Lately, I’ve all too regularly discovered myself passing over an lively wildfire when flying from London to my circle of relatives house in Greece all the way through the summer time months. The sky glows an eerie, apocalyptic pink, and the odor of smoke fills the cabin. Silence falls as we turn out to be unwilling witnesses to a sad spectacle.
Now wildfires are once more raging around the Mediterranean. However the flames themselves are best a part of the tale. As wildfires turn out to be extra intense and widespread, they’re atmosphere off a deadly chain response – one that still features a emerging possibility of devastating floods.
Writer’s photograph from a aircraft touchdown in Athens final summer time.
Ioanna Stamataki
In January 2024, Nasa reported that weather alternate is intensifying wildfire prerequisites, noting that the frequency of essentially the most excessive wildfires had greater than doubled during the last twenty years. Whilst a few of that is pushed by way of herbal climate variability, human-induced warming is obviously enjoying a significant function. A long time of emerging temperatures mixed with longer and extra critical droughts have created superb prerequisites for wildfires to ignite and unfold.
This yr, any other brutal Mediterranean wildfire season is unfolding proper prior to our eyes, with a lot of lively wildfire fronts around the area. As of July 22 2025, 237,153 hectares have burned within the EU – an build up of just about 78% from the similar duration final yr. The collection of fires rose by way of about 45%, and CO₂ emissions greater by way of 23% in comparison to 2024. Those are terrifying statistics.
Local weather phenomena are carefully interconnected
The fires themselves are unhealthy sufficient. However they’re additionally carefully attached to different climate-related extremes, together with floods.
Herbal hazards regularly cause chain reactions, turning one crisis into many. When it comes to floods, wildfires play a large function each via climate patterns and the way the land responds to rain.

In 2023, quickly after a sequence of large wildfires, Greece confronted the torrential rains of Typhoon Daniel.
EPA/HATZIPOLITIS NICOLAOS
At the climate facet, upper temperatures result in extra excessive rainfall, as hotter air can dangle extra moisture and fuels more potent storms. Intense wildfires can now and again get so scorching they generate their very own climate methods, like pyrocumulus clouds – towering hurricane clouds shaped by way of warmth, smoke and water vapour. Those clouds can spark surprising, localised storms all the way through or in a while after the fireplace.
The wear and tear doesn’t finish when the flames die down. Satellite tv for pc information displays that burned land can stay as much as 10°C warmer for almost a yr, because of misplaced crops and broken soil.
As the arena warms, the ambience is in a position to dangle about 7% extra moisture for each further level. Fresh temperatures of 40°C or extra in Greece recommend a capability for extra downpours and extra flooding.
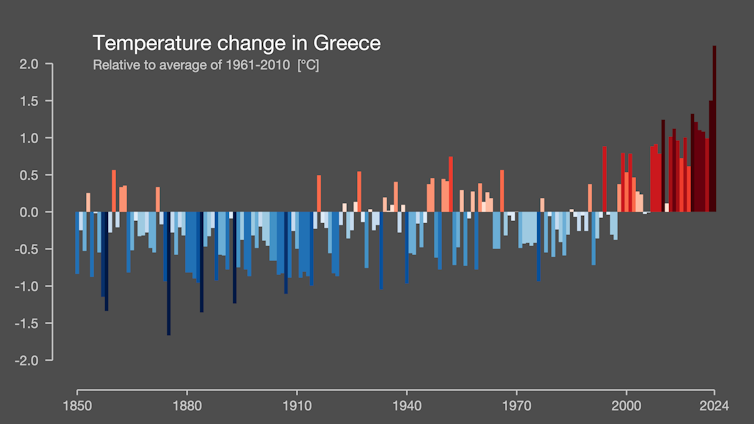
Greece is getting warmer and warmer (Every stripe represents three hundred and sixty five days, with blue indicating cooler and pink indicating hotter than the 1961-2010 reasonable).
Ed Hawkins / Display Your Stripes (Information: Berkeley Earth & ERA5-Land), CC BY-SA
Wildfires additionally make the land itself extra susceptible to flooding. Burnt spaces reply a lot quicker to rain, as there’s much less crops to decelerate the water. Wildfires additionally alternate the soil construction, regularly making it water-repellent. This implies extra water runs off the skin, erosion will increase, and it takes much less rain to cause a flood.
Below those prerequisites, a hurricane anticipated as soon as each ten years may cause any such catastrophic flooding anticipated best each 100 to 200 years. Water strikes a lot quicker throughout scorched landscapes with out crops to sluggish it down. Wildfires additionally depart at the back of a large number of particles, which can also be swept up by way of fast-moving floodwaters.
Whilst EU-wide information on post-wildfire flood possibility remains to be restricted, more than a few case research from southern Europe be offering robust proof of the relationship. In Spain’s Ebro River Basin, as an example, analysis discovered that if emissions stay top and weather coverage is restricted, wildfires will build up the likelihood of top flood possibility by way of 10%.

Firefighting within the hills of central Spain, July 30 2025.
EPA/RAUL SANCHIDRIAN
Nature’s talent to regenerate is little short of magical, however getting better from a wildfire takes time. Burnt soil takes years to go back to standard and, all the way through that point, the dangers of maximum rainfall are upper. Past the have an effect on of wildfires on soil and water, it is crucial to not omit the devastating lack of plant and animal species and even complete ecosystems, making the wildlife much less biodiverse and resilient.
To scale back the frequency and severity of maximum occasions, we will have to center of attention on repairing weather injury. This implies shifting past remoted views and adopting a multi-hazard way that recognises how screw ups are attached.
Flooding after wildfires is only one instance of the way one disaster can cause any other. We wish to recognise those cascading dangers and concentrate on long-term resilience over temporary fixes.






