A 12 months after the Paris Summit for Motion on Synthetic Intelligence, the global neighborhood will meet in New Delhi this week for the Global Summit on Synthetic Intelligence, which is able to purpose to advertise the common use of man-made intelligence in growing nations. In Africa, funding in era and synthetic intelligence stays concentrated within the “big four” – South Africa, Egypt, Kenya and Nigeria – to the detriment of alternative nations at the continent. This research explores the reasons of this imbalance and the levers that can be utilized to raised direct capital.
This newsletter used to be written in collaboration with Anastasia Taieb, Innovation Undertaking Supervisor at AFD and Emma Pericard, Virtual Africa EU Consultant.
Between 2015 and 2022, funding in African start-ups noticed exceptional enlargement: the choice of start-ups receiving investment greater greater than sevenfold, fueled by means of the increase in cell gadgets, fintech and large inflows of global capital. On the other hand, since 2022, tightening financial stipulations have resulted in a discount in investment (aid in project capital funding) that has been extra important for African start-ups than in different areas of the sector. This phenomenon greater the focus of capital within the nations the place the preliminary ecosystem used to be maximum evolved, specifically South Africa, Egypt, Kenya and Nigeria.
On the other hand, it might be of passion to unfold those investments higher around the continent. Along with stimulating economies, the technological inventions of those start-ups constitute crucial lever of building as a result of they provide answers tailored to the native context: particular monetary answers, growth of agricultural productiveness, strengthening of the well being and schooling machine, reaction to precedence local weather problems, and many others.
Evolution of Fairness and Debt Finances Granted to Tech Startups in Africa Between 2019 and 2024 Partech, 2024 Africa Tech Project Capital Funding Focus within the Giant 4
Within the early 2020s, the time period “Big Four” emerged to explain Africa’s primary era markets: South Africa, Egypt, Kenya and Nigeria. This concept, indisputably impressed by means of the time period Giant Tech, signifies that there will probably be “champion countries” within the box of era.
Within the early 2020s, the time period “Big Four” emerged to explain Africa’s primary era markets: South Africa, Egypt, Kenya and Nigeria. This concept, indisputably impressed by means of the time period Giant Tech, signifies that there will probably be “champion countries” within the box of era.
In 2024, the Giant 4 will seize 67% of tech fairness investment (making an investment in opposition to shares in tech corporations). Intimately, the chances captured by means of every nation are dispensed as follows: roughly 24% for Kenya, 20% for South Africa and 13.5% for Egypt and Nigeria.
This focus of investment is not just geographical: it additionally has a robust sectoral measurement. We understand that capital is principally directed against sectors which are perceived as much less dangerous corresponding to virtual finance “fintech”, to the detriment of, as an example, edtech or cleantech, i.e. applied sciences devoted to schooling and the surroundings.
About 60 to 70% of the quantities raised in Africa would come from global traders, particularly for investment rounds above $10-20 million. Those investments, continuously concentrated in structured markets, constitute probably the most visual transactions, but in addition the least dangerous.
Rising peripheral ecosystems and possible insufficiently transformed into investments
If the “big four” listen many of the investments, a number of African nations these days have a confirmed possible in AI and various promising start-ups, with out taking pictures the amount of investments commensurate with this possible.
Nations corresponding to Ghana, Morocco, Senegal, Tunisia and Rwanda shape an rising crew whose participants have AI-friendly basics however are nonetheless underfunded. This distinction is much more hanging for the reason that Ghana, Morocco and Tunisia, all of that have a dynamic pool of start-ups, by myself account for round 17% of Africa’s tech corporations, except the Giant 4. Moreover, native monetary buildings aren’t ready to hide those wishes in those geographical spaces that are thought to be peripheral.
This issue in attracting investments is especially defined by means of the institutional and trade ecosystems that will have to be bolstered, the efficiency of era corporations that depend at the life of structured entrepreneurial ecosystems that offer get entry to to wisdom, certified hard work, in addition to give a boost to methods (accelerators, incubators and traders).
After all, it is vital to understand that those weaknesses are a part of a much broader context: in 2020, all of the African continent represented handiest 0.4% of worldwide project capital flows and represented handiest 2.5% of the worldwide synthetic intelligence marketplace; rising nations out of doors the “big four” subsequently in finding themselves routinely penalized on this already extremely concentrated pageant.
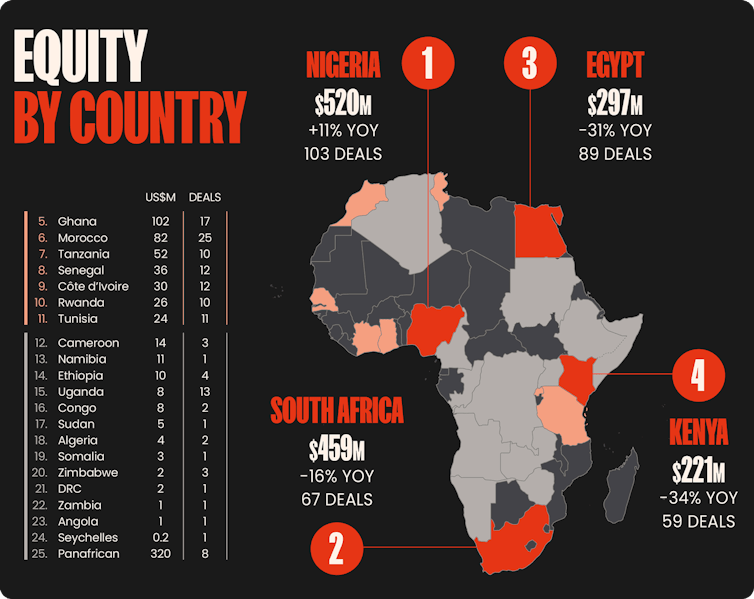
Distribution a gamble capital (fairness) funding in African era start-ups by means of nation. Partech, 2024 Africa Tech Project Capital Directing investments to organize nations for synthetic intelligence
To draw capital to those AI startups, the rustic will have to be AI-ready itself. AI adoption at nation degree does no longer handiest rely on technological elements: Synthetic Intelligence Funding Attainable (AIIPI) is a analysis paper that highlights that this adoption additionally is determined by financial, political and social elements. So, to extend its AI possible, the rustic will want to support no longer handiest its power and connectivity infrastructure, but in addition the extent of governance, the potency of its public government and its human capital.
Movements to be appreciated range relying at the degree of development in AI nations. In additional complex nations, corresponding to South Africa or Morocco, the problem is extra in supporting analysis, optimizing AI programs and attracting strategic investments. In nations with a extra reasonable ranking, priorities center of attention on consolidating connectivity infrastructure, human capital and regulatory frameworks.
The platform aipotentialindek.org lets in, amongst different issues, to visualise the result of the index on the world degree and the spaces wherein nations can make investments so as to build up their funding possible in synthetic intelligence (analysis, potency of public motion, connectivity, human capital, synthetic intelligence methods, and many others.). AIIPI lets in traders not to handiest determine complex nations in AI, but in addition the ones the place the prospective is underutilized. For public decision-makers and building actors, it gives a framework for prioritizing reforms and investments.
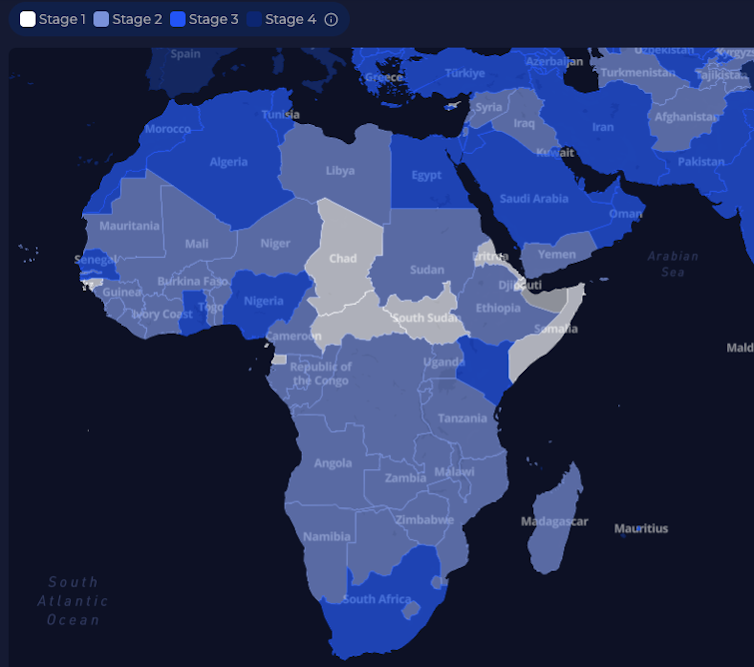
Visualizing the Funding Attainable of Synthetic Intelligence in Africa: The Darker the Colour, the Higher the Attainable. aipotentialindex.org
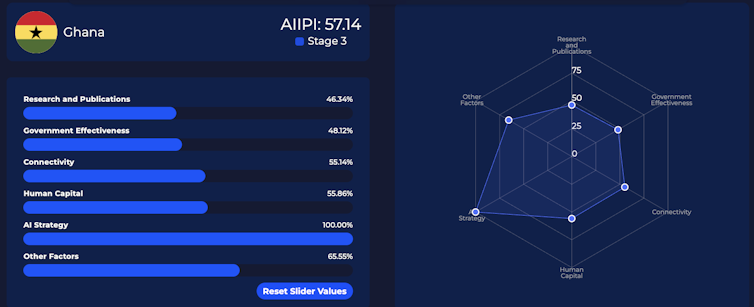
The Nation Profile software carried out to Ghana. Ghana has sturdy funding possible in AI. Get started-ups corresponding to Virtual Africa-backed Ghana Likuifi, which facilitates bill fee for SMEs, are appearing their entrepreneurial emulation. aipotentialindek.org State price range and methods devoted to new applied sciences
When defining a rustic’s AI funding technique, the query of AI financing tools arises. On the continental degree, a number of tools devoted to applied sciences and synthetic intelligence are rising. Construction finance establishments, such because the African Construction Financial institution and the West African Construction Financial institution, are launching tasks aimed toward supporting the expansion of the continent’s virtual economic system.
On the nationwide degree, African Sovereign Wealth Finances (ASFs) supply an extra street to give a boost to the financing of AI and start-ups at the continent. Those price range, such because the Mohammed VI fund in Morocco or the Pula fund in Botswana, mobilize public financial savings for long-term financial building and paintings in partnership with building banks.
Partnerships, tough levers for financing startups
Investment virtual and synthetic intelligence infrastructure isn’t sufficient to have a startup ecosystem that may stimulate the economic system. World public-private partnerships additionally play crucial position: the Make a choice Africa 2 initiative, supported by means of AFD and Bpifrance, objectives to reply to the financing constraints of entrepreneurship at the continent, particularly on the earliest phases. At this level, give a boost to methods corresponding to the ones in Virtual Africa, which carry in combination public actors and native companions, permit small investments in younger “Tech for Good” start-ups, whose applied sciences create a strategic social and environmental affect.
Partnerships between African and Ecu establishments, such because the Make a choice Africa 2 initiative led by means of AFD and Bpifrance, purpose to handle investment constraints for entrepreneurship at the continent, particularly on the earliest phases. At this level, preliminary schemes that carry in combination public actors and native companions, together with Virtual Africa, permit investments of small quantities to finance new companies that give a contribution to the growth of virtual infrastructure and a part of the “Technology for Good” method, whose applied sciences create a favorable social and environmental affect this is essential for the continent.
Those mechanisms, whilst no longer enough to proper funding imbalances, can however give a contribution to increasing get entry to to finance past the historically best-equipped ecosystems.
Central political, strategic and prison give a boost to
Monetary investments aren’t sufficient and will have to be pushed by means of political ambitions. Legislative and strategic measures applied on the nationwide and continental degree are structural levers for the expansion of virtual start-up corporations in Africa.
At the one hand, the methods supported by means of the African Union – the Virtual Transformation Technique for Africa, the Continental Technique on Synthetic Intelligence and the African Virtual Compact – supply highway maps for nations to boost up the virtual transformation of nations. There also are nationwide methods, corresponding to in Tunisia with the Startup Regulation, or nationwide methods on synthetic intelligence, corresponding to the only printed by means of Ghana that displays its ambition to develop into the “AI center of Africa”.
After all, a big political dedication used to be made remaining April, all the way through the World AI Summit in Kigali, the place 52 African nations introduced the advent of a 60 billion Africa AI Fund combining public, deepest and philanthropic capital. This initiative illustrates Africa’s strategic want: to place itself on those new technological demanding situations. On the other hand, those AI price range may just face control and monetary structuring demanding situations. Certainly, the chance stays that they might reproduce already present asymmetries in state price range if transparency mechanisms aren’t installed position. Their affect will subsequently rely at the status quo of requirements and control gear tailored to new technological demanding situations.
Those methods create the primary stipulations essential for the emergence of native AI answers in addition to a structural strategic framework. Their affect on investor self belief will, on the other hand, rely on their articulation with suitable financing and native capability.





