In the future between conception and early adolescence, ache makes its debut. But if precisely that occurs stays certainly one of medication’s maximum difficult questions.
Some have claimed that foetuses as younger as twelve weeks can already be noticed wincing in agony, whilst others have flat-out denied that even babies display any true indicators of ache till lengthy after delivery.
New analysis from College Faculty London provides recent insights into this puzzle. By way of mapping the improvement of pain-processing networks within the mind – what researchers name the “pain connectome” – scientists have begun to track precisely when and the way our capability for ache emerges. What they found out demanding situations easy solutions about when ache “begins”.
The researchers used complex mind imaging to match the neural networks of foetuses and babies with the ones of adults, monitoring how other parts of ache processing mature over the years. Till about 32 weeks after conception, all pain-related mind networks stay considerably underdeveloped when compared with grownup brains. However then construction speeds up dramatically.
The sensory sides of ache – the elemental detection of destructive stimuli – mature first, changing into practical round 34 to 36 weeks of being pregnant. The emotional parts that make ache distressing observe in a while after, creating between 36 and 38 weeks. Alternatively, the cognitive centres answerable for consciously deciphering and comparing ache lag a long way in the back of, and stay in large part immature by the point of delivery, about 40 weeks after conception.
This staged construction means that whilst late-term foetuses and newborns can hit upon and reply to destructive stimuli, they almost definitely revel in ache very otherwise from older kids and adults. Most importantly, newborns almost definitely can’t consciously assessment their ache – they may be able to’t shape the concept: “This hurts and it’s bad!”
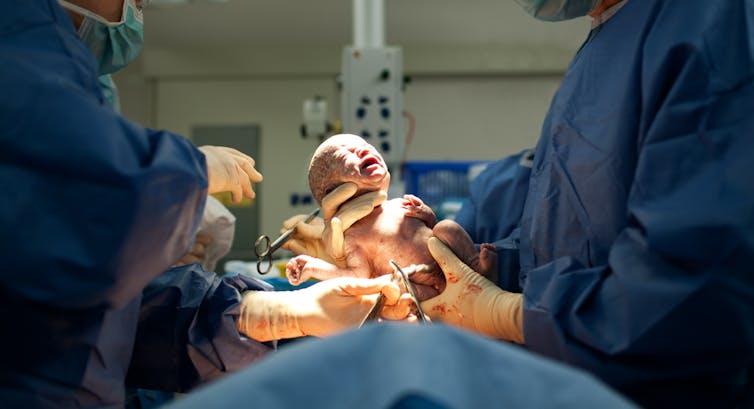
Does it harm?
Martin Valigursky/Shutterstock.com
A historical past of fixing perspectives
Those findings constitute the newest bankruptcy in a long-running clinical debate that has swung dramatically over the centuries, incessantly with profound penalties for clinical follow.
For many physiologists within the 18th and nineteenth centuries, the perceived delicacy of the newborn’s frame intended that it will have to be exquisitely delicate to ache, such a lot in order that some have had their doubts if babies ever felt anything. Start, specifically, was once alleged to be a particularly painful match for a new child.
Alternatively, advances in embryology all over the 1870s reversed this considering. As scientists found out that toddler brains and worried techniques had been a long way much less evolved than grownup variations, many started wondering whether or not young children may just in reality really feel ache in any respect. If the neural equipment wasn’t absolutely shaped, how may just authentic ache reports exist?
This scepticism had troubling sensible penalties. For almost a century, many docs carried out surgical operation on babies with out anaesthesia, satisfied that their sufferers had been necessarily resistant to struggling. The follow endured smartly into the Eighties in some clinical centres.
Against the tip of the twentieth century, public outrage concerning the clinical remedy of babies and new clinical effects grew to become the tables all over again. It was once discovered that newborns exhibited lots of the indicators (neurological, physiological and behavioural) of ache in the end, and that, if the rest, ache in babies had almost definitely been underestimated.
The ambiguous mind
The explanation why there was unending war of words about toddler ache is that we can not get admission to their reports without delay.
Positive, we will apply their behaviour and learn about their brains, however those aren’t the similar factor. Ache is an revel in, one thing that’s felt within the privateness of an individual’s personal thoughts, and that’s inaccessible to any individual however the individual whose ache it’s.
In fact, ache reports are generally accompanied by means of telltale indicators: be it the retraction of a frame phase from a pointy object or the larger process of positive mind areas. The ones we will measure. However the bother is that nobody behaviour or mind match is ever unambiguous.
The truth that an toddler pulls again their hand from a pin prick would possibly imply that it reports the pricking as painful, however it might also simply be an subconscious reflex. In a similar fashion, the truth that the mind is concurrently appearing pain-related process could also be an indication of ache, however it can be that the processing unfolds totally unconsciously. We merely don’t know.
Most likely the newborn is aware of. However even though they do, they may be able to’t let us know about their reports but, and till they may be able to, scientists are left guessing. Thankfully, their guesses are changing into more and more smartly knowledgeable, however for now, this is all they may be able to be – guesses.
What would it not take to get sure bet? Neatly, it might require a proof that connects our brains and behavior to our mindful reports. However thus far, no scientifically decent rationalization of this type has been drawing close.




