Biotech corporate Colossal Biosciences made headlines in April 2025 after claiming it had “successfully restored … the dire wolf to its rightful place in the ecosystem.” 3 wolf doggies – Romulus, Remus and Khaleesi – have been born via this de-extinction venture.
However in the back of the scenes lies a extra sophisticated truth.
What Colossal in fact did used to be edit a small selection of grey wolf genes, aiming to create bodily characteristics that resemble the ones of the extinct dire wolf. The edited embryos have been implanted into surrogate home canine.
Many scientists and newshounds expressed skepticism in regards to the declare that this quantities to restoring the dire wolf. Mavens identified that tweaking a handful of genes does now not reflect the entire organic truth of a long-extinct species. Lots of the dire wolf’s genetic make-up stays unknown and unreplicated.
Is equivalent to a dire wolf sufficient for one thing to be a dire wolf?
James St. John/Wikimedia Commons, CC BY-SA
This hole between look and organic identification raises a deeper query: What precisely is a species, and the way do making a decision whether or not one thing belongs to at least one species relatively than any other?
Biologists name the solution a species idea – a principle about what a species is and the way researchers type organisms into other teams. As a thinker of science who research what defines a species, I will say this: Whether or not de-extinction tasks prevail relies on which species idea you suppose is correct – and in reality, even scientists don’t agree.
How scientists outline a species
When scientists speak about biodiversity – the number of life-forms present in nature – species are the fundamental construction blocks. A species is meant to mirror an actual department between distinct teams of organisms within the flora and fauna, now not only a handy label.
In classifying residing issues into species, scientists are looking to “carve nature at its joints” to mirror actual patterns formed by means of evolution. Even so, deciding what counts as a species seems to be strangely tricky and extremely debatable. Scientists have proposed dozens of distinct species ideas – some students have counted over 32 tactics to outline a species – and every attracts the strains somewhat in a different way. Those definitions don’t all the time agree on whether or not an organism is a part of one species relatively than any other.
Two of probably the most influential species ideas spotlight the problem. The organic species idea defines a species as a bunch of organisms that may naturally breed with every different and convey fertile offspring. Beneath this view, African wooded area elephants and African savanna elephants have been as soon as categorized as the similar species as a result of they might mate and feature younger in combination, although they lived in numerous habitats and regarded other.
Every other manner, the phylogenetic species idea, emphasizes ancestry as a substitute of breeding. A species, on this view, is a bunch that stocks a singular evolutionary historical past, forming its personal distinct department at the tree of lifestyles. By way of this same old, researchers discovered that wooded area and savanna elephants have been genetically evolving one at a time for tens of millions of years, lengthy sufficient to be regarded as other species even though they might nonetheless interbreed.

African savanna elephants, left, and African wooded area elephants are regarded as two distinct species.
Charles J. Sharp, Thomas Breuer/Wikimedia Commons, CC BY-SA
Figuring out those other species ideas is an important for comparing claims about de-extinction. If Romulus, Remus and Khaleesi may just naturally mate with historic dire wolves and convey fertile offspring, then they’d be regarded as true dire wolves below the organic species idea.
However for definitions of species that emphasize evolutionary historical past, such because the phylogenetic species idea, the lab-created wolves would now not qualify as actual dire wolves – even though they have been indistinguishable from the originals – as a result of they didn’t descend from historic dire wolves.
Regardless of variations on how easiest to outline species, there’s a unexpected level of consensus amongst scientists and philosophers on one giant thought: What makes one thing a part of a species isn’t an inner characteristic, comparable to a selected set of genes, however a courting to one thing else – to its atmosphere, to different organisms, or to a shared evolutionary historical past.
By way of this frame of mind – what’s regularly referred to as relationalism – there’s no particular “lemon gene” that makes a lemon and no hidden genetic marker that mechanically makes an animal a dire wolf. Often shared throughout a majority of these theories is the perception that belonging to a specific species relies on connections and context, now not on anything else throughout the organism itself.
However what if that consensus is fallacious?
On warblers and mitochondria
In the beginning look, the usual tactics of defining a species appear to paintings smartly. However from time to time, nature throws a curveball – or even probably the most depended on definitions don’t fairly are compatible.
Take the case of the blue-winged and golden-winged warblers. Those two songbirds appearance and sound other. They put on other plumage, sing other songs and like other habitats. Birders and organizations such because the American Ornithological Society have all the time categorized them as separate species.
But below two of the commonest medical definitions of species, the organic and phylogenetic species ideas, blue-winged and golden-winged warblers are regarded as the similar species. Those birds steadily mate and convey younger in combination. They’ve been swapping genes for 1000’s of years. And when scientists checked out their nuclear DNA – the genetic subject matter tucked throughout the nucleus of every mobile – they discovered the 2 birds are 99.97% similar. This discovering means that even cautious, extensively accredited species definitions can leave out one thing vital.

The golden-winged warbler, left, and blue-winged warbler are regarded as two distinct species, however in step with many species ideas they’d depend as the similar.
Wildreturn, Ken Janes/Wikimedia Commons, CC BY-SA
So what if, as a substitute, the important thing to being a part of a species lies deep throughout the organism, in the best way its elementary programs of lifestyles are compatible in combination?
Contemporary paintings in biology and philosophy suggests differently of fascinated about species that specializes in a hidden however essential machine within cells: the partnership between two units of genetic subject matter. I and my colleague Kyle B. Heine discover this concept by means of drawing on analysis in mitonuclear ecology – the find out about of the way other portions of an organism’s genetic subject matter adapt and paintings in combination to provide power.
Nearly each and every mobile incorporates two sorts of DNA. One set, saved within the nucleus, acts like an instruction handbook that guides lots of the mobile’s actions. The opposite, present in constructions referred to as mitochondria – the mobile’s power facilities – incorporates its personal a lot smaller set of directions aimed at supporting its distinctive function in retaining the mobile operating.
Generating power relies on actual teamwork between nuclear DNA and mitochondrial DNA, like two musicians taking part in in best possible team spirit. Over tens of millions of years, the nuclear and mitochondrial DNA of every species have developed in combination to shape a singular, finely tuned machine.
This perception has resulted in a brand new frame of mind about species, referred to as the mitonuclear compatibility species idea. In keeping with this concept, an organism belongs to a species if its two units of genes – the ones within the nucleus and the ones within the mitochondria – are optimized to paintings in combination to generate life-sustaining power. If the cell partnership between those two genetic programs is mismatched, the organism would possibly fight to provide the power it must continue to exist, develop and reproduce.
By way of this same old, other species aren’t simply outlined by means of how they appear or behave, however by means of whether or not their nuclear and mitochondrial genes shape a uniquely coadapted crew. As an example, although blue-winged and golden-winged warblers are just about similar of their nuclear DNA, they fluctuate by means of about 3% of their mitochondrial DNA – a clue that their power programs are distinct. And that’s precisely what the mitonuclear compatibility species idea predicts: They truly are two separate species.
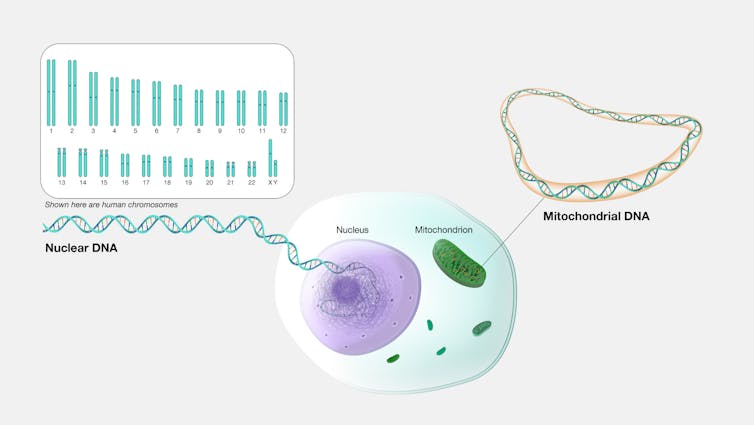
Nuclear DNA and mitochondrial DNA evolve in combination for cells – and species – to thrive.
Nationwide Human Genome Analysis Institute
Rethinking the that means of de-extinction
Bringing again a species just like the dire wolf isn’t only a subject of having the fur proper or tweaking a couple of visual characteristics. In keeping with my most well-liked species idea, even though a recreated animal seems to be the phase, it gained’t in point of fact be a dire wolf except its internal genetic programs – those that energy its cells – are finely tuned to paintings in combination, simply as they have been within the authentic species.
That’s a tall order. And with out restoring the entire internal equipment of the unique species, any lab-grown look-alike would fall brief.
Figuring out how scientists outline species – and the way the ones definitions form the probabilities of de-extinction – provides greater than only a lesson in organic bookkeeping. It displays that classification isn’t just about names or lineages, however about spotting the deep organic patterns that maintain lifestyles, providing a deeper appreciation of what it truly approach to deliver again the previous.
Reviving an extinct species isn’t like assembling a style from spare portions. It approach recreating a residing, respiring machine – one whose portions will have to paintings in live performance, now not simply appearance the phase.
And that’s why philosophy and science each subject right here: To grasp what we’re bringing again, we will have to first perceive what used to be in point of fact misplaced.



