Coming into the coed global disrupts the way of life of younger other folks. Does this transition to autonomy then result in the adoption of environmentally appropriate conduct? Some insights from the newest result of the Observatory for Scholar Lifestyles survey.
Except for financial incentives, that are regularly transient, schooling generally is a lasting lever for pro-environmental conduct (CPE). If a top stage of schooling promotes figuring out of environmental problems, its results on CPE stay variable and on occasion even damaging. Different elements come into play: gender, age, source of revenue, social background or way of life.
We seemed on the determinants of scholars’ nutritional practices and mobility in accordance with the 2023 Scholar Dwelling Prerequisites survey, together with the next two questions: “Have you changed your eating habits for environmental reasons (less meat, eat organic, etc.)?”; “For environmental reasons, have you changed your transportation habits, other transportation habits (travel less)?”
Wisdom and feelings, elements of exchange
An environmentally mindful particular person can scale back their intake, desire a plant-based, native or seasonal nutrition and undertake a minimal impact nutrition. In shipping, they’ll make a choice low-emission modes or prohibit shuttle. On the other hand, well being, conduct, social norms and financial constraints additionally affect those possible choices, the place environmental motivations are combined with social and academic dimensions.
Higher knowledgeable people extra simply undertake pro-environmental behaviors. Schooling, formal or casual, imparts environmental wisdom and values, strengthening vital considering and sustainable consciousness. The social surroundings stays decisive: better-off families have more uncomplicated get right of entry to to natural merchandise or electrical cars, whilst poorer ones rely on public shipping.
The scholar’s way of life additionally impacts: the transition to autonomy adjustments conduct and results in the differentiation of various profiles, from devoted to detached, and so on. After all, game is an increasing number of spreading environmental values.
Equipped through the writer
Feelings, particularly damaging ones, are crucial lever for converting conduct. Eco-anxiety – discomfort and fear about international warming – impacts conduct, even supposing its results range from learn about to check.
Eco-anxious graduates
As of 2020, the “Student Living Conditions” survey measures this phenomenon via questions on local weather problems. In 2023, 87% of respondents say they’re frightened, particularly ladies, and this share stays strong regardless of the worsening disaster. Eco-anxiety additionally varies through social and academic background.
After all, residing prerequisites additionally affect conduct: scholars who reside with their oldsters exchange much less, whilst monetary difficulties advertise nutritional adaptation however decelerate sustainable mobility.
Equipped through the writer
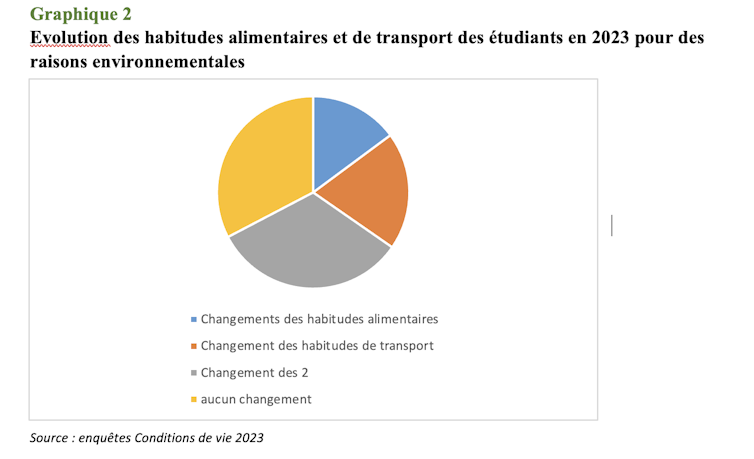
Amongst scholars surveyed in 2023, a 3rd have modified their consuming and transportation conduct for environmental causes. Those adjustments range relying on gender, social background, stage of schooling and sensitivity to local weather.
Feminine scholars modify their nutrition extra (18% in comparison to 9% of guys), whilst feminine scholars adjust their transportation extra regularly (23% in comparison to 18%). Probably the most trained, from prosperous, environmentally traumatic or dedicated backgrounds, are much more likely to modify their behaviour: 35% of scholars are desirous about local weather exchange and each, in comparison to 7% who aren’t involved.
Participation in meetings or occasions, in addition to sports activities observe, advertise conduct in desire of our surroundings: 34% of athletes have modified their conduct, whilst the results of tobacco or alcohol are nonetheless unsure. Subject material constraints additionally play a task: city citizens customise their transportation extra (21% in comparison to 15% in rural spaces) however much less so their meals (14% in comparison to 21%). Unbiased scholars (38%) exchange extra regularly than those that reside with their oldsters (19%).
Financial and geographical boundaries
The criteria related to adjustments in nutrition and transportation are an identical: ladies, athletic scholars, those that are involved concerning the local weather, or those that are higher trained are much more likely to modify their practices. The extent of analysis stays decisive: Grasp’s scholars extra regularly undertake sustainable behaviors, supporting the position of schooling.
Dwelling surroundings may be vital: rurality encourages nutritional adjustments however slows down sustainable mobility, whilst residing in a area or place of dwelling encourages them. Monetary constraints, alternatively, typically prohibit transportation adjustments. After all, 34% of scholars wish to exchange their nutrition, and 27% their shipping, however are not able to take action, hampered through their financial or geographic prerequisites: residing with their oldsters limits their nutritional choices, whilst city distance and loss of assets prohibit sustainable mobility.
Positive traits – wealthy social background, excellent stage of schooling, dedication to the surroundings, fear for the local weather or sports activities observe – advertise pro-environmental conduct in meals and shipping.
The Dwelling Prerequisites of Scholars survey is, on the other hand, nonetheless restricted: it does no longer supply main points on particular movements or the chronology of adjustments, making it tricky to evaluate leverage or comments results. On the other hand, schooling, formal or casual, stays a central lever for encouraging pro-environmental conduct via awareness-raising, wisdom dissemination and intergenerational transmission.
Strengthening environmental schooling and loose get right of entry to to workshops or meetings, particularly in threatened spaces, illustrate this trail. Different levers can supplement this motion: sustainable sports activities, energetic mobility and social insurance policies that scale back inequalities.





