Till rather just lately, people had been restricted by way of the horizon. Local weather scientists of the early twentieth century may acquire information from the arena round them and most likely what they had been in a position to peer from a scorching air balloon or aircraft. However the truly large image – the worldwide snapshot – remained out of sight.
The primary satellite tv for pc of any sort used to be the USSR’s Sputnik 1, introduced in 1957. However it wasn’t till the Nineteen Sixties that satellites designed particularly to look at the Earth and its local weather made it into orbit and gave us the primary review of climate patterns. Through the Nineteen Seventies Nasa’s Landsat satellites had been in a position to watch such things as tree quilt.
Jonathan Bamber, a local weather scientist on the College of Bristol, says this “revolutionised our ability to carry out a comprehensive and timely health check on the planetary systems we rely on for our survival”. Information that when required months and even years of fieldwork used to be abruptly to be had within the time it took a satellite tv for pc to orbit the planet.
In this day and age, this information will also be remarkably exact and detailed. Bamber says: “We can measure changes in sea level down to a single millimetre, changes in how much water is stored in underground rocks, the temperature of the land and ocean and the spread of atmospheric pollutants and greenhouse gases, all from space.”
Right here’s a map of sea stage upward thrust, from Bamber’s article highlighting 5 satellite tv for pc photographs that display how briskly our planet is converting:
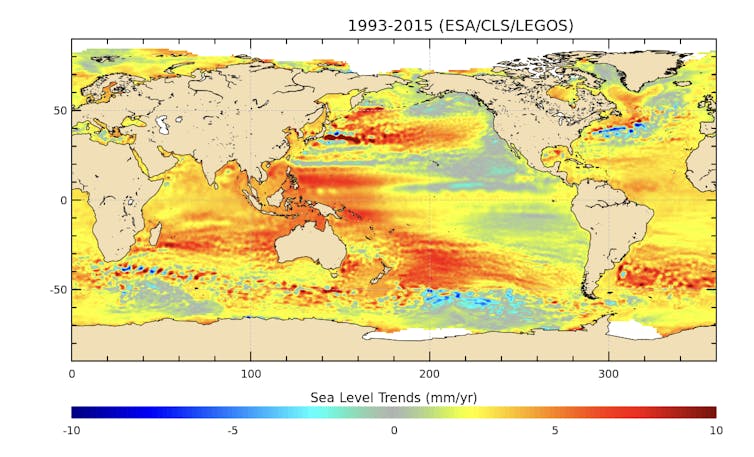
The ocean is emerging temporarily – however no longer frivolously.
ESA/CLS/LEGOS, CC BY-SA
“This image,” writes Bamber, “shows mean sea level trends over 13 years in which the global average rise was about 3.2mm a year. But the rate was three or four times faster in some places, like the south western Pacific to the east of Indonesia and New Zealand, where there are numerous small islands and atolls that are already very vulnerable to sea level rise.”
In recent times, scientists have used AI to sift thru and analyse satellite tv for pc information. Bamber’s newest analysis, revealed in January this 12 months, illustrates this effectively.
A workforce of scientists, lead by way of Tian Li additionally of the College of Bristol, accumulated hundreds of thousands of satellite tv for pc photographs of glaciers in Svalbard, a faraway and icy archipelago within the Arctic Ocean. Of their write up, they observe that human researchers as soon as painstakingly regarded thru this kind of information.
“This process”, they write, “is highly labour-intensive, inefficient and particularly unreproducible as different people can spot different things even in the same satellite image. Given the number of satellite images available nowadays, we may not have the human resources to map every region for every year.”
Their answer used to be to make use of AI to “quickly identify glacier patterns across large areas”. The satellite-AI combo supposed they might read about Svalbard’s backing out glaciers – unquestionably some of the least available puts on the earth – in “unprecedented scale and scope”.
They discovered that 91% of the various glaciers that go with the flow into the ocean across the archipelago had been “shrinking significantly”. They observe that the similar kinds of glacier will also be discovered around the Arctic, and “what happens to glaciers in Svalbard is likely to be repeated elsewhere”.
Lots of the ones glaciers will also be present in Greenland, house of the northern hemisphere’s greatest ice sheet. In analysis revealed previous this month, Tom Chudley of Durham College used satellite tv for pc photographs to evaluate crevasses (cracks within the glaciers) in Greenland.

A big glacier in west Greenland flows into the ocean. That iceberg crammed fjord is a number of miles broad.
Copernicus Sentinel / lavizzara / shutterstock
Chudley additionally mixed satellite tv for pc photographs with computerised research. His paintings made use of “ArcticDEM”, 3 dimensional maps of the polar areas in keeping with prime solution satellite tv for pc photographs.
“By applying image-processing techniques to over 8,000 maps, we could estimate how much water, snow or air would be needed to “fill” every crevasse around the ice sheet. This enabled us to calculate their intensity and quantity, and read about how they developed.“
His conclusion used to be very blunt: the Greenland ice sheet is falling aside.
Well being watchdogs
Lots of you’re going to be smartly conscious that satellites are getting used to watch the well being of the planet. What’s much less widely known is the position they may be able to play in tracking human well being.
Dhritiraj Sengupta, a satellite tv for pc scientist at Plymouth Marine Laboratory, says satellites have turn into Earth’s new well being and nature watchdog. His article main points how satellites can map mosquito breeding websites to struggle malaria, as an example, or can determine air air pollution hotspots in towns.
In his personal analysis, he’s used satellite-derived chlorophyll information to evaluate the chance of cholera. Chlorophyll is the golf green pigment in crops that is helping them use daylight to make their meals and develop.
“Many micro organism like Vibrio cholerae which reasons cholera, thrive in stagnant water,” Sengupta writes. “My team worked with the European Space Agency to show that its presence can be modelled using the concentration of chlorophyll found on the surface of bodies of water.”
Up to now, so just right. Satellites have undeniably been helpful for local weather scientists. However within the longer-term, the satellites themselves can have an unexpected impact at the local weather.
Ultimate 12 months, SpaceX introduced it could “deorbit” 100 of its Starlink satellites to expend within the setting. Fionagh Thomson is an area professional, additionally at Durham College. She says that “atmospheric scientists are increasingly concerned that this sort of apparent fly-tipping by the space sector will cause further climate change down on Earth.”
Debris from the satellites themselves gained’t have a huge impact in comparison to the “440 tonnes of meteoroids that enter the atmosphere daily, along with volcanic ash and human-made pollution from industrial processes on Earth.”
However one workforce “recently, and unexpectedly, found potential ozone-depleting metals from spacecraft in the stratosphere, the atmospheric layer where the ozone layer is formed.” The concern is that satellite tv for pc particles might assist shape sure kinds of clouds that result in ozone loss and might upload to the greenhouse impact.
She notes that that is all unsure and desires extra analysis. “But,” she writes, “we’ve also learnt that if we wait until indisputable evidence is available, it may be too late, as with the loss of ozone. It’s a constant dilemma.”
One thing for SpaceX scientists to seem into, most likely, after they’ve completed rescuing stranded astronauts from the Global Area Station.





