Because the Atlantic warms, many fish alongside the east coast of North The us have moved northwards to stay inside their most popular temperature vary. Black sea bass, as an example, have shifted loads of miles up the coast.
Within the Mediterranean, the image may be very other. With out a very easy get away course against the poles, many species are successfully trapped in a sea this is warming swiftly. Some local fish are even being changed by way of extra heat-tolerant species that experience slipped in throughout the Suez Canal.
It’s a procedure affecting coastal species world wide: and not using a steady pathway to cooler waters, many are in hassle. Break out turns into tough the place coastlines run east–west or are damaged into enclosed basins and islands. In those settings, species have to transport massive distances simply to realize a couple of levels of latitude – the so-called “latitudinal trap”.
It’s additionally a procedure that has repeated all the way through historical past. Once we analysed 540 million years of fossil information for a up to date learn about revealed within the magazine Science, we discovered that species alongside east-west coastlines had been much more likely to head extinct than the ones with more straightforward motion north-south.
Malanoski et al (2026) / Science
We hypothesised that the form and orientation of coastlines may lend a hand species get away – or entice them. If coastlines supply direct, steady pathways to transport north or south, species must have the ability to higher monitor transferring climates. However, the place species must go back and forth far for minimum latitude achieve, their extinction possibility is raised all over episodes of environmental exchange.
Coastlines themselves aren’t mounted. Over hundreds of thousands of years, plate tectonics rearrange continents, occasionally generating lengthy north-south coasts, like the ones of the Americas these days, and at different occasions sprawling east-west seaways equivalent to all over the Ordovician a little over 400 million years in the past.
This implies local weather shocks can produce very other extinction results relying at the format of continents on the time.
To check this speculation, we analysed fossil information for roughly 13,000 teams of similar shallow-marine invertebrate species, equivalent to clams, snails, sponges and starfish, spanning the closing 540 million years. We then paired those information with reconstructions of historic geography.
For each and every fossil, we estimated how tough it could were for that species to shift its latitude alongside shallow coastlines. We measured this because the shortest collection of steps to go back and forth 5°, 10°, or 15° latitude north or south. (For context, Nice Britain covers about 9° from best to backside). Brief distances suggest a moderately direct get away; lengthy distances suggest an extended or possibly not possible get away course.
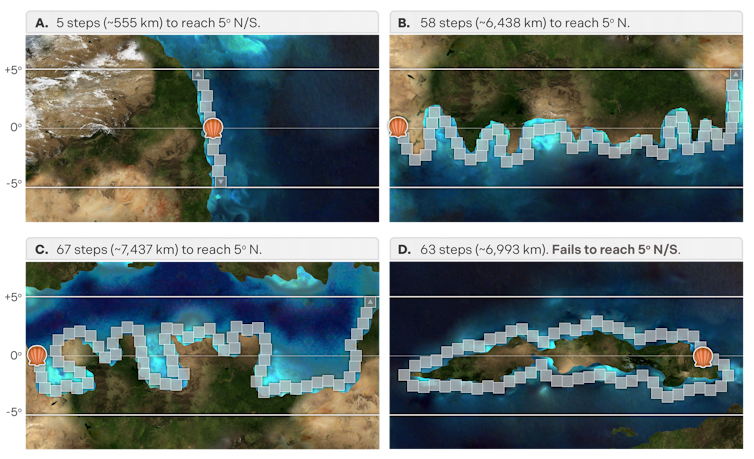
A 5° shift in latitude may also be reached temporarily alongside a easy north–south beach (A), however calls for for much longer routes—or can’t be reached in any respect—alongside convoluted east–west margins (B), internal seaways (C), and islands (D).
Malanoski et al (2026) / Science
We discovered that, over the past 540 million years, extinction possibility was once persistently upper for marine animals with lengthy get away routes.
Geography amplifies disaster
This development intensified all over Earth’s 5 mass extinction occasions. In our fashions, species with longer distances confirmed will increase in extinction possibility of as much as 400% all over mass extinctions, when put next with about 60% all over different durations, highlighting that geography turns into way more consequential when local weather exchange intensifies.
Even supposing our analyses eager about geologic timescales, our effects lend a hand us know how shallow marine species would possibly reply to local weather exchange these days. Species dwelling within the Mediterranean or the Gulf of Mexico or different areas with semi-enclosed geography, or across the margins of islands, will have extra problem as the sea warms.
Sea coast geometry would possibly topic much less for species which might be just right at dispersing themselves, on the other hand, particularly those who have an extended planktonic larvae segment the place they glide across the ocean sooner than turning into mounted in position. The survival of the ones species relies extra on components like ocean currents than beach orientation.
Estimating whether or not a species is liable to extinction is usually carried out with regards to attributes equivalent to frame dimension or geographic vary dimension. However our paintings displays that extinction possibility additionally relies on geography. Survival all over local weather upheaval relies now not simplest on a species’ biology – however on whether or not the map itself gives an get away.




