Lately, roughly 1,800,000 acres of land in america is used for landfill waste disposal. With regards to quantity, the U.S on my own generated over 290 million heaps of forged waste in 2018, an quantity identical to about 235,000 Olympic-size swimming swimming pools, assuming a mean forged waste density of a part ton according to cubic meter.
Kind of 9% – about 26 million heaps – of this waste is made up of iron and metal. Those are assets with a solid marketplace worth utilized in more than a few civil infrastructure tasks. As a staff of environmental engineers, we would have liked to grasp whether or not shall we use iron-rich waste to supply iron oxide nanoparticles – a useful gizmo for preventing water air pollution and construction engineering {hardware}.
All about nanoparticles
Iron oxide nanoparticles encompass iron and oxygen atoms and, on account of their length, they showcase distinctive bodily and chemical houses. They’re extraordinarily small, in most cases on the nanoscale – one-billionth of a meter – in diameter.
The iron oxide nanoparticles we synthesized had been a particular crew referred to as magnetite and maghemite. Preliminary research have proven that nanoparticles on this crew may just assist medication get to the suitable a part of the frame, make batteries in electrical cars extra environment friendly and strengthen sensors for detecting poisonous fuel, in addition to sound and movement.
As a result of those nanoparticles are product of iron, they’re each magnetic and solid. Their tiny length offers them a big floor space relative to their quantity, letting them take hold of pollution in water. Moreover, their magnetic nature makes them splendid for construction extraordinarily small and skinny electric parts.
In our paintings, we would have liked to discover a new strategy to produce them the usage of waste fabrics. In our latest find out about, revealed within the RSC Sustainability magazine, we advanced an eco-friendly technique to synthesize iron oxide nanoparticles from expired over the counter iron dietary supplements. This method no longer best offers worth to discarded merchandise but in addition helps a extra sustainable and round approach of manufacturing.
The analysis procedure
To behavior our find out about, we used one way referred to as hydrothermal carbonization to supply those magnetic nanoparticles. We had been ready to supply a considerable amount of expired iron dietary supplements from a neighborhood well being care heart.
The hydrothermal carbonization procedure makes use of a turbocharged model of the type of force cooker you may have to your kitchen. For our recipe, we blended 20 grams every of expired iron dietary supplements and water in a specialised force reactor. We then cooked the combination at 527 levels Fahrenheit (275 levels Celsius) for 6 to twelve hours. Beneath this intense temperature and force, the dietary supplements broke down, which produced tiny – 10- to 11-nanometer – debris.
The top product incorporated a forged charcoal-like subject matter referred to as hydrochar, which made up about 20% to 22% of the product. The hydrochar consisted of the iron oxide nanoparticles and graphite, a carbon-rich subject matter that gave the hydrochar its charcoal-like glance. The remainder become fuel and a depressing, tarlike liquid break away the hydrochar.
Hydrothermal carbonization isn’t the one approach used to make iron oxide nanoparticles. There are different standard strategies similar to coprecipitation, which comes to blending chemical substances to shape solids. Some other approach is pyrolysis, the place fabrics are heated within the absence of oxygen. And in spite of everything, gasification, which heats fabrics within the presence of oxygen.
Those strategies typically require the next power enter, round 1,292 to one,832 levels Fahrenheit (700 to one,000 C), or harsh salt chemical substances. Against this, hydrothermal carbonization, the process we used, is water-based and will occur at a low temperature.
Preliminary analysis presentations that nanoparticles constructed from iron clears some pollution from wastewater. After growing the nanoparticles, researchers take a look at them the usage of quite a lot of clinical tactics. The nanoparticles have a number of possible long run programs within the generation box.
Ahmed Yunus
We when compared our hydrothermal carbonization procedure’s power use with different strategies and located it had the bottom environmental affect.
From polluted water to scrub
The iron oxide nanoparticles we created are very helpful for water remedy. They’re in particular excellent at eliminating oil and heavy metals similar to lead, cadmium, zinc and chromium from water. Those are pollution identified to purpose critical well being problems, together with most cancers.
You’ll both combine them with polluted water or permit the water to go via them, very similar to a not unusual family clear out.
To check their functionality, we combined our iron oxide nanoparticles in wastewater samples containing methylene blue dye, a not unusual pollutant in textile and production wastewater. We discovered they got rid of over 95% of the dye, and as the debris are magnetic, shall we take away them from the handled water the usage of a magnet so that they didn’t contaminate the water.
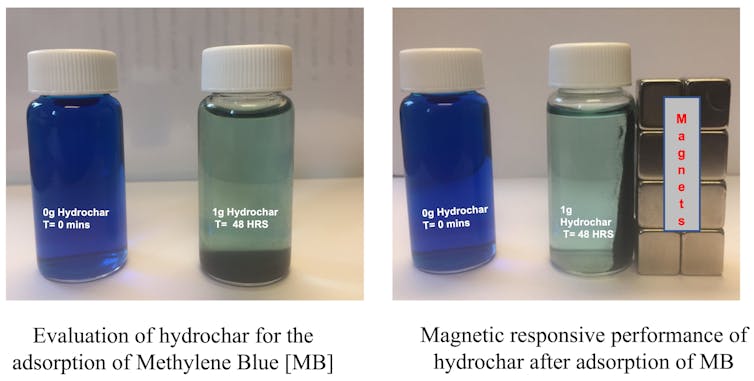
Water polluted with methylene blue cleared up after remedy with iron oxide nanoparticles over 48 hours, and the nanoparticles connect to a magnet.
Yunus et al., 2025
Relying on the kind of pollution within the water, iron oxide nanoparticles can on occasion be reused once they’re heated once more.
Transferring ahead
We produced a small quantity of those nanoparticles within the lab for this find out about. Then again, huge amounts of iron waste are despatched to landfills. Those come with fabrics similar to metal sludge and steel scraps. So in idea, many extra of those nanoparticles may well be produced one day. If produced in sufficiently big amounts, huge water and wastewater plant filtration programs may just use those debris to regard a lot better quantities of water.
However landfill waste isn’t all one form of waste. Iron-rich waste could also be infected with different fabrics, making its sourcing, sorting and recycling each resource-intensive and dear. To scale up this generation sustainably, researchers will wish to first triumph over those demanding situations.
At the shiny facet, economists expect that selection metals, together with iron oxide nanoparticles, might assist meet manufacturing calls for for long run applied sciences and synthetic intelligence. Those nanoparticles can be utilized to fabricate high-performance computing parts. Those parts come with magnetic reminiscence garage and semiconductors present in our on a regular basis applied sciences.
A lot of the essential metals these days used are dear, scarce or geopolitically delicate: cobalt, nickel and lithium. Consequently, our staff is beginning to discover how this hydrothermal carbonization-based approach will also be scaled and implemented to different forms of waste fabrics.
Our long-term function is to increase the instrument package for sustainable nanoparticle manufacturing whilst proceeding to handle each environmental demanding situations and fabrics calls for for long run inventions.






