Sturgeons are one of the crucial oldest teams of fishes. Carrying an armor of 5 rows of bony, changed scales known as dermal scutes and a sharklike tail fin, this staff of several-hundred-pound beasts has survived for about 160 million years. As a result of their bodily look has modified little or no through the years, supported through a sluggish fee of evolution, sturgeon had been known as dwelling fossils.
In spite of their survival thru a number of geological time sessions, many present-day sturgeon species are at danger of extinction, with 17 of 27 species indexed as “critically endangered.”
Conservation practitioners such because the Virginia Commonwealth College tracking group are operating arduous to give a boost to restoration of Atlantic sturgeon within the Chesapeake Bay house. Nevertheless it’s now not transparent what baseline inhabitants stage other folks will have to try towards restoring. How do as of late’s sturgeon populations evaluate with the ones of the previous?
VCU tracking group releases an grownup Atlantic sturgeon again into the estuary.
Matt Balazik
We’re a molecular anthropologist and a biodiversity scientist who focal point on species that individuals depend on for subsistence. We find out about the evolution, inhabitants well being and resilience of those species through the years to higher perceive people’ interplay with their environments and the sustainability of meals techniques.
For our fresh sturgeon venture, we joined forces with fisheries conservation biologist Matt Balazik, who conducts on-the-ground tracking of Atlantic sturgeon, and Torben Rick, a expert in North American coastal zooarchaeology. In combination, we needed to seem into the previous and spot how a lot sturgeon populations have modified, specializing in the James River in Virginia. A extra nuanced working out of the previous may just assist conservationists higher plan for the long run.
Sturgeon loomed massive for millennia
In North The us, sturgeon have performed essential subsistence and cultural roles in Local communities, which marked the seasons through the fishes’ behavioral patterns. Massive summertime aggregations of lake sturgeon (Acipenser fulvescens) within the Nice Lakes house impressed one folks title for the August complete moon – the sturgeon moon. Wooded area Technology pottery remnants at archaeological websites from so long as 2,000 years in the past display that the autumn and springtime runs of Atlantic sturgeon (Acipenser oxyrinchus) upstream have been celebrated with feasting.
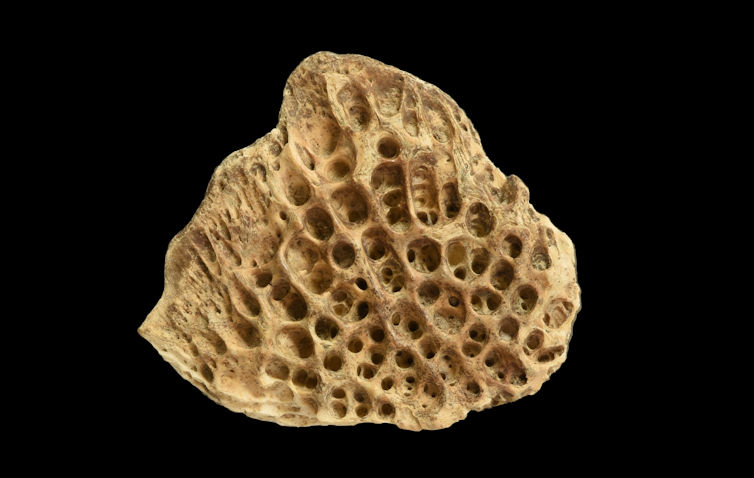

Archaeologists discover bony scutes – changed scales that resemble armor for the dwelling fish – in puts the place other folks trusted sturgeon for subsistence.
Logan Kistler and Natalia Przelomska
Archaeological unearths of sturgeon stays give a boost to that early colonial settlers in North The us, particularly those that established Jamestown within the Chesapeake Bay house in 1607, additionally prized those fish. When Captain John Smith was once main Jamestown, he wrote “there was more sturgeon here than could be devoured by dog or man.” The fish could have helped the survival of this fortress-colony that was once each bothered with drought and fostering turbulent relationships with the Local population.
This abundance is in stark distinction to as of late, when sightings of migrating fish are sparse. Exploitation all through the previous 300 years was once the important thing driving force of Atlantic sturgeon decline. Call for for caviar drove the relentless fishing power during the nineteenth century. The Chesapeake was once the second-most exploited sturgeon fishery at the Jap Seaboard up till the early twentieth century, when the fish become scarce.

Conservation biologists seize the large fish for tracking functions, which incorporates clipping a tiny a part of the fin for DNA research.
Matt Balazik
At that time, native coverage rules have been established, however most effective in 1998 was once a moratorium on harvesting those fish declared. In the meantime, abundance of Atlantic sturgeon remained very low, which will also be defined partially through their lifespan. Brief-lived fish corresponding to herring and shad can get better inhabitants numbers a lot quicker than Atlantic sturgeon, which are living for as much as 60 years and take a very long time to achieve reproductive age – as much as round 12 years for men and as many as 28 years for women.
To assist set up and repair an endangered species, conservation biologists generally tend to separate the inhabitants into teams in response to levels. The Chesapeake Bay is one among 5 “distinct population segments” the U.S. Endangered Species Act list in 2012 created for Atlantic sturgeon.
Since then, conservationists have pioneered genetic research on Atlantic sturgeon, demonstrating during the energy of DNA that natal river – the place a person fish is born – and season of spawning are each essential for distinguishing subpopulations inside each and every regional staff. Scientists have additionally described genetic variety in Atlantic sturgeon; extra genetic selection suggests they have got extra capability to evolve when dealing with new, probably difficult prerequisites.
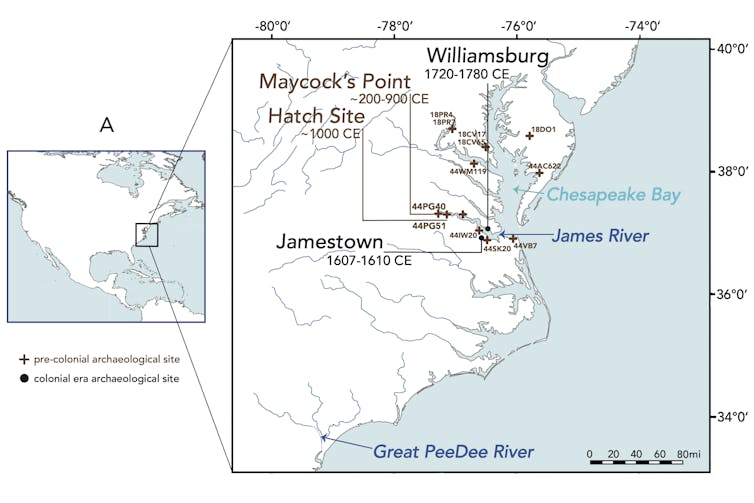
The find out about concerned with Atlantic sturgeon from the Chesapeake Bay area, previous and reward. The 4 archaeological websites integrated are highlighted.
Przelomska NAS et al., Proc. R. Soc. B 291: 20241145, CC BY
Sturgeon DNA, then and now
Archaeological stays are an instantaneous supply of knowledge on genetic variety up to now. We will be able to analyze the genetic make-up of sturgeons that lived loads of years in the past, prior to intense overfishing depleted their numbers. Then we will be able to evaluate that baseline with as of late’s genetic variety.
The James River was once an ideal case find out about for checking out out this way, which we name an archaeogenomics time sequence. Having got knowledge at the archaeology of the Chesapeake area from our collaborator Leslie Reeder-Myers, we sampled stays of sturgeon – their scutes and spines – at a precolonial-era web site the place other folks lived from about 200 C.E. to about 900 C.E. We additionally sampled from essential colonial websites Jamestown (1607-1610) and Williamsburg (1720-1775). And we complemented that knowledge from the previous with tiny clips from the fins of present-day, are living fish that Balazik and his group sampled all through tracking surveys.
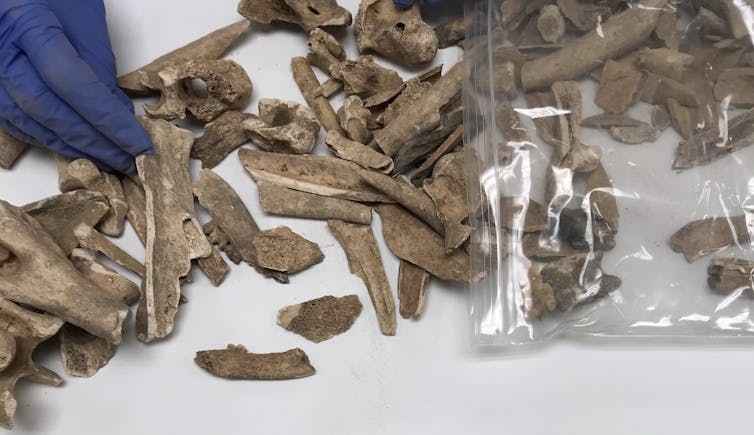

Scientists separate Atlantic sturgeon scute fragments from greater collections of zooarchaeological stays, to then paintings at the scutes in a lab devoted to finding out historical DNA.
Torben Rick and Natalia Przelomska
DNA has a tendency to get bodily damaged up and biochemically broken with age. So we trusted particular protocols in a lab devoted to finding out historical DNA to attenuate the chance of contamination and reinforce our possibilities of effectively accumulating genetic subject matter from those sturgeon.
Atlantic sturgeon have 122 chromosomes of nuclear DNA – over 5 instances as many as other folks do. We concerned with a couple of genetic areas, simply sufficient to get an concept of the James River inhabitants groupings and the way genetically distinct they’re from one every other.
We weren’t shocked to look that fall-spawning and spring-spawning teams have been genetically distinct. What stood out, although, was once how starkly other they have been, which is one thing that may occur when a inhabitants’s numbers drop to near-extinction ranges.
We additionally seemed on the fishes’ mitochondrial DNA, a compact molecule this is more uncomplicated to procure historical DNA from when compared with the nuclear chromosomes. With our collaborator Audrey Lin, we used the mitochondrial DNA to substantiate our speculation that the fish from archaeological websites have been extra genetically various than present-day Atlantic sturgeon.
Strikingly, we came upon that mitochondrial DNA didn’t all the time staff the fish through season and even through their natal river. This was once surprising, as a result of Atlantic sturgeon generally tend to go back to their natal rivers for breeding. Our interpretation of this genetic discovering is that over very lengthy timescales – many hundreds of years – adjustments within the world local weather and in native ecosystems would have pushed a given sturgeon inhabitants emigrate into a brand new river gadget, and most likely at a later level again to its authentic one. This perception is supported through different fresh documentation of fish from time to time migrating over lengthy distances and combining with new teams.
Our find out about used archaeology, historical past and ecology in combination to explain the decline of Atlantic sturgeon. In keeping with the lowered genetic variety we measured, we estimate that the Atlantic sturgeon populations we studied are a couple of 5th of what they have been prior to colonial agreement. Much less genetic variability method those smaller populations have much less doable to evolve to converting prerequisites. Our findings will assist conservationists plan into the long run for the ongoing restoration of those dwelling fossils.



