Many of us in the United Kingdom really feel they’re operating tougher than ever. A better value of dwelling and extra precarious paintings preparations push many families to tackle longer hours and more than one jobs. Information again this sense: from 2010 to 2024, the United Kingdom had the biggest build up in hours labored consistent with individual amongst OECD nations.
But headlines stay telling us that UK productiveness is stagnating. So if everybody is operating extra, why isn’t the economic system rising sooner? Sadly, there’s much more in play than simply what number of hours we installed each and every week.
Labour productiveness, measured as the full GDP produced consistent with hour labored, is decrease for the United Kingdom than for plenty of of its friends, corresponding to France, Germany and the US. But from 2000 to 2010, UK labour productiveness larger through 11%, greater than France and Germany, the place positive aspects have been 10.6% and 10.2% respectively.
Since then, regardless that, the United Kingdom has confronted a chain of cases that experience harmed the economic system. From 2010 to 2024, fortunes shifted. Whilst productiveness within the euro house larger through about 10% and nearly 15% in the United States, the rise in the United Kingdom used to be most effective 6.2%.
So what came about to the United Kingdom all over this time to wreck its productiveness, enlargement and profits? 4 forces stand out.
1. A protracted dose of austerity
Starting in 2010, the United Kingdom launched into cuts to departmental spending and public funding concurrently elevating taxes. Austerity suppresses call for within the quick run. Extra importantly, regardless that, it reduces public funding and spending on such things as infrastructure, talents, analysis and construction, and public products and services that non-public corporations want to increase and modernise.
The result’s a slower diffusion of generation that may make stronger productiveness. My analysis has exposed chronic “scarring” results on output, employment and funding greater than a decade after austerity.
2. Political uncertainty – Brexit and past
Financial uncertainty in Europe and the United Kingdom:
Index of Financial Uncertainty.
Financial Coverage Uncertainty Index.
This results in continual under-investment. The United Kingdom has had the bottom stage of funding amongst G7 nations for nearly once a year since 1990. And analysis has proven this to be the one maximum essential part within the stagnation of UK productiveness.
3. Susceptible commercial technique
Around the OECD there was a revival of recent commercial coverage – multi-year programmes concentrated on inexperienced applied sciences, semiconductors, complex production and their provide chains.
The United Kingdom revealed an commercial technique previous this 12 months, however the combine has been relatively gentle on direct public funding and explicit sectors. Evaluating commercial coverage methods is hard, however proof means that the United Kingdom’s means has been smaller in scale, much less predictable and not more centered than that of its friends.
4. An economic system tilted in opposition to finance
A last side that is helping provide an explanation for basic productiveness in the United Kingdom is its financial construction – particularly, its focus in finance. Round 8.7% of the United Kingdom’s GDP is within the monetary and insurance coverage actions, a lot more than that of the EU (4.6%) and greater than double that of nations like Germany and France.
Alternatively, the percentage of producing in the United Kingdom economic system is 8.9%, in comparison to 15.7% within the EU, 10.7% in France, and 19.9% in Germany. This issues as a result of sectors range systematically in productiveness ranges and enlargement charges. During the last 3 a long time, sectors like equipment and kit, chemical substances and prescription drugs, and knowledge and communications have proven a lot more potent productiveness enlargement than finance.
Productiveness enlargement in the United Kingdom:
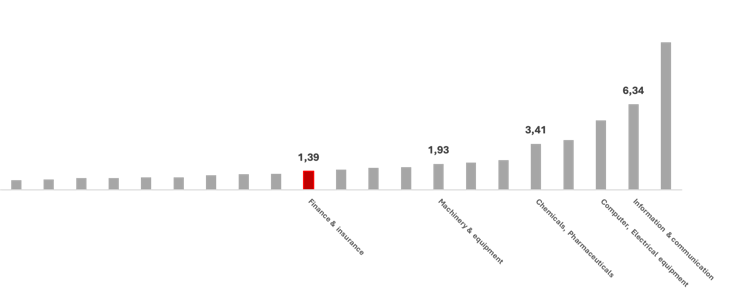
Productiveness enlargement through sector (1994-2020) – 1994=1.
Workplace for Nationwide Statistics.
De-industrialisation isn’t distinctive to the United Kingdom, and a few of it displays automation and reorganisation of world provide chains. However complex economies that retained and upgraded segments of producing – specifically the ones closest to the generation frontier – have tended to revel in more potent productiveness enlargement and extra innovation of their carrier sectors.
Taken in combination, those forces have interaction and compound. Austerity got rid of public funding and corresponding advantages simply when corporations wanted them, whilst uncertainty raised obstacles and inspired corporations to attend moderately than make investments.
In that setting, the absence of coordinated commercial coverage supposed there have been no transparent indicators or platforms for scaling new applied sciences. And the United Kingdom’s finance-heavy construction channelled ability and financial savings into monetary property moderately than into initiatives that would increase capability and boost up innovation. In the end, this ends up in a prolonged shortfall of productive funding.
A direction out is easy, if politically hard. Decide to a multi-year public funding programme that still draws pastime from the non-public sector. And undertake a more potent and extra centered commercial technique across the inexperienced, tech and science sectors (matched with making plans and abilities reform).
If those levers are pulled in combination – and sustained – UK productiveness, and with it actual wages, needn’t stay caught.






