For many years, army medical doctors confronted a crucial problem: What’s one of the simplest ways to securely and successfully ship oxygen to sufferers in far flung battle zones, rural hospitals or disaster-stricken spaces?
Oxygen tanks are heavy, pricey and perilous in battle zones. A right away hit from a missile or a bullet can flip a lifesaving useful resource into a dangerous danger.
Marine Corps Gen. Ernest T. Cook dinner as soon as stated, “Logistics is the hard part of fighting a war.” It is going past oxygen. For deployed U.S. troops, the provides to be had throughout battle for treating wounded squaddies can imply the adaptation between lifestyles and loss of life.
The Division of Protection grew to become to us, army physicians and educational researchers in army medication on the College of Colorado Heart for COMBAT Analysis, to check whether or not the army must deliver oxygen to the battlefield for squaddies – and, if that is so, how a lot.
This technique to analysis is referred to as a military-civilian partnership. Those partnerships purpose to avoid wasting lives at the battlefield. However additionally they save lives around the U.S. by way of turning army clinical good points into higher well being take care of all.
Innovation and agility
Within the civilian global, it takes 17 years on reasonable for a analysis discovery to modify clinical apply. One of the vital well known examples of that is the usage of tranexamic acid for trauma sufferers. Tranexamic acid is injected to prevent bleeding throughout surgical treatment or after trauma. It was once found out in 1962 however no longer licensed by way of the FDA till 1986. It wasn’t used for hectic bleeding till 2012.
The converting nature of conflict and threats in opposition to U.S. forces require army medication to transport sooner. Accidents and infections in battle push researchers to search out higher techniques to avoid wasting lives, steadily sooner than in civilian well being care.
Army medication will have to transfer temporarily to stay alongside of the tempo of conflict.
Contributor/Anadolu by way of GettyImages
On the middle, scientists paintings aspect by way of aspect with army clinical groups to check, expand and check answers adapted for the battlefield.
Whether or not it’s addressing oxygen use, hectic mind accidents, burn remedies or trauma care, those partnerships permit army and civilian researchers to translate discoveries into apply unexpectedly.
Rethinking oxygen
The instant management of oxygen to an injured or unwell affected person has lengthy been a cornerstone of trauma and burn care. The good judgment appeared easy: When sufferers are in surprise or have critical accidents, their our bodies battle to get sufficient oxygen, so medical doctors equipped further.
Our analysis, and that of others, discovered that an excessive amount of oxygen can if truth be told be destructive. Extra oxygen triggers oxidative tension – an overload of risky molecules known as loose radicals that may injury wholesome cells. That may end up in extra irritation, slower therapeutic or even organ failure.
In brief, whilst oxygen is very important, extra isn’t all the time higher.
We performed a chain of military-civilian collaborative trials known as Technique to Keep away from Over the top Oxygen, or SAVE-O2. We found out that seriously injured sufferers steadily require much less oxygen than in the past believed. If truth be told, very little supplemental oxygen is had to safely take care of 95% of those sufferers.
This discovering demanding situations a long time of standard clinical knowledge. It’s going to reshape how clinical pros method crucial care in no longer most effective army settings, however civilian hospitals as smartly.
Inside a 12 months of presenting our findings to army clinical leaders, those insights have already influenced adjustments and updates to affected person care pointers, medic coaching or even choices on clinical apparatus purchases.
To construct on our findings, we’ve introduced an ordeal to check the usage of synthetic intelligence to automate oxygen supply. This military-funded learn about may provide higher take care of wounded squaddies in far flung battle zones and for injured civilians in ambulances or rural hospitals prior to they achieve huge referral and trauma facilities.
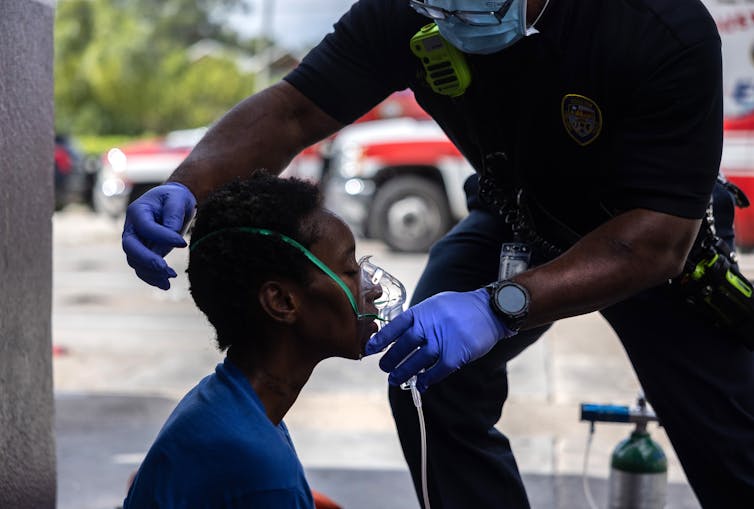
An oxygen masks that makes use of synthetic intelligence may just assist medics in rural battle zones and rural U.S. hospitals.
John Moore/GettyImages
In rural or far flung spaces of the U.S., get right of entry to to supplemental oxygen will also be restricted because of provide chain demanding situations, top prices and shortages. That is in particular true in small hospitals and impacts first responders after a herbal catastrophe or twist of fate. Within the extensive care devices of those hospitals, the usage of oxygen extra successfully may just maintain restricted oxygen provides for sufferers who want it.
Extended casualty care: A brand new frontier
Whilst researching oxygen wishes in battle zones, we learned some other urgent factor: the demanding situations of extended casualty care. Right through a warfare, army medics steadily want to deal with seriously injured squaddies for hours and even days prior to the wounded individual will also be evacuated.
In a long run warfare with a “near-peer” adversary akin to China or Russia, the U.S. won’t be capable of evacuate wounded troops temporarily. With out dependable helicopter or aircraft delivery, many casualties won’t achieve trauma care inside the “golden hour.” That is the crucial first 60 mins after a critical harm, when fast remedy is very important.
The continued conflict in Ukraine illustrates the problem of extended casualty care. In hospitals throughout Ukraine, medical doctors are increasingly more having bother treating the injuries of civilian and army sufferers on account of emerging antibiotic resistance.
Long run army conflicts within the Indo-Pacific areas will provide identical demanding situations, together with lengthy affected person delivery occasions and considerations about wound infections because of extended casualty care.
Alternatively, this problem isn’t distinctive to the battlefield. Extended casualty care additionally occurs in civilian crises. For instance, throughout a herbal catastrophe, emergency responders will have to organize sufferers with out fast get right of entry to to hospitals.
As soon as sufferers are handled within the box or in catastrophe situations, suppliers will have to steadily maintain care with restricted sources. They’ve to prioritize crucial interventions, decrease useful resource use and stabilize sufferers for eventual switch to raised ranges of care.
Innovation in well being care flourishes on collaboration. Army-civilian partnerships are one approach to advance clinical answers sooner and extra successfully. Those inventions save lives in battle, give a boost to care and make allowance us to use our 98% survival fee in conflict to our trauma facilities, rural hospitals and catastrophe zones within the U.S.




