The sector has witnessed a resurgence of protectionism since Donald Trump returned to the White Space. So-called “reciprocal” price lists, imposed on all US buying and selling companions at various levels in accordance with the tax they price on American items, were some of the hallmark options of Trump’s financial coverage. They target to right kind what he perceives as “unfair” industry practices.
In early April, Trump mentioned many nations had “ripped us off left and right” and declared “now it’s our turn to do the ripping”. His management abruptly imposed sweeping tariff will increase, with one of the vital very best charges falling on poorer international locations like Laos and Lesotho.
A 90-day suspension used to be ultimately made for some of these price lists, and Trump has now softened tasks on imported automobiles and automotive portions. However the threat stays top. Nobody can also be sure that the preliminary reciprocal price lists may not be reinstated.
Creating international locations, lots of which depend closely at the export of manufactured items to the USA, might be protecting a willing eye on what occurs subsequent.
Staff at a garment manufacturing unit in Lesotho, which Trump threatened with a top tariff price.
Kim Ludbrook / EPA
We hired the International Business Research Challenge fashion to analyse the conceivable results of US price lists on industry and financial expansion. The fashion captures interactions and comments amongst financial brokers (families, companies and governments), markets, sectors and areas on the planet economic system.
It may be used to forecast the impact of industry reforms on quite a lot of signs corresponding to manufacturing, welfare, source of revenue, costs and industry flows. In response to sure assumptions, the adjustments usually are noticed in between two and 3 years.
We used simulations to compute the results of Trump’s tariff regime underneath two selection eventualities. Within the first, which displays the worldwide industry scenario on the time of writing, baseline price lists are levied on all international locations at 10%. The tasks are 25% on items from Canada and Mexico, and 145% on China. Retaliatory tasks via China on US items are set at 125%.
In the second one, across-the-board reciprocal price lists are imposed on international locations on the ranges Trump declared in his preliminary plan on April 2. That is along with the 145% tariff on Chinese language items, 25% on the ones from Canada and Mexico and a 125% accountability via China on imports from the USA.
Winners and losers
As proven via the graph beneath, our simulations counsel the USA tariff regime will distort export patterns international. Probably the most painful results will fall on China and the USA itself.
Chinese language exports would shrink via 10.8% within the first situation and 10.9% in the second one. The USA would undergo a good better lack of 11.7% and 14.9%, respectively.
The fashion means that different main US buying and selling companions corresponding to Canada and Mexico would additionally enjoy deep export declines of over 5% in each eventualities. Kind of 75% of Canada’s exports head south against the USA.
A few of the growing Asian economies, Nepal, Pakistan and the Philippines would enjoy really extensive export declines. That is specifically the case in the second one situation, with losses starting from 2% to 4.4%. Those international locations are specifically prone to reciprocal price lists as a result of they depend closely on exports and are deeply tied to international provide and manufacturing chains.
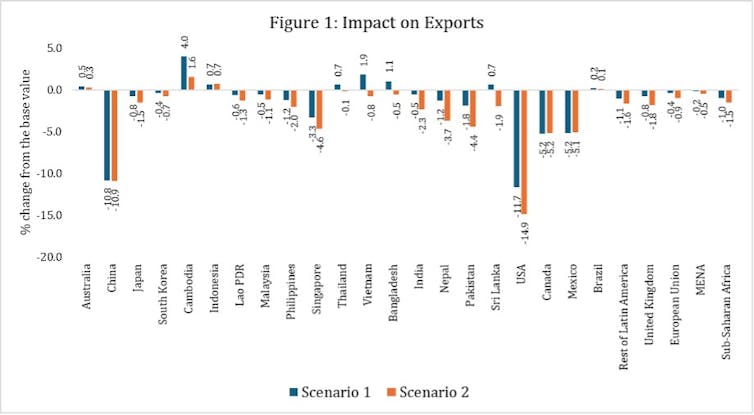
Bangladesh, Cambodia, Indonesia, Sri Lanka and Vietnam could gain advantage within the first situation because of a conceivable diversion of industry. Those international locations, which can be recognized for having one of the vital lowest labour prices on the planet, be offering affordable choices for items that US importers would up to now have sourced from China.
However they’re anticipated to lose nearly all of those advantages in the second one situation underneath a complete reciprocal tariff regime. The exceptions are Cambodia and Indonesia, which our simulations counsel will retain sure export expansion – albeit diminished to at least one.6% from 4% for Cambodia and unchanged at 0.7% for Indonesia.
This can be as a result of Cambodia and Indonesia have quite extra various export baskets than international locations like Bangladesh and Sri Lanka, and industry with extra companions. On the other hand, those good points usually are brief lived if international uncertainties proceed.
Primary complicated economies corresponding to Japan, the United Kingdom and EU will lose exports via a reasonable quantity. And the Heart East, north Africa, sub-Saharan Africa and Latin The us (except Brazil) will see equivalent declines.
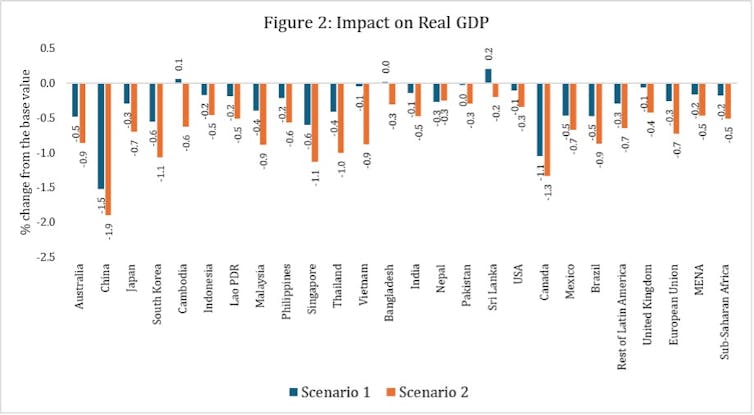
The second one graph items a relating to image of ways industry disruption may just have an effect on GDP, which economists use to measure the dimensions of a rustic’s economic system. The USA and China are once more set to undergo the steepest GDP losses, of 0.3% in the USA and 1.9% in China underneath the second one situation. This confirms the well-established financial consensus that industry wars are mutually harmful.
Below the second one situation, maximum rising and growing economies would undergo modest GDP declines between 0.3% and 1%. Thailand (1%), Malaysia (0.9%), Brazil (0.9%) and Vietnam (0.9%) are the worst hit international locations on this class.
Like lots of the growing international locations in Asia, which aren’t at once concerned within the industry warfare, many nations in Latin The us, the Heart East, north Africa and sub-Saharan Africa would nonetheless face hits to their GDP. This underscores the worldwide interconnectedness of industry and funding flows.
The simulations verify what economists were saying for years: industry wars shouldn’t have winners. Whilst some international locations do receive advantages within the brief time period by the use of industry diversion, the full losses are top and growing international locations aren’t immune from the wear and tear.
On the other hand, there are tactics growing international locations can make use of to support their resilience to international industry disruptions. This contains diversifying their export markets via, as an example, setting up more potent industry ties in regional blocs.
One instance is the Regional Complete Financial Partnership, a unfastened industry settlement between the Asia-Pacific international locations of Australia, Brunei, Cambodia, China, Indonesia, Japan, South Korea, Laos, Malaysia, Myanmar, New Zealand, the Philippines, Singapore, Thailand and Vietnam. Such ties can also be bolstered additional.
Creating international locations must additionally use this turbulent duration to streamline customs, improve port infrastructure and support logistics. It will scale back prices, fortify competitiveness and assist growing economies interact extra deeply in global industry.
No nation is exempt from disruptions to international industry. However the ones with various economies, robust regional linkages and resilient industry infrastructure will climate the turbulence extra effectively.



