused for 2028. A reputable, near-term human go back alerts that the U.S. is shifting past experimentation and towards a sustained presence.
The Artemis II project, detailed from release to splashdown.
2 other fashions for going again to the Moon
The distinction between U.S. and Chinese language lunar methods is increasingly more transparent.
China’s program is centrally directed and tightly managed by way of the state. Its partnerships are selective, and it has launched few information about how actions at the Moon could be coordinated with different international locations or industrial actors.
The U.S. method, in contrast, is deliberately open. The Artemis program is designed so companions, each different international locations and corporations, can perform inside a shared framework for exploration, useful resource use and floor process.
This openness displays a strategic selection. Coalitions amongst international locations and corporations amplify their functions and form expectancies about how actions equivalent to touchdown, running floor apparatus and the use of native assets are performed.
When imprecise regulations begin to subject
World area regulation already incorporates a framework related to this rising festival. Article IX of the 1967 outer area treaty calls for international locations to habits their actions with “due regard” for the pursuits of others and to steer clear of damaging interference. In easy phrases, this implies international locations are anticipated to steer clear of movements that might disrupt or hinder the actions of others.
For many years, this legal responsibility remained in large part theoretical. On Earth, then again, in a similar way open-ended regulations, specifically in maritime contexts, created global conflicts as site visitors on delivery lanes, useful resource extraction and army process higher. Disputes intensified as some states asserted claims that prolonged past what global regulation identified.
The Moon is now drawing near a similar section.
As extra actors converge on resource-rich areas, specifically close to the lunar south pole, due regard turns into a direct operational query fairly than a theoretical long term factor. How it’s interpreted – whether or not it method merely staying out of one another’s means or actively coordinating actions – will form who can perform the place, and beneath what stipulations.
Washington is naming the race − with out panic
Right through his 2nd Senate Trade Committee affirmation listening to, NASA Administrator Jared Isaacman used to be requested without delay about festival with China in lunar exploration. He emphasised the significance of conserving U.S. area efforts not off course through the years, linking the good fortune of the Artemis program to long-term American management in area.
A identical point of view seems in a contemporary U.S. govt review, the U.S.-China Financial and Safety Overview Fee’s 2025 annual report back to Congress. Bankruptcy 7 addresses area as a website of strategic festival, highlighting China’s rising functions. The document frames human spaceflight and deep-space infrastructure – together with spacecraft, lunar bases and supporting applied sciences – as a part of broader strategic efforts. It emphasizes rising a human area program through the years, fairly than converting path in accordance with person setbacks or the accomplishments of alternative international locations.
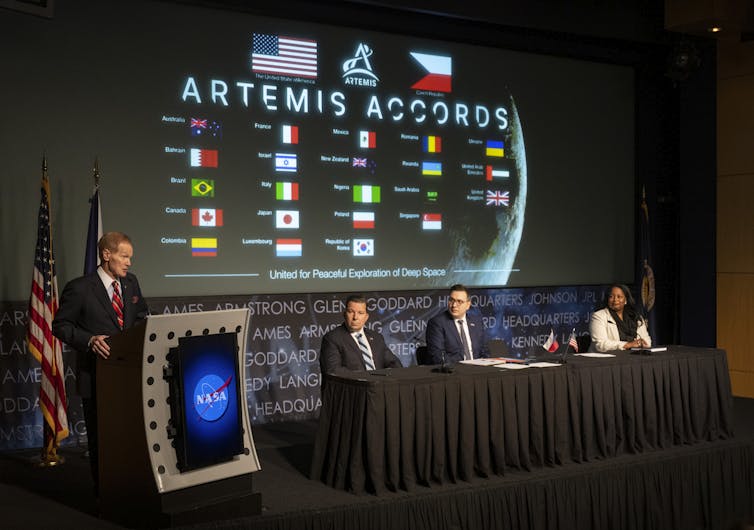

The U.S. technique to spaceflight is emphasizing global cooperation.
Joel Kowsky/NASA by way of Getty Pictures
Contemporary U.S. coverage displays this emphasis on continuity. A brand new govt order affirms federal assist for sustained lunar operations, in addition to industrial participation and coordination throughout businesses. Somewhat than treating the Moon as a non permanent problem, the order anticipates long-term process the place transparent regulations, partnerships and predictability subject.
Artemis II aligns with this posture as one step within the U.S.’s plans for sustained process at the Moon.
A unique more or less take a look at
As Artemis II heads towards the Moon, China will even proceed to advance its lunar ambitions, and festival will form the tempo and way of process across the Moon. However festival on my own does no longer resolve management. In my opinion, management emerges when a rustic demonstrates that its method reduces uncertainty, helps cooperation and interprets ambition into a collection of strong running practices.
Artemis II won’t settle the way forward for the Moon. It does, then again, illustrate the American fashion of area process constructed on coalitions, transparency and shared expectancies. If sustained, that fashion may affect how the following technology of lunar, and sooner or later Martian, exploration unfolds.






