For someone who depends on espresso to start out their day, espresso wilt illness is also crucial illness you’ve by no means heard of. This fungal illness has again and again reshaped the worldwide espresso provide during the last century, with penalties that extend from African farms to cafe counters international.
An infection with the fungus Fusarium xylarioides ends up in a function “wilt” in espresso crops via blockading and lowering the plant’s skill to move water. This blockage in the end kills the plant.
One of the vital maximum damaging plant pathogens on the earth infect their hosts on this manner. For the reason that Nineties, outbreaks of espresso wilt have price over US$1 billion, pressured numerous farms to near and brought about dramatic drops in nationwide espresso manufacturing. In Uganda, one in every of Africa’s biggest manufacturers, espresso manufacturing didn’t get well to pre-outbreak ranges till 2020, many years after espresso wilt used to be first detected there. And in 2023, researchers discovered proof that espresso wilt illness had resurfaced throughout all coffee-producing areas of Ivory Coast.
Learning the genetics of plant pathogens is a very powerful to figuring out why this illness continues to go back and easy methods to save you any other main outbreak.
Upward thrust and fall of espresso wilt illness in Africa
Whilst early outbreaks of espresso wilt illness affected quite a lot of espresso sorts, later epidemics essentially affected the 2 espresso species dominating world markets these days: arabica and robusta.
First known in 1927, espresso wilt illness decimated a number of forms of espresso grown in western and central Africa. Even though farmers combated the fungus with a shift to supposedly resistant robusta vegetation within the Fifties, the reprieve used to be short-lived.
The illness reemerged within the Seventies on robusta espresso, spreading via jap and central Africa. Through the mid-Nineties, yields had collapsed and occasional manufacturing may just no longer get well in nations just like the Democratic Republic of Congo.
One after the other, researchers known the illness on arabica espresso in Ethiopia within the Fifties and watched it turn into common via the Seventies
Espresso wilt illness has unfold extensively in Africa. The primary outbreak earlier than the Fifties affected basically central and western Africa (left map) whilst the second one outbreak originated in central Africa and unfold east (proper map). Affected nations are coloured via the last decade the illness used to be first detected.
Peck et al 2023/Plant Pathology, CC BY-SA
Even though espresso wilt illness is these days endemic at low and manageable ranges throughout jap and central Africa, any long term resurgence of the illness may well be catastrophic for African espresso manufacturing. Espresso wilt additionally poses a danger to manufacturers in Asia and the Americas.
New kinds of illness emerge
Espresso wilt illness advanced along espresso itself. Over the last century, it has again and again reemerged, attacking various kinds of espresso each and every time. However did those shifts replicate the fast evolution of recent kinds of illness, or one thing else fully?
Fungal illness has devastated crops for millennia, with the earliest information of outbreaks relationship from the biblical plagues. Like people, crops have an immune machine that protects them in opposition to assaults from pathogens like fungi.
Whilst maximum fungal makes an attempt at an infection fail, a small quantity do be successful due to the consistent evolutionary power on pathogens to triumph over host plant defenses. On this evolutionary palms race, pathogens and hosts often adapt to one another via genetically converting their DNA. Growth and bust cycles of illness happen as one beneficial properties benefit over the opposite.
The upward thrust of contemporary agriculture has resulted in common monocultures of genetically uniform vegetation. Whilst monocultures have considerably boosted meals manufacturing, they’ve additionally contributed to environmental degradation and higher plant vulnerability to illness.
Crop breeders have tried to give protection to monocultures via introducing illness resistance genes, with farms extensively making use of fungicides and different environmentally destructive merchandise. However those reasonably susceptible protections for loads of acres of an identical crops have led to outbreaks decimating vegetation that folks rely on.
It’s most probably that fashionable agriculture’s reliance on monocultures has enabled and speeded up the evolution of recent kinds of pathogen able to overcoming resistance in crops. In consequence, vegetation turn into extra at risk of illness outbreaks.
Resurrecting fungal traces
Working out the teachings of the previous is very important to fending off long term plant pandemics. However this may also be difficult, since the explicit pathogen traces that brought about earlier illness outbreaks would possibly not exist in nature or can have modified considerably.
In my analysis at the evolutionary palms race between host and pathogen in espresso wilt illness, I sought to deal with those issues via “resurrecting” ancient traces of the fungus that reasons the illness, Fusarium xylarioides. Researchers know little about why the sooner and later outbreaks centered various kinds of espresso, so I explored the genetic adjustments in F. xylarioides that underlie this narrowing of its hosts.
I reconstructed ancient genetic adjustments within the main espresso wilt illness outbreaks during the last seven many years via the use of traces from a fungus library – tradition collections that maintain residing fungi. Those libraries retailer long-term residing information and replicate the fungal genetic range provide on the time of assortment.
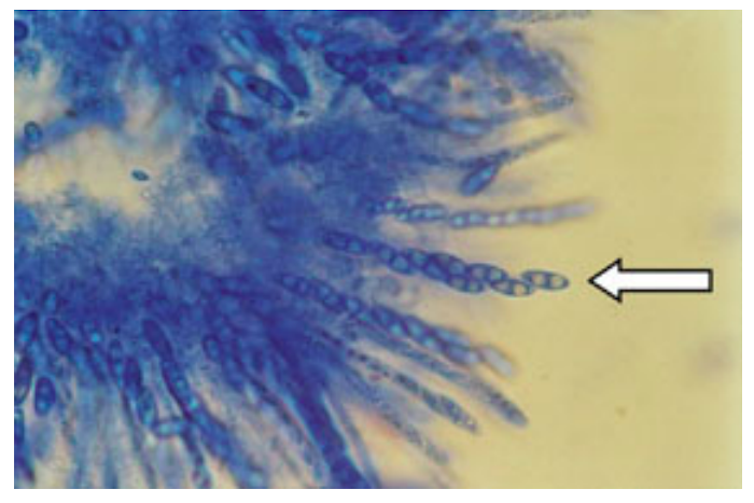
Gibberella (Fusarium) xylarioides, with arrow pointing to its spore-containing sac.
Julie Flood
Whether or not a pathogen takes the higher hand within the evolutionary palms race is determined by its skill to generate new kinds of genes. It will possibly achieve this both via converting and rearranging its DNA collection or via shifting DNA sequences between organisms in a procedure known as horizontal gene switch. Those mechanisms can create new effector genes that allow pathogens to contaminate and colonize a number plant.
To begin with, I sequenced six entire genomes of traces inquisitive about outbreaks earlier than the Seventies in addition to later outbreaks that in particular centered arabica or robusta espresso crops. I discovered that traces of F. xylarioides explicit to arabica or robusta genetically differed from each and every different, with all these variations inherited from dad or mum to offspring. This procedure is named vertical inheritance.
Genes that leap between species
On the other hand, I additionally discovered that a number of areas of the F. xylarioides genome had been doubtlessly got horizontally from F. oxysporum, an international plant pathogen that infects over 120 vegetation, together with bananas and tomatoes. Those integrated other areas of the genome throughout traces explicit to arabica and robusta espresso.
However did those adjustments introduce new effector genes within the F. xylarioides traces that infect arabica and robusta espresso crops in particular? To respond to this query, I first sequenced and assembled the primary F. xylarioides reference genome, sewing in combination lengthy stretches of DNA. I then sequenced and when compared this reference genome to the entire genomes of 3 extra pre-Seventies F. xylarioides traces and 10 further ancient Fusarium traces discovered on or round diseased espresso timber, in addition to F. xylarioides traces from inflamed arabica espresso seedlings.
I discovered considerable proof for horizontal switch of disease-causing genes between species of Fusarium. This contains the presence of big genetic parts known as Starships in Fusarium. Those so-called leaping genes elevate their very own molecular equipment, permitting them to transfer round or between genomes. Genes inquisitive about adaptation, akin to the ones connected to virulence, metabolism or host interplay, additionally transfer with them. Scientists assume Starships would possibly doubtlessly allow fungi to conform to converting environmental stipulations.
I discovered that giant and extremely equivalent genetic areas, together with Starships and energetic effector genes inquisitive about illness, had moved from F. oxysporum to F. xylarioides. Importantly, other genetic areas had been provide throughout traces of F. xylarioides explicit to arabica and robusta, however they had been absent from different comparable Fusarium species. This implies that those genes had been received from F. oxysporum.
Arming farmers with wisdom
Nowadays, a 3rd of all world crop yields are misplaced to pest and illness. Reconciling the stress between agricultural productiveness and environmental coverage is vital to stability humanity’s wishes for the longer term. Central to this problem is lowering the unfold of illness and new outbreaks.
At the turn facet to monocultures, many plant species surrounding and inside of small and family-run espresso farms in sub-Saharan Africa would possibly act as illness reservoirs, the place fungi pathogens can lurk. Those come with banana timber and Solanum weeds within the tomato kin which are at risk of fungal an infection.
Human farming practices can have inadvertently created a synthetic area of interest for those fungi, with espresso timber introduced into common touch with banana crops and Solanum weeds. If fungi in the similar genus can continuously alternate genetic subject material, it would boost up the power of plant pathogens to conform to new hosts.

Balancing agricultural productiveness with sustainability will in the long run get advantages each vegetation and other folks.
Wayne Hutchinson/Farm Pictures/Common Pictures Staff by means of Getty Pictures
Checking out noncoffee crops for F. xylarioides an infection may just disclose selection plant species the place other Fusarium fungi come into touch and alternate genetic subject material. This issues as a result of throughout sub-Saharan Africa, espresso crops steadily percentage fields with banana timber and weeds. If those neighboring crops can harbor fungi that act as new resources of genetic variation, they are going to lend a hand gas new illness traces.
Figuring out the crops that may act as hosts to fungi may just give farmers sensible choices to cut back espresso crops’ possibility of illness, from centered weed control to fending off the planting of inclined vegetation facet via facet.







