Damaging flash flooding in Texas and different states is elevating questions in regards to the country’s flood maps and their skill to be sure that communities and house owners can get ready for emerging dangers.
The U.S. Federal Emergency Control Company’s flood maps are meant to be the country’s number one device for figuring out flood dangers.
In the beginning advanced within the Nineteen Seventies to strengthen the Nationwide Flood Insurance coverage Program, those maps, referred to as Flood Insurance coverage Charge Maps, or FIRMs, are used to decide the place flood insurance coverage is needed for federally sponsored mortgages, to tell native construction codes and land-use selections, and to lead flood simple control methods.
A federal flood map of Kerrville, Texas, with the Guadalupe River winding during the center in crimson, presentations spaces regarded as to have a 1% annual likelihood of flooding in blue and a zero.2% annual likelihood of flooding in tan. All the way through a flash flood on July 4, 2025, the river rose greater than 30 ft at Kerrville.
FEMA
In idea, the maps allow house owners, companies and native officers to know their flood menace and take suitable steps to arrange and mitigate attainable losses.
However whilst FEMA has progressed the accuracy and accessibility of the maps over the years with higher knowledge, virtual equipment and group enter, the maps nonetheless don’t seize the whole lot – together with the converting weather. There are spaces of the rustic that flood, some frequently, that don’t display up at the maps as in peril.
I learn about flood-risk mapping as a university-based researcher and at First Boulevard, a company created to quantify and keep in touch weather menace. In a 2023 evaluate the use of newly modeled flood zones with climate-adjusted precipitation information, we discovered that greater than two times as many homes around the nation had been prone to a 100-year flood than the FEMA maps recognized.
Even in puts the place the FEMA maps recognized a flood menace, we discovered that the federal mapping procedure, its overreliance on ancient knowledge, and political affect over the updating of maps can result in maps that don’t absolutely constitute a space’s menace.
What FEMA flood maps omit
FEMA’s maps are crucial equipment for figuring out flood dangers, however they have got important gaps that restrict their effectiveness.
One primary limitation is they don’t believe flooding pushed by means of intense bursts of rain. The maps basically focal point on river channels and coastal flooding, in large part apart from the danger of flash flooding, specifically alongside smaller waterways reminiscent of streams, creeks and tributaries.
This limitation has transform extra vital lately because of weather exchange. Emerging international temperatures can lead to extra common excessive downpours, leaving extra spaces prone to flooding, but unmapped by means of FEMA.
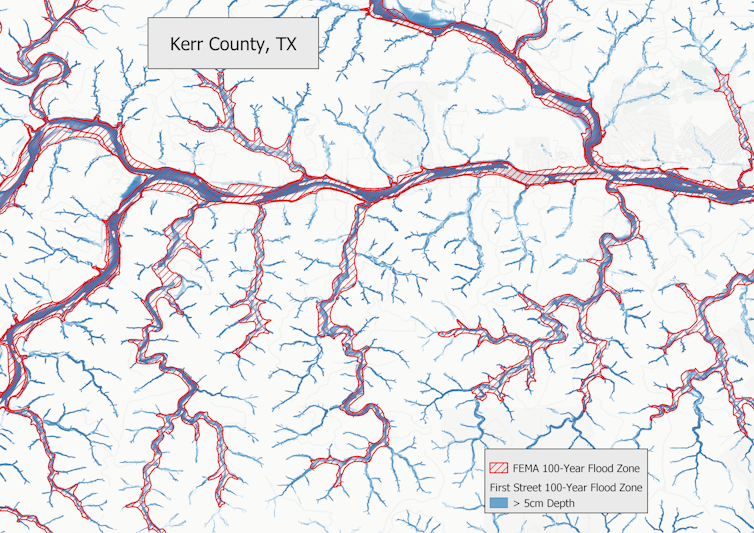
A map of a piece of Kerr County, Texas, the place a perilous flood struck on July 4, 2025, compares the FEMA flood map’s 100-year flood zone (purple) to First Boulevard’s extra detailed 100-year flood zone (blue). The extra detailed map comprises flash flood dangers alongside smaller creeks and streams.
Jeremy Porter
As an example, when flooding from Storm Helene hit unmapped spaces round Asheville, North Carolina, in 2024, it led to an enormous quantity of uninsured harm to homes.
Even in spaces which might be mapped, just like the Camp Mystic website in Kerr County, Texas, that was once hit by means of a perilous flash flood on July 4, 2025, the maps might underestimate their menace on account of a reliance on historical knowledge and old-fashioned menace tests.
Political affect can gasoline lengthy delays
Moreover, FEMA’s mapping procedure is ceaselessly formed by means of political pressures.
Native governments and builders once in a while combat to steer clear of high-risk designations to steer clear of insurance coverage mandates or restrictions on building, resulting in maps that can understate precise dangers and go away citizens unaware in their true publicity.
An instance is New York Town’s enchantment of a 2015 FEMA Flood Insurance coverage Charge Maps replace. The prolong in resolving the town’s considerations has left it with maps which might be more or less two decades outdated, and the present mapping challenge is tied up in felony purple tape.
On moderate, it takes 5 to seven years to broaden and put in force a brand new FEMA Flood Insurance coverage Charge Map. Because of this, many maps around the U.S. are considerably old-fashioned, ceaselessly failing to replicate present land use, city building or evolving flood dangers from excessive climate.
This prolong at once impacts construction codes and infrastructure making plans, as native governments depend on those maps to lead building requirements, building approvals and flood mitigation tasks. In the end, old-fashioned maps can result in underestimating flood dangers and permitting prone constructions to be inbuilt spaces that face rising flood threats.
How generation advances can assist
New advances in satellite tv for pc imaging, rainfall modeling and high-resolution lidar, which is analogous to radar however makes use of mild, make it conceivable to create quicker, extra correct flood maps that seize dangers from excessive rainfall and flash flooding.
On the other hand, absolutely integrating those equipment calls for important federal funding. Congress controls FEMA’s mapping finances and units the felony framework for the way maps are created. For years, updating the flood maps has been an unpopular matter amongst many publicly elected officers, as a result of new flood designations can cause stricter construction codes, upper insurance coverage prices and building restrictions.
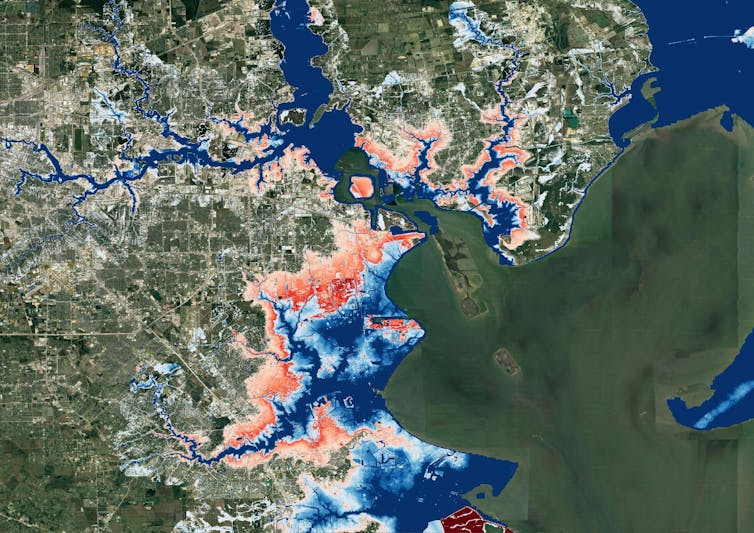

A map of Houston, produced for a 2022 learn about by means of researchers at universities and First Boulevard, presentations flood menace converting over the following 30 years as weather exchange worsens. Blue spaces are as of late’s 100-year flood-risk zones. The purple spaces replicate the similar zones in 2050.
Oliver Wing et al., 2022
In recent times, the upward push of weather menace analytics fashions and personal flood menace knowledge have allowed the actual property, finance and insurance coverage industries to depend much less on FEMA’s maps. Those new fashions incorporate forward-looking weather knowledge, together with projections of utmost rainfall, sea-level upward thrust and converting hurricane patterns – elements FEMA’s maps usually exclude.
Actual property portals like Zillow, Redfin, Realtor.com and Houses.com now supply property-level flood menace rankings that believe each ancient flooding and long term weather projections. The fashions they use establish dangers for lots of homes that FEMA maps don’t, highlighting hidden vulnerabilities in communities throughout the US.
Analysis presentations that the supply, and accessibility, of weather knowledge on those websites has began riding property-buying selections that an increasing number of take weather become account.
Implications for the longer term
As homebuyers perceive extra a few estate’s flood dangers, that can shift the desirability of a few places over the years. The ones shifts may have implications for estate valuations, group tax-revenue tests, inhabitants migration patterns and a slew of different issues.
On the other hand, whilst those might really feel like adjustments being attributable to new knowledge, the danger was once already there. What’s converting is other folks’s consciousness.
The government has a very powerful function to play in making sure that correct menace tests are to be had to communities and American citizens all over the place. As higher equipment and fashions evolve for assessing menace evolve, FEMA’s menace maps wish to evolve, too.



