When polar ice sheets soften, the consequences ripple the world over. The melting ice raises moderate international sea point, alters ocean currents and impacts temperatures in puts some distance from the poles.
However melting ice sheets don’t have an effect on sea point and temperatures in the similar approach in every single place.
In a brand new learn about, our workforce of scientists investigated how ice melting in Antarctica impacts international local weather and sea point. We blended pc fashions of the Antarctic ice sheet, forged Earth and international local weather, together with atmospheric and oceanic processes, to discover the complicated interactions that melting ice has with different portions of the Earth.
Working out what occurs to Antarctica’s ice issues, as it holds sufficient frozen water to boost moderate sea point by means of about 190 toes (58 meters). Because the ice melts, it turns into an existential downside for folks and ecosystems in island and coastal communities.
Sea point is inching up on properties on Tierra Bomba Island, Colombia, the place a cemetery already washed away.
Luis Acosta/AFP by way of Getty Photographs
Adjustments in Antarctica
The level to which the Antarctic ice sheet melts depends on how a lot the Earth warms. And that will depend on long run greenhouse gasoline emissions from resources together with cars, energy crops and industries.
Research counsel that a lot of the Antarctic ice sheet may continue to exist if international locations cut back their greenhouse gasoline emissions in keeping with the 2015 Paris Settlement function to stay international warming to one.5 levels Celsius (2.7 Fahrenheit) in comparison to sooner than the commercial generation. Then again, if emissions proceed emerging and the ambience and oceans heat a lot more, that would purpose really extensive melting and far upper sea ranges.
Our analysis presentations that prime emissions pose dangers no longer simply to the steadiness of the West Antarctic ice sheet, which is already contributing to sea-level upward thrust, but additionally for the a lot greater and extra solid East Antarctic ice sheet.
It additionally presentations how other areas of the arena will enjoy other ranges of sea-level upward thrust as Antarctica melts.
Working out sea-level alternate
If sea ranges rose just like the water in a tub, then as ice sheets soften, the sea would upward thrust by means of an identical quantity in every single place. However that isn’t what occurs.
As a substitute, many puts enjoy upper regional sea-level upward thrust than the worldwide moderate, whilst puts as regards to the ice sheet may also see sea ranges drop. The principle explanation why has to do with gravity.
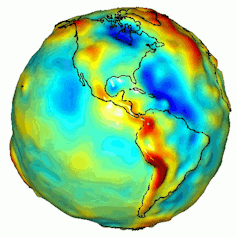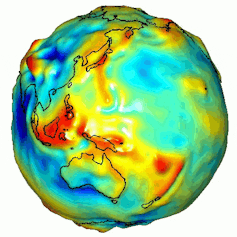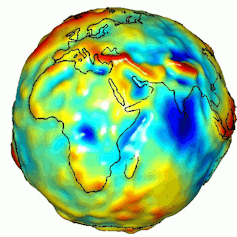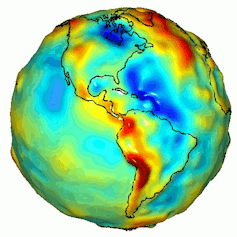
A visualization of Earth’s gravity box. Gravity is decided by means of mass, and Earth’s mass isn’t disbursed similarly. NASA/JPL/College of Texas Heart for House Analysis.
Ice sheets are huge, and that mass creates a powerful gravitational pull that pulls the encompassing ocean water towards them, very similar to how the gravitational pull between Earth and the Moon impacts the tides.
Because the ice sheet shrinks, its gravitational pull at the ocean declines, resulting in sea ranges falling in areas as regards to the ice sheet coast and emerging farther away. However sea-level adjustments don’t seem to be just a serve as of distance from the melting ice sheet. This ice loss additionally adjustments how the planet rotates. The rotation axis is pulled towards that lacking ice mass, which in flip redistributes water around the world.
2 components that may sluggish melting
As the large ice sheet melts, the forged Earth underneath it rebounds.
Beneath the bedrock of Antarctica is Earth’s mantle, which flows slowly like maple syrup. The extra the ice sheet melts, the fewer it presses down at the forged Earth. With much less weight on it, the bedrock can rebound. It will carry portions of the ice sheet out of touch with warming ocean waters, slowing the speed of melting. This occurs faster in puts the place the mantle flows quicker, reminiscent of beneath the West Antarctic ice sheet.
This rebound impact may lend a hand maintain the ice sheet – if international greenhouse gasoline emissions are stored low.
NASA explains how land rebounds when ice sheets melts. NASA by way of Digital Palaeosciences.
Any other issue that may sluggish melting would possibly appear counterintuitive.
Whilst Antarctic meltwater drives emerging sea ranges, fashions display it additionally delays greenhouse gas-induced warming. That’s as a result of icy meltwater from Antarctica reduces ocean floor temperatures within the Southern Hemisphere and tropical Pacific, trapping warmth within the deep ocean and slowing the upward push of world moderate air temperature.
However as melting happens, even supposing it slows, sea ranges upward thrust.
Mapping our sea-level effects
We blended pc fashions that simulate those and different behaviors of the Antarctic ice sheet, forged Earth and local weather to grasp what may occur to sea point world wide as international temperatures upward thrust and ice melts.
For instance, in a reasonable state of affairs by which the arena reduces greenhouse gasoline emissions, even though no longer sufficient to stay international warming underneath 2 levels Celsius (3.6 Fahrenheit) in 2100, we discovered the common sea-level upward thrust from Antarctic ice soften can be about 4 inches (0.1 meters) by means of 2100. By means of 2200, it could be greater than 3.3 toes (1 meter).
Take into account that that is handiest sea-level upward thrust led to by means of Antarctic soften. The Greenland ice sheet and thermal enlargement of seawater because the oceans heat will even lift sea ranges. Present estimates counsel that general moderate sea-level upward thrust – together with Greenland and thermal enlargement – can be 1 to two toes (0.32 to 0.63 meters) by means of 2100 underneath the similar state of affairs.
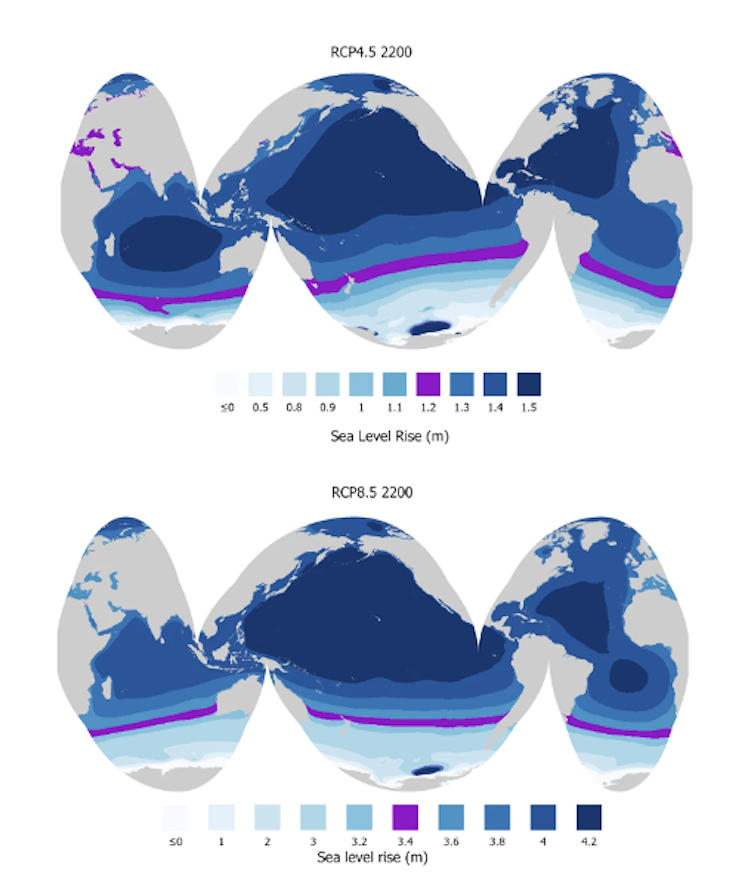
Fashions display Antarctica’s contribution to sea-level upward thrust in 2200 underneath medium (best) and prime (backside) emissions. The worldwide imply sea-level upward thrust is in pink. Locally upper than moderate sea-level upward thrust seems in darkish blue.
Sadai et al., 2025
We additionally display how sea-level upward thrust from Antarctica varies world wide.
In that reasonable emissions state of affairs, we discovered the absolute best sea-level upward thrust from Antarctic ice soften on my own, as much as 5 toes (1.5 meters) by means of 2200, happens within the Indian, Pacific and western Atlantic ocean basins – puts some distance from Antarctica.
Those areas are house to many of us in low-lying coastal spaces, together with citizens of island international locations within the Caribbean, reminiscent of Jamaica, and the central Pacific, such because the Marshall Islands, which might be already experiencing damaging affects from emerging seas.
Underneath a prime emissions state of affairs, we discovered the common sea-level upward thrust led to by means of Antarctic melting can be a lot upper: about 1 foot (0.3 meters) in 2100 and as regards to 10 toes (greater than 3 meters) in 2200.
Underneath this state of affairs, a broader swath of the Pacific Ocean basin north of the equator, together with Micronesia and Palau, and around the center of the Atlantic Ocean basin would see the absolute best sea-level upward thrust, as much as 4.3 meters (14 toes) by means of 2200, simply from Antarctica.
Even though those sea-level upward thrust numbers appear alarming, the arena’s present emissions and up to date projections counsel this very prime emissions state of affairs is not going. This workout, alternatively, highlights the intense penalties of prime emissions and underscores the significance of decreasing emissions.
The takeaway
Those affects have implications for local weather justice, in particular for island international locations that experience achieved little to give a contribution to local weather alternate but already enjoy the devastating affects of sea-level upward thrust.
Many island international locations are already dropping land to sea-level upward thrust, and they have got been main international efforts to reduce temperature upward thrust. Protective those international locations and different coastal spaces would require decreasing greenhouse gasoline emissions quicker than international locations are committing to do these days.







