Tropical reefs would possibly seem like inanimate rock, however those colourful seascapes are constructed by way of tiny jellyfish-like animals known as corals. Whilst grownup corals construct cast constructions which can be firmly connected to the ocean flooring, child corals aren’t confined to their reefs. They may be able to waft with ocean currents over nice distances to new places that would possibly give them a greater probability of survival.
The underwater towns that corals assemble are house to a few quarter of all identified marine species. They’re extremely necessary for people, too, contributing a minimum of one thousand billion greenbacks according to yr in ecosystem products and services, comparable to protective coastlines from wave injury and supporting fisheries and tourism.
Sadly, coral reefs are a number of the maximum susceptible environments on this planet to local weather trade.
Since 2023, exceptionally heat ocean water has been fueling the planet’s fourth mass coral bleaching tournament on file, inflicting well-liked mortality in corals all over the world. This type of hurt is projected to irritate significantly over the approaching many years as ocean temperatures upward thrust.
A wholesome coral reef in American Samoa, left, experiencing coral bleaching because of a critical marine heatwave, middle, and in the end death, proper.
The Ocean Company and Ocean Symbol Financial institution., CC BY-NC
Corals can develop in new spaces, however will they thrive?
Child corals can waft freely with ocean currents, probably touring loads of miles earlier than settling in new places. That permits the distribution of corals to shift through the years.
Primary ocean currents can lift child corals to temperate seas. If new coral reefs shape there because the waters heat, those spaces would possibly act as refuges for tropical corals, decreasing the corals’ chance of extinction.
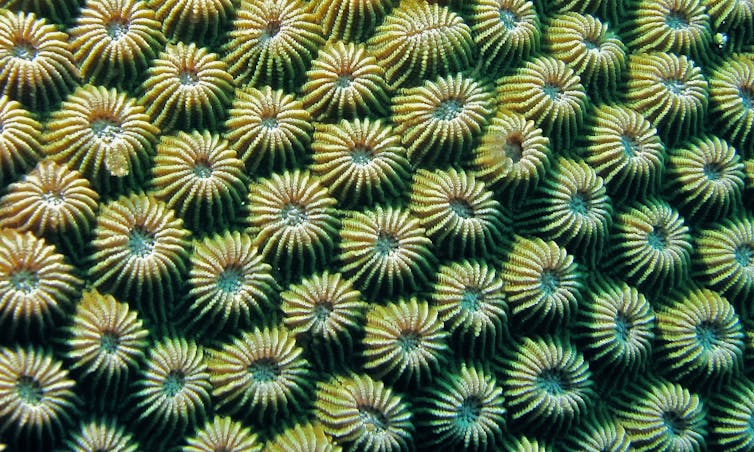

A detailed-up of double big name corals (Diploastrea heliopora) off Indonesia.
Bernard DuPont/Flickr, CC BY-SA
Scientists know from the fossil file that coral reef expansions have came about earlier than. On the other hand, a large query stays: Can corals migrate speedy sufficient to stay tempo with local weather trade led to by way of people? We evolved a state of the art simulation to uncover the answer.
Box and laboratory research have measured how coral enlargement is determined by temperature, acidity and light-weight depth. We blended this knowledge with knowledge on ocean currents to create an international simulation that represents how corals reply to a converting surroundings – together with their skill to evolve via evolution and shift their levels.
Then, we used long term local weather projections to expect how coral reefs might reply to local weather trade.
We discovered that it’s going to take centuries for coral reefs to shift clear of the tropics. That is a ways too sluggish for temperate seas to avoid wasting tropical coral species – they’re going through critical threats at this time and within the coming many years.
How coral reefs shape.
Underwater towns in movement?
Beneath nations’ present greenhouse fuel emissions insurance policies, our simulations recommend that coral reefs will decline globally by way of an extra 70% this century as ocean temperatures proceed to upward thrust. As dangerous as that sounds, it’s in reality fairly extra constructive than earlier research that predicted losses as top as 99%.
Our simulations recommend that coral populations may just increase in a couple of places this century, basically southern Australia, however those expansions might best quantity to round 6,000 acres (2,400 hectares). Whilst that would possibly sound so much, we think to lose round 10 million acres (4 million hectares) of coral over the similar length.
In different phrases, we’re not likely to peer vital new tropical-style coral reefs forming in temperate waters inside our lifetimes, so maximum tropical corals is not going to in finding shelter in upper latitude seas.
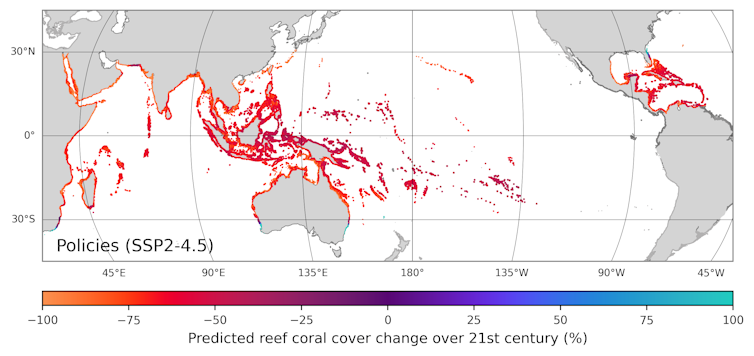
Simulations display little enlargement (blue) in coral reef distribution this century below situations in step with present executive insurance policies all over the world.
Noam Vogt-Vincent
Even supposing the appropriate water temperatures for corals are forecast to increase poleward by way of about 25 miles (40 kilometers) according to decade, corals would face different demanding situations in new environments.
Our analysis means that coral vary enlargement is basically restricted by way of slower coral enlargement at upper latitudes, no longer by way of dispersal. Clear of the equator, gentle depth falls and temperature turns into extra variable, decreasing enlargement, and due to this fact the speed of vary enlargement, for lots of coral species.
It’s most probably that new coral reefs will in the end shape past their present vary, as historical past presentations, however our effects recommend this may increasingly take centuries.
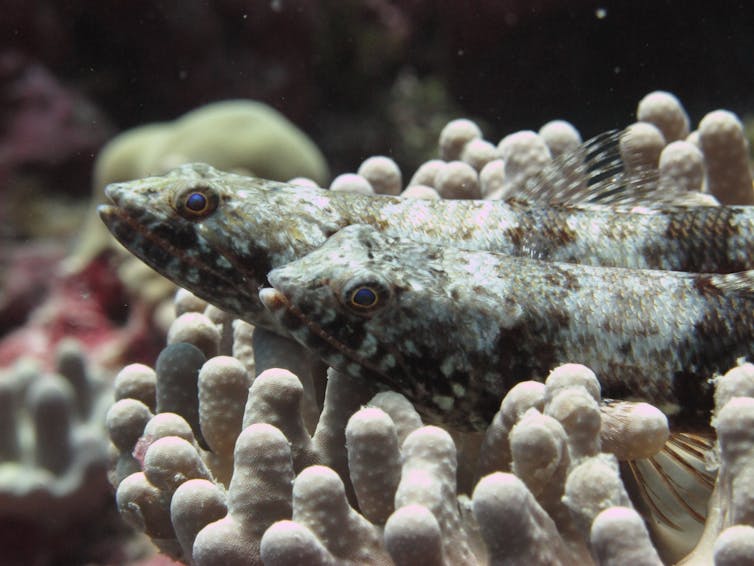

Fish conceal out within the protection of Kingman Reef, within the Pacific Ocean between the Hawaiian Islands and American Samoa. Coral reefs supply coverage for lots of species, specifically younger fish.
USFWS, Pacific Islands
Some coral species are tailored to the more difficult environmental prerequisites at upper latitudes, and those corals are expanding in abundance, however they’re much much less various and structurally advanced than their tropical opposite numbers.
Scientists have used human-assisted migration to take a look at to revive broken coral reefs by way of transplanting reside corals. On the other hand, coral recovery is arguable, as it’s dear and can’t be scaled up globally. Since coral vary enlargement seems to be restricted by way of difficult environmental prerequisites at upper latitudes relatively than by way of dispersal, human-assisted migration could also be not likely to assist them increase extra briefly.
Importantly, those doable upper latitude refuges have already got wealthy, distinct ecosystems. Organising tropical corals inside the ones ecosystems would possibly disrupt current species, so speedy expansions may not be a just right factor within the first position.
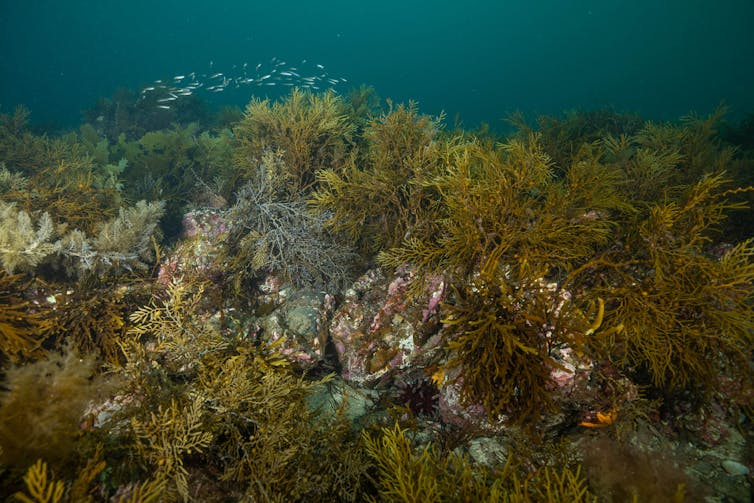

A temperate reef close to southern Australia, which may well be threatened by way of expansions of tropical coral species.
Stefan Andrews/Ocean Symbol Financial institution, CC BY-NC
No identified selection to reducing emissions
Regardless of enthusiasm for coral recovery, there’s little proof to signify that strategies like this will mitigate the worldwide decline of coral reefs.
As our learn about presentations, migration would take centuries, whilst probably the most critical local weather trade hurt for corals will happen inside many years, making it not likely that subtropical and temperate seas can act as coral refuges.
What can assist corals is decreasing greenhouse fuel emissions which can be riding international warming. Our learn about means that decreasing emissions at a sooner tempo, in keeping with the Paris local weather settlement, may just minimize the coral loss by way of part in comparison with present insurance policies. That might spice up reef well being for hundreds of years to return.
Which means that there’s nonetheless hope for those irreplaceable coral ecosystems, however time is working out.




