If the seas and oceans labored like an enormous bath, the water would upward thrust far and wide in the similar approach. That is not what is going down. The melting of the ice in Antarctica, underneath the affect of worldwide warming, ends up in an asymmetric upward thrust in sea point, particularly because of gravity and the position of the Earth’s mantle.
When the polar ice caps soften, the consequences unfold around the globe. Melting ice raises moderate sea ranges, adjustments ocean currents, and impacts temperatures in areas some distance from the poles. However this melting does now not have an effect on sea ranges and temperatures far and wide in the similar approach.
In a brand new find out about, our workforce of scientists tested how melting Antarctic ice impacts world local weather and sea ranges. We blended pc fashions of the Antarctic ice sheet, Earth, and world local weather, together with atmospheric and oceanic processes, to analyze the complicated interactions between melting ice and different Earth parts.
Working out what occurs to the ice in Antarctica is very important, because it incorporates sufficient frozen water to lift moderate sea point through about 58 meters. When this ice melts, it turns into an existential drawback for the populations and ecosystems of island and coastal communities.
Adjustments in Antarctica
The level to which the Antarctic ice sheet melts depends upon the level of worldwide warming. Warming that depends upon long run emissions of greenhouse gases from automobiles, energy crops and business. Research recommend that a lot of Antarctica’s ice sheet may just stay if international locations minimize their greenhouse gasoline emissions consistent with the 2015 Paris Settlement’s objective of restricting world warming to one.5°C above pre-industrial occasions. Alternatively, if emissions proceed to upward thrust and the ambience and oceans heat a lot more, this is able to motive important melting and far upper sea ranges.
Our analysis presentations that top emissions pose a possibility now not simplest to the steadiness of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet, which is already contributing to sea point upward thrust, but additionally to the a lot better and extra strong East Antarctic Ice Sheet. In addition they display that areas of the arena will revel in other ranges of sea point upward thrust as Antarctica melts.
Working out sea point alternate
If the ocean behaved like water in a tub, then ocean ranges would upward thrust far and wide in the similar approach. However that is not what is going down. To the contrary, many puts are experiencing sea point upward thrust above the worldwide moderate, whilst in spaces close to the ice sheet sea point can even fall. The primary reason why is gravity.
Visualization of the Earth’s gravitational box. Gravity is decided through mass, and the Earth’s mass isn’t calmly disbursed. NASA/JPL/College of Texas Area Analysis Heart.
The ice sheets are massive, and this mass has a robust gravity that draws the encircling ocean water in opposition to it, similar to the gravitational drive between the Earth and the Moon impacts the tides.
Because the ice sheet shrinks, its gravitational drive at the ocean decreases, inflicting sea ranges to fall in areas close to the ice cabinets and to upward thrust in areas additional away. However sea-level adjustments do not simply rely at the distance from the melting ice sheet. This ice loss additionally adjustments the planet’s rotation. The axis of rotation is drawn to this mass of lacking ice, which in flip redistributes water around the globe.
Two components that may gradual melting
As the large ice sheet melts, the Earth’s mantle underneath rises. Underneath the Antarctic rock lies this mantle, which slowly drains away, similar to maple syrup. The extra the ice sheet melts, the fewer drive there may be at the forged Earth. With this lowered weight, the bottom will also be raised. This may transfer portions of the ice sheet clear of hotter ocean waters, slowing the velocity of melting. This phenomenon is quicker in areas the place the mantle flows quicker, reminiscent of underneath the West Antarctic Ice Sheet. This comments impact may just lend a hand keep the ice sheet—supplied world greenhouse gasoline emissions stay low.
Some other issue that might gradual melting might appear counterintuitive.
Whilst Antarctic meltwater contributes to sea point upward thrust, fashions display it additionally delays warming brought about through greenhouse gases. Certainly, ice water from Antarctica reduces the outside temperature of the oceans within the Southern Hemisphere and the tropical Pacific, trapping warmth within the depths and slowing the rise in world moderate air temperature.
However at the same time as melting slows, sea ranges proceed to upward thrust.
Mapping our effects at sea point
We blended pc fashions that simulate those behaviors and different options of the Antarctic ice sheet, Earth’s mantle, and local weather to know what may occur to sea ranges around the globe as world temperatures upward thrust and ice melts.
As an example, in a reasonable state of affairs the place the arena reduces greenhouse gasoline emissions, however now not sufficient to stay world warming beneath 2°C through 2100, we discovered that moderate sea point upward thrust from melting Antarctic ice could be about ten centimeters through 2100. By means of 2200, it could exceed one meter.
It must be stored in thoughts that it is just an issue of sea point upward thrust brought about through the melting of Antarctica. The Greenland ice sheet and the thermal growth of seawater because of ocean warming may also give a contribution to sea point upward thrust. Present estimates recommend that total moderate sea point upward thrust – together with Greenland and thermal growth – could be between 30 centimeters and 60 centimeters through 2100 underneath the similar state of affairs.
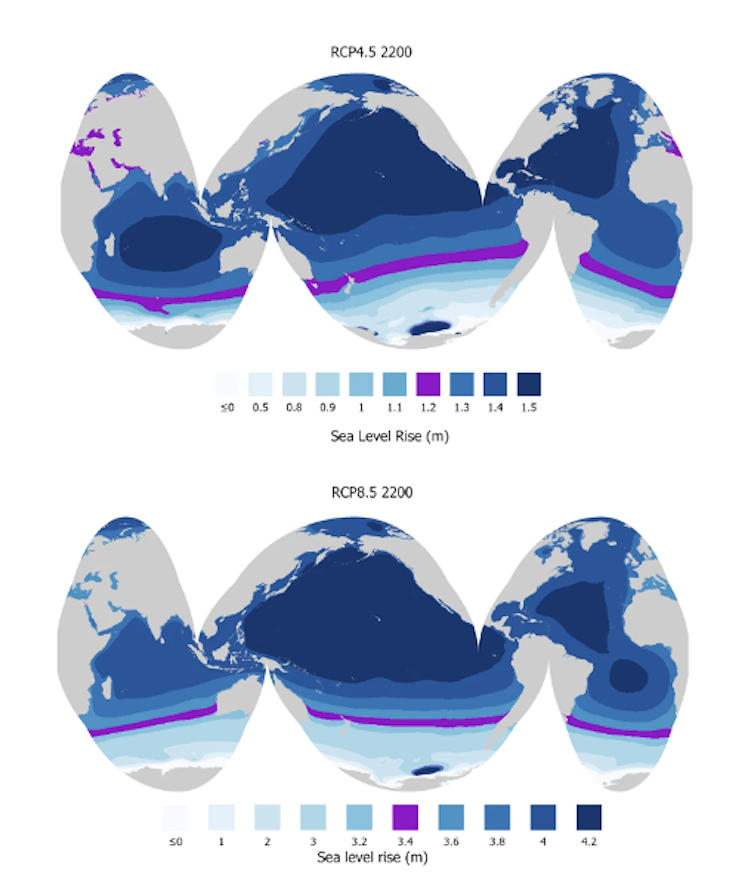
The fashions display the contribution of Antarctica to sea point upward thrust in 2200, underneath medium (best) and excessive (backside) emissions situations. Reasonable world sea point upward thrust is in red. Spaces the place sea point exceeds the regional moderate seem darkish blue. Sadai et al., 2025
We additionally display how sea point upward thrust because of Antarctica varies around the globe. Within the reasonable emissions state of affairs, we discovered that the biggest sea point upward thrust because of Antarctic ice soften on my own, as much as 1.5 m through 2200, happens within the Indian, Pacific and western Atlantic Ocean basins – areas some distance from Antarctica.
Those areas are house to many populations residing in low-lying coastal spaces, together with citizens of Caribbean islands reminiscent of Jamaica and the central Pacific such because the Marshall Islands, which can be already experiencing the hostile affects of emerging seas.
Within the high-emissions state of affairs, we discovered that the typical sea-level upward thrust because of Antarctic melting could be a lot upper: about 30 centimeters through 2100 and nearly 3 meters through 2200.
On this state of affairs, a lot of the Pacific basin north of the equator, together with Micronesia and Palau, in addition to the central Atlantic basin, would revel in the biggest sea-level upward thrust, as much as 4.3 m through 2200, because of Antarctica on my own.
Whilst those numbers might appear alarming, present emissions and up to date projections point out that this very excessive emissions state of affairs is not going. This workout however presentations the intense penalties of excessive emissions and highlights the significance of decreasing them.
There are not any conclusions
Those affects have implications for local weather justice, in particular for island states that experience contributed little to local weather alternate however are already experiencing the devastating results of sea point upward thrust.
Many island countries are already shedding land to emerging seas and feature been at the vanguard of worldwide efforts to restrict warming. Protective those international locations and different coastal spaces would require decreasing greenhouse gasoline emissions quicker than countries are committing to nowadays.






