Image an ocean global so deep and darkish it looks like some other planet – the place creatures glow and existence survives underneath crushing power.
That is the midwater zone, a hidden ecosystem that starts 650 ft (200 meters) underneath the sea floor and sustains existence throughout our planet. It comprises the twilight zone and the middle of the night zone, the place bizarre and mild animals thrive within the close to absence of daylight. Whales and commercially treasured fish similar to tuna depend on animals on this zone for meals. However this distinctive ecosystem faces an unparalleled danger.
Because the call for for electrical automotive batteries and smartphones grows, mining corporations are turning their consideration to the deep sea, the place valuable metals similar to nickel and cobalt may also be present in potato-size nodules sitting at the ocean flooring.
Photographs of marine existence noticed within the midwater zone.
Bucklin, et al., Marine Biology, 2021. Footage by means of R.R. Hopcroft and C. Clarke (College of Alaska Fairbanks) and L.P. Madin (Woods Hollow Oceanographic Establishment), CC BY, CC BY
Deep-sea mining analysis and experiments over the last 40 years have proven how the removing of nodules can put seafloor creatures in peril by means of disrupting their habitats. Then again, the method too can pose a threat to what lives above it, within the midwater ecosystem. If long term deep-sea mining operations unlock sediment plumes into the water column, as proposed, the particles may just intervene with animals’ feeding, disrupt meals webs and change animals’ behaviors.
As an oceanographer learning marine existence in a space of the Pacific wealthy in those nodules, I consider that prior to international locations and firms rush to mine, we wish to perceive the dangers. Is humanity keen to possibility collapsing portions of an ecosystem we slightly perceive for assets which are necessary for our long term?
Mining the Clarion-Clipperton Zone
Underneath the Pacific Ocean southeast of Hawaii, a hidden treasure trove of polymetallic nodules may also be discovered scattered around the seafloor. Those nodules shape as metals in seawater or sediment gather round a nucleus, similar to a work of shell or shark’s enamel. They develop at a surprisingly gradual charge of a couple of millimeters in keeping with million years. The nodules are wealthy in metals similar to nickel, cobalt and manganese – key components for batteries, smartphones, wind generators and army {hardware}.
As call for for those applied sciences will increase, mining corporations are concentrated on this faraway space, referred to as the Clarion-Clipperton Zone, in addition to a couple of different zones with an identical nodules around the globe.
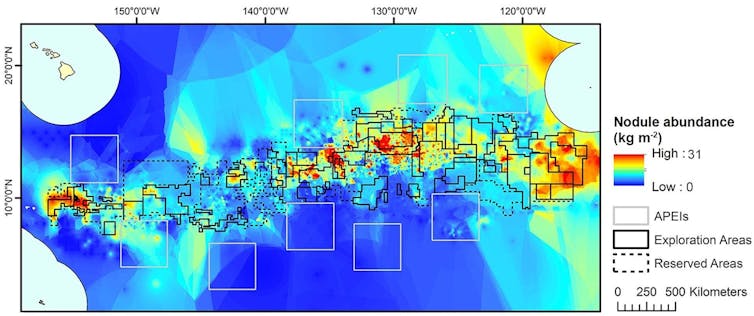
A map presentations mining objectives within the Clarion-Clipperton Zone, southeast of Hawaii, higher left. APEIs are secure spaces.
McQuaid KA, Attrill MJ, Clark MR, Cobley A, Glover AG, Smith CR and Howell KL, 2020, CC BY
Thus far, most effective check mining has been performed. Then again, plans for full-scale business mining are hastily advancing.
Exploratory deep-sea mining started within the Nineteen Seventies, and the World Seabed Authority was once established in 1994 underneath the United International locations Conference at the Regulation of the Sea to keep watch over it. Nevertheless it was once no longer till 2022 that The Metals Corporate and Nauru Ocean Sources Inc. absolutely examined the primary built-in nodule assortment machine within the Clarion-Clipperton Zone.
The firms at the moment are making plans full-scale mining operations within the area and be expecting to post their software to the ISA by means of June 27, 2025. The ISA will convene in July 2025 to talk about crucial problems similar to mining rules, pointers and benefit-sharing mechanisms.
A visualization of a deep-sea mining operation presentations two sediment plumes. Supply: MIT Mechanical Engineering.
The proposed mining procedure is invasive. Collector automobiles scrape alongside the sea flooring as they scoop up nodules and fan the flames of sediments. This eliminates habitats utilized by marine organisms and threatens biodiversity, doubtlessly inflicting irreversible harm to seafloor ecosystems. As soon as accumulated, the nodules are introduced up with seawater and sediments via a pipe to a boat, the place they’re separated from the waste.
The leftover slurry of water, sediment and beaten nodules is then dumped again into the center of the water column, developing plumes. Whilst the release intensity continues to be underneath dialogue, some mining operators suggest liberating the waste at midwater depths, round 4,000 ft (1,200 meters).
Then again, there’s a crucial unknown: The sea is dynamic, repeatedly moving with currents, and scientists don’t absolutely know how those mining plumes will behave as soon as launched into the midwater zone.
Those clouds of particles may just disperse over vast spaces, doubtlessly harming marine existence and disrupting ecosystems. Image a volcanic eruption – no longer of lava, however of excellent, murky sediments increasing all through the water column, affecting the entirety in its trail.
The midwater ecosystem in peril
As an oceanographer learning zooplankton within the Clarion-Clipperton Zone, I’m involved concerning the affect of deep-sea mining in this ecologically necessary midwater zone. This ecosystem is house to zooplankton – tiny animals that flow with ocean currents – and micronekton, which contains small fish, squid and crustaceans that depend on zooplankton for meals.
Sediment plumes within the water column may just hurt those animals. High quality sediments may just clog respiration constructions in fish and feeding constructions of clear out feeders. For animals that feed on suspended debris, the plumes may just dilute meals assets with nutritionally deficient subject matter. Moreover, by means of blockading gentle, plumes may intervene with visible cues crucial for bioluminescent organisms and visible predators.
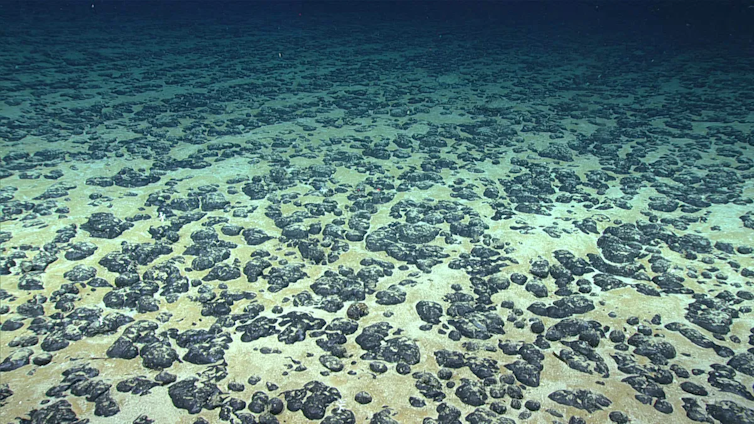

Manganese nodules may also be discovered at the seafloor off the southeastern United States.
NOAA Administrative center of Ocean Exploration and Analysis, 2019 Southeastern U.S. Deep-Sea Exploration
For refined creatures similar to jellyfish and siphonophores – gelatinous animals that may develop over 100 ft lengthy – sediment accumulation can intervene with buoyancy and survival. A contemporary find out about discovered that jellies uncovered to sediments greater their mucous manufacturing, a not unusual rigidity reaction this is energetically dear, and their expression of genes associated with wound restore.
Moreover, noise air pollution from equipment can intervene with how species be in contact and navigate.
Disturbances like those have the possible to disrupt ecosystems, extending a long way past the release intensity. Declines in zooplankton populations can hurt fish and different marine animal populations that depend on them for meals.
Existence within the deep sea has different values. Supply: The Economist
The midwater zone additionally performs an important position in regulating Earth’s local weather. Phytoplankton on the ocean’s floor seize atmospheric carbon, which zooplankton eat and switch during the meals chain. When zooplankton and fish respire, excrete waste, or sink after dying, they give a contribution to carbon export to the deep ocean, the place it may be sequestered for hundreds of years. The method naturally eliminates planet-warming carbon dioxide from the ambience.
Extra analysis is wanted
In spite of rising pastime in deep-sea mining, a lot of the deep ocean, specifically the midwater zone, stays poorly understood. A 2023 find out about within the Clarion-Clipperton Zone discovered that 88% to 92% of species within the area are new to science.
Present mining rules center of attention essentially at the seafloor, overlooking broader ecosystem affects. The World Seabed Authority is making ready to make key choices on long term seabed mining in July 2025, together with regulations and pointers with regards to mining waste, discharge depths and environmental coverage.
A map presentations spaces with nodules being thought to be for exploration and mining. Supply: World Seabed Authority
Those choices may just set the framework for large-scale business mining in ecologically necessary spaces such because the Clarion-Clipperton Zone. But the effects for marine existence aren’t transparent. With out complete research at the affect of seafloor mining ways, the arena dangers making irreversible alternatives that would hurt those fragile ecosystems.

