If you’re sneezing this spring, you aren’t on my own. Once a year, vegetation liberate billions of pollen grains into the air, specks of male reproductive subject matter that many people realize most effective after we get watery eyes and runny noses.
Then again, pollen grains are excess of allergens – they’re nature’s time tablets, conserving clues about Earth’s previous environments for hundreds of thousands of years.
Pollen’s tricky outer shell permits it to live to tell the tale lengthy after its mother or father vegetation have disappeared. When pollen grains transform trapped in sediments on the backside of lakes, oceans and riverbeds, fossil pollen can give scientists with a singular historical past of the environments the ones pollen-producing vegetation had been born into. They may be able to let us know concerning the crops, local weather or even human job thru time.
Fossil pollen grains of Carya (hickory) had been present in southeastern Missouri which can be hundreds of thousands of years previous.
Francisca Oboh Ikuenobe
The varieties of pollen and the amounts of pollen grains discovered at a website lend a hand researchers reconstruct historic forests, observe sea-level adjustments and determine the fingerprints of important occasions, corresponding to asteroid affects or civilizations collapsing.
As palynologists, we find out about those historic pollen fossils around the globe. Listed here are a couple of examples of what we will be informed from those microscopic pollen grains.
Missouri: Pollen and the asteroid
When an asteroid struck Earth some 66 million years in the past, the only blamed for wiping out the dinosaurs, it’s believed to have despatched a tidal wave crashing onto North The us.
Marine fossils and rock fragments present in southeastern Missouri seem to have been deposited there by means of an enormous wave generated by means of the asteroid hitting what’s now Mexico’s Yucatan Peninsula.
A number of the rocks and marine fossils, scientists have discovered fossilized pollen from the Overdue Cretaceous and Early Paleocene classes that displays adjustments within the surrounding ecosystems. The pollen finds how ecosystems had been right away disrupted on the time of the asteroid, sooner than steadily rebounding over masses to 1000’s of years.
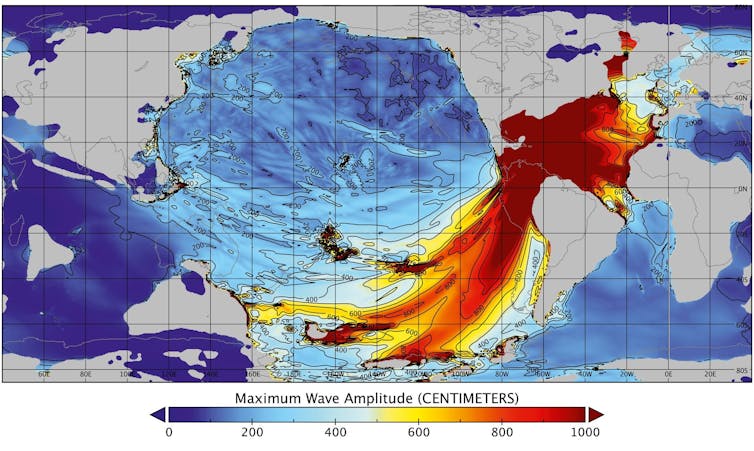
A College of Michigan-led find out about the use of knowledge from the Chicxulub asteroid have an effect on crater modeled how a ways the ensuing tsunami most probably would have reached. Historic pollen grains and marine fossils present in southeastern Missouri and analyzed by means of scientists on the Missouri College of Science and Generation be offering exhausting proof of the flooding.
Molly M. Vary, et al., 2022, CC BY
Pollen from gymnosperms, corresponding to pines, in addition to ferns and flowering vegetation, corresponding to grasses, herbs and palm timber, all file a transparent trend: Some wooded area pollen disappeared after the have an effect on, suggesting that the areas’ crops modified. Then the pollen slowly started to reemerge as the surroundings stabilized.
US Gulf Coast: Sequoia pollen and sea-level upward push
Fossilized pollen grains have additionally helped scientists hint slower however similarly dramatic adjustments alongside the jap Gulf Coast states of Mississippi and Alabama.
Right through the Early Oligocene, round 33.9 to twenty-eight million years in the past, sea ranges rose and flooded low-lying conifer forests within the area. Researchers recognized a definite exchange in pollen launched by means of Sequoia-type timber, large conifers that when ruled the coastal plains.
Scientists had been in a position to make use of the ones pollen data to reconstruct how a ways the coastline moved inland by means of monitoring the share of pollen grains within the geologic file to the upward push of marine microfossils.
The proof displays how the ocean flooded land ecosystems masses of miles from as of late’s coast. Pollen is a organic marker and geographic tracer of this historic exchange.
Western Australia: From swamp to salinity
In Western Australia, sediment cores from the beds of Lake Aerodrome, Gastropod Lake and Prado Lake disclose how long-term drying can exchange the ecology of a area.
Right through the Eocene, a length from about 55.8 million to 33.9 million years in the past, lush swamp forests surrounded freshwater lakes there. That’s mirrored by means of considerable pollen from tropical timber and moisture-loving shrubs and fern spores at the moment. Then again, crops modified dramatically because the Australian tectonic plate drifted northward and the local weather changed into extra arid.
The higher layers of the sediment cores, which seize newer occasions, comprise pollen most commonly from wind-pollinated, salt- and drought-tolerant vegetation – proof of moving crops beneath rising environmental pressure.
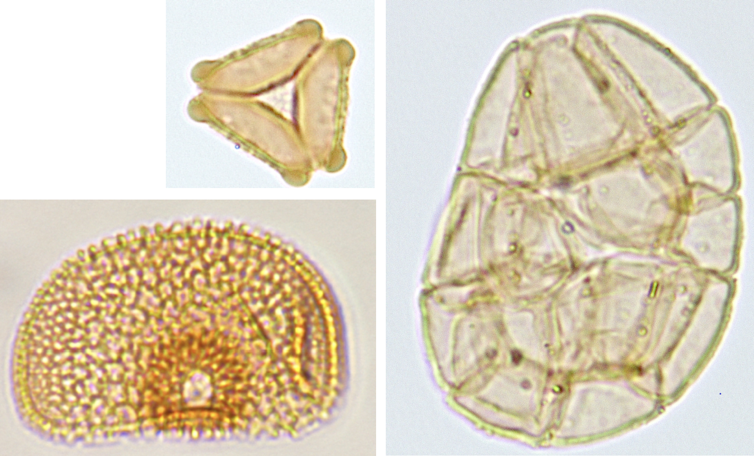
Magnified photographs of fossil pollen studied in Australia. Clockwise from higher left, they’re pollen from acacia, aglaonema and eucalyptus.
Francisca Oboh-Ikuenobe
The presence of Dunaliella, a inexperienced alga that flourishes in very salty water, along sparse pollen from vegetation that might live to tell the tale dry environments, confirms that lakes that when supported forests changed into extremely saline.
Guatemala: Maya historical past and wooded area restoration
Nearer to the tropics, Lake Izabal in Guatemala gives a newer archive spanning the previous 1,300 years. This accretion file displays each herbal local weather variation and the profound have an effect on of human land use, particularly all over the upward push and fall of the Maya civilization.
Round 1,125 to at least one,200 years in the past, pollen from vegetation corresponding to maize and opportunistic herbs surged, on the similar time tree pollen dropped, reflecting well-liked deforestation. Ancient data display political facilities within the area collapsed no longer lengthy later on.
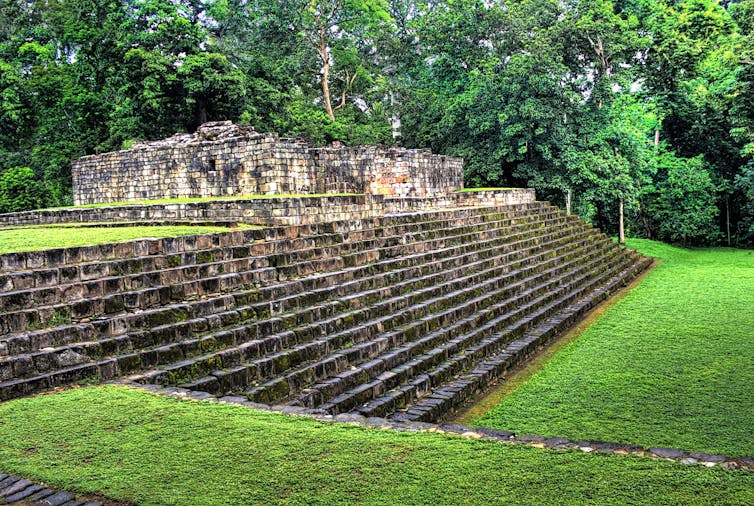

Quiriguá used to be an historic Mayan town close to Lake Izabal, the place pollen research display the upward push in deforestation and the restoration. Quiriguá started to say no within the 9th century and used to be sooner or later deserted.
Daniel Mennerich/Flickr, CC BY-SA
Simplest after inhabitants drive eased did the wooded area start to get well. Pollen from hardwood tropical timber greater, indicating crops rebounded whilst rainfall declined all over the Little Ice Age between the 14th and mid-Nineteenth centuries.
The fossil pollen displays how historic societies remodeled their landscapes, and the way ecosystems spoke back, offering extra proof and explanations for different historic accounts.
Fashionable pollen tells a tale, too
Those research depended on examining fossil pollen grains in accordance with their shapes, floor options and wall constructions. Through counting grains – masses to 1000’s according to pattern – scientists can statistically construct photos of historic crops, the species provide, their abundances, and the way the composition of each and every shifted with the local weather, sea-level adjustments or human job.
That is why trendy pollen additionally tells a tale. As as of late’s local weather warms, the conduct of pollen-producing vegetation is converting. In temperate areas such because the U.S., pollen seasons get started previous and last more because of warming temperatures and emerging carbon dioxide within the environment from cars, factories and different human actions.
All of this is being recorded within the fossil pollen file within the sediment layers on the bottoms of lakes around the globe.
So, the following time you be afflicted by hypersensitive reactions, take into account that the tiny grains floating within the air are organic time tablets that can sooner or later inform long run population about Earth’s environmental adjustments.


