The wetlands discovered around the Rocky Mountains of Colorado slightly below tree line are magical puts. Dripping with mosses and deep inexperienced sedges, those open expanses flanked through evergreens are a wide ranging sight for passing hikers. Moose graze there, and elk accumulate throughout their mating season.
Those subalpine wetlands also are a very powerful for regulating the availability of unpolluted water from the highlands to metropolitan areas downslope, together with Denver.
Alternatively, new analysis displays the wetlands additionally harbor a well being possibility. In a brand new learn about, my analysis staff discovered that slightly below the outside of subalpine wetland soils, the very best prerequisites exist for the manufacturing of methylmercury, a potent, poisonous type of the heavy steel mercury that may threaten the well being of flora and fauna and folks.
As emerging temperatures thaw ice and erode the mountain rocks, and mercury air pollution from energy vegetation around the globe falls with rain, this poisonous type of mercury may also be produced within the wetlands.
A map displays the distribution of subalpine wetlands within the Boulder Creek Watershed, defined in black. The wetlands have mosses, sedges and shrubs, and they’re surrounded through evergreen timber.
Eve-Lyn Hinckley/College of Colorado
The Goldilocks downside
Methylmercury is a neurotoxin that biomagnifies and bioaccumulates, that means it turns into extra concentrated because it strikes up the meals chain. Predatory birds and fish top at the meals chain are maximum liable to its devastating results at the apprehensive and reproductive techniques, as are the human populations that eat them.
Within the Fifties, loads of folks in Minamata and Niigata, Japan, died from methylmercury poisoning attached to drinking water, fish and shellfish from close to the place chemical vegetation had been discharging mercury into the water.
Mercury methylation is a fickle procedure. The micro organism concerned require resources of inorganic mercury and effort, in addition to oxygen-free prerequisites.
Sulfate concentrations are specifically essential. Like in “Goldilocks and the Three Bears,” an excessive amount of or too little sulfate is unsatisfactory to the methylating microbes – the ones growing methylmercury. Too little sulfate, they usually gained’t stimulate mercury methylation. An excessive amount of sulfate, and mercury will get sequestered in mineral shape, minimizing its possibility to residing organisms.
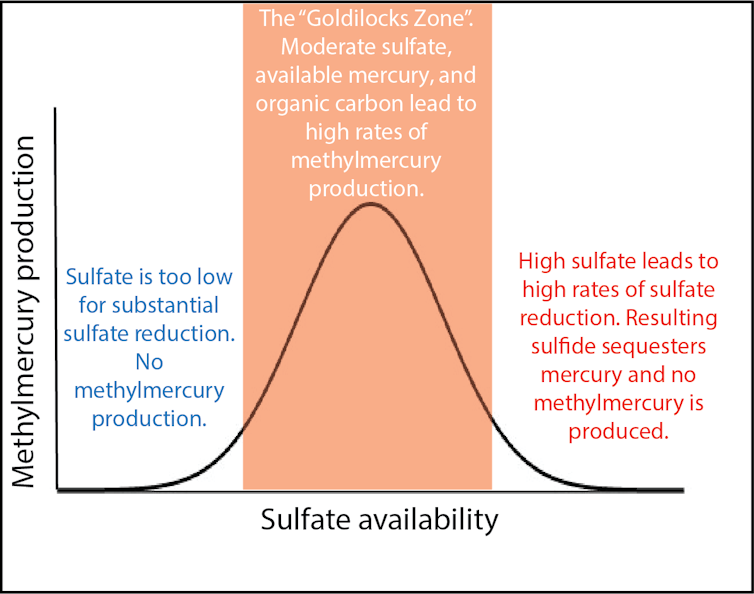
The perfect concentrations of methylmercury are produced when sulfate concentrations are within the Goldilocks zone: now not too top or too low, however excellent.
Eve-Lyn Hinckley/College of Colorado
But, when reasonable sulfate concentrations combine with inorganic mercury and natural carbon in a low-oxygen setting, the prerequisites are dangerously “just right,” as Goldilocks would say, and methylmercury manufacturing is top.
New proof of methylmercury
Previous to our learn about, maximum wetlands discovered to have methylmercury air pollution had been in lowland spaces, such because the Florida Everglades, the place the method is fed through sulfate runoff from agriculture fields. Alternatively, our learn about demonstrates that methylmercury manufacturing happens in reputedly faraway mountain places, too.
There are a couple of explanation why prerequisites in Colorado’s subalpine wetlands are excellent.
First, the soil has abundant natural subject, offering a deep retailer of power within the type of carbon to gasoline methylation. In Colorado’s subalpine wetlands, thick soils are wealthy in layer upon layer of historic natural subject that saturates with snowmelt flowing from the perfect peaks.
2nd, mercury air pollution from business facilities reaches the Rocky Mountains. Lots of the mercury that enters subalpine wetlands has in reality traveled the entire manner from China and India. In the end, it falls out of the ambience in rain or mud, and top elevations obtain extra of it than low elevations.
3rd – and that is the important thing stimulating impact for methylating micro organism – subalpine wetlands obtain extra sulfate from warming alpine spaces in elevations above them. As emerging air temperatures pressure the thawing of ice and sooner charges of mineral weathering, extra sulfate than was once already within the flooring flows into streams to the subalpine area.
The result’s that those components combine within the flooded, continuously oxygen-free setting of the wetland soils, and micro organism have the whole lot they want to produce methylmercury.
Our learn about confirmed that the concentrations of methylmercury are upper on the outlet than the inlet of subalpine wetlands that we studied within the Colorado Rockies, offering additional proof that wetlands could be a supply of the contaminant.
Except the native results of methylmercury on flora and fauna, our discovery highlights a priority for water provides. Over 3 million folks within the Boulder-Denver metropolitan house depend on blank, recent water from the mountains. Contamination of the supply house through methylmercury can have large-scale ramifications, similar to expensive remedy measures, for all of the Colorado Entrance Vary’s consuming water provide.
The best way to decrease the chance
Prime-elevation ecosystems around the globe are experiencing many results that may feed the manufacturing of methylmercury.
In each and every state within the U.S., there’s a minimum of one mercury toxicity caution for floor waters, most often urging folks to not consume fish or shellfish stuck there or to restrict the quantity they consume. Higher manufacturing of methylmercury, and its danger to meals and water resources, is now part of our converting international.
So, what may also be achieved to keep away from the chance?
Reducing mercury deposition calls for curtailing business emissions. In 2013, over 140 countries, together with the U.S., signed the Minamata Conference on Mercury, committing to keep watch over and observe business mercury resources. Last dedicated to this settlement is significant.
Lowering the float of sulfate from ice and rock weathering within the mountains – some other key aspect to this procedure – calls for addressing local weather trade.
Folks, governments and industries can take many steps to gradual the upward push of air temperatures which can be expanding ice thaw, from now not riding gas-powered cars as a lot to regulating carbon dioxide emissions from energy vegetation and factories. Our new analysis on methylmercury displays one more reason why taking steps to gradual local weather trade are well worth the effort.





