How does the digicam at the James Webb House Telescope paintings and spot to this point out? – Kieran G., age 12, Minnesota
Consider a digicam so robust it will possibly see mild from galaxies that shaped greater than 13 billion years in the past. That’s precisely what NASA’s James Webb House Telescope is constructed to do.
Because it introduced in December 2021, Webb has been orbiting greater than 1,000,000 miles from Earth, shooting breathtaking pictures of deep house. However how does it if truth be told paintings? And the way can it see to this point? The name of the game lies in its robust cameras – particularly ones that don’t see mild the way in which our eyes do.
I’m an astrophysicist who research galaxies and supermassive black holes, and the Webb telescope is an implausible device for staring at probably the most earliest galaxies and black holes within the universe.
When Webb takes an image of galaxy, astronomers like me are if truth be told seeing what that galaxy seemed like billions of years in the past. The sunshine from that galaxy has been touring throughout house for the billions of years it takes to succeed in the telescope’s replicate. It’s like having a time system that takes snapshots of the early universe.
Through the use of a large replicate to assemble historical mild, Webb has been finding new secrets and techniques concerning the universe.
A telescope that sees warmth
Not like common cameras and even the Hubble House Telescope, which take pictures of visual mild, Webb is designed to look a type of mild that’s invisible on your eyes: infrared mild. Infrared mild has longer wavelengths than visual mild, which is why our eyes can’t locate it. However with the correct tools, Webb can seize infrared mild to check probably the most earliest and maximum far-off gadgets within the universe.
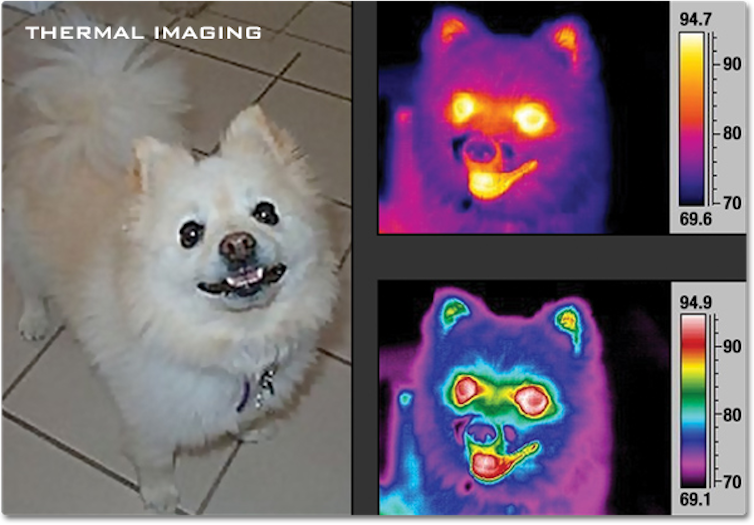
Infrared cameras, like night-vision goggles, help you ‘see’ the infrared waves emitting from heat gadgets reminiscent of people and animals. The temperatures for the photographs are in levels Fahrenheit.
NASA/JPL-Caltech
Even if the human eye can’t see it, other folks can locate infrared mild as a type of warmth the use of specialised generation, reminiscent of infrared cameras or thermal sensors. For instance, night-vision goggles use infrared mild to locate heat gadgets at nighttime. Webb makes use of the similar concept to check stars, galaxies and planets.
Why infrared? When visual mild from far flung galaxies travels around the universe, it stretches out. It’s because the universe is increasing. That stretching turns visual mild into infrared mild. So, essentially the most far-off galaxies in house don’t shine in visual mild anymore – they glow in faint infrared. That’s the sunshine Webb is constructed to locate.
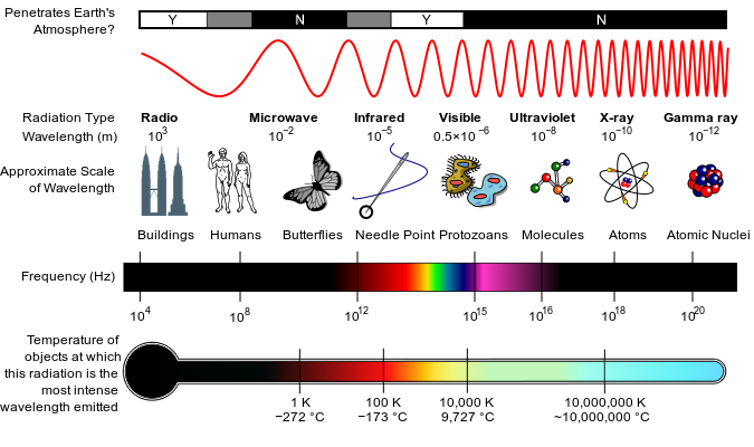
The rainbow of visual mild that you’ll see is just a small slice of all of the types of mild. Some telescopes can locate mild with an extended wavelength, reminiscent of infrared mild, or mild with a shorter wavelength, reminiscent of ultraviolet mild. Others can locate X-rays or radio waves.
Inductiveload, NASA/Wikimedia Commons, CC BY-SA
A golden replicate to collect the faintest glow
Prior to the sunshine reaches the cameras, it first needs to be amassed via the Webb telescope’s huge golden replicate. This replicate is over 21 toes (6.5 meters) large and fabricated from 18 smaller replicate items that have compatibility in combination like a honeycomb. It’s covered in a skinny layer of actual gold – no longer simply to seem fancy, however as a result of gold displays infrared mild extraordinarily neatly.
The replicate gathers mild from deep house and displays it into the telescope’s tools. The larger the replicate, the extra mild it will possibly gather – and the farther it will possibly see. Webb’s replicate is the most important ever introduced into house.
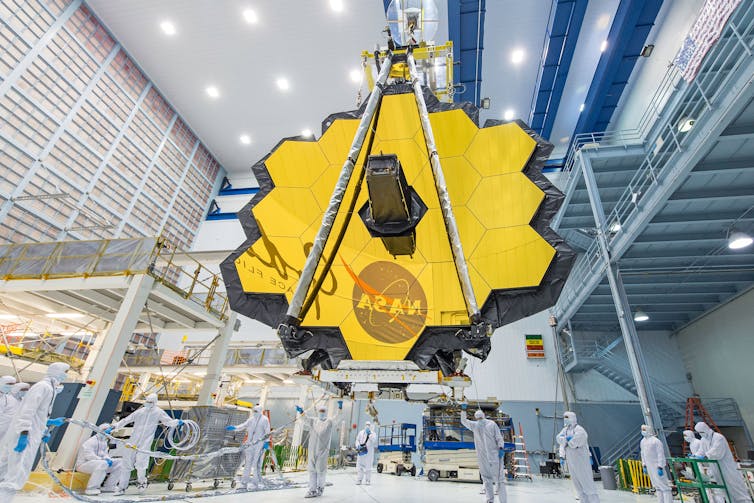

Webb’s 21-foot number one replicate, fabricated from 18 hexagonal mirrors, is covered with a plating of gold.
NASA
Throughout the cameras: NIRCam and MIRI
A very powerful “eyes” of the telescope are two science tools that act like cameras: NIRCam and MIRI.
NIRCam stands for near-infrared digicam. It’s the principle digicam on Webb and takes shocking pictures of galaxies and stars. It additionally has a coronagraph – a tool that blocks out starlight so it will possibly {photograph} very faint gadgets close to shiny resources, reminiscent of planets orbiting shiny stars.
NIRCam works via imaging near-infrared mild, the sort closest to what human eyes can virtually see, and splitting it into other wavelengths. This is helping scientists be informed no longer simply what one thing seems like however what it’s fabricated from. Other fabrics in house take in and emit infrared mild at explicit wavelengths, developing a type of distinctive chemical fingerprint. Through learning those fingerprints, scientists can discover the homes of far-off stars and galaxies.
MIRI, or the mid-infrared device, detects longer infrared wavelengths, that are particularly helpful for recognizing cooler and dustier gadgets, reminiscent of stars which are nonetheless forming within clouds of gasoline. MIRI will even lend a hand to find clues concerning the varieties of molecules within the atmospheres of planets that would possibly fortify existence.
Each cameras are way more delicate than the usual cameras used on Earth. NIRCam and MIRI can locate the tiniest quantities of warmth from billions of light-years away. In the event you had Webb’s NIRCam as your eyes, it is advisable to see the warmth from a bumblebee at the Moon. That’s how delicate it’s.
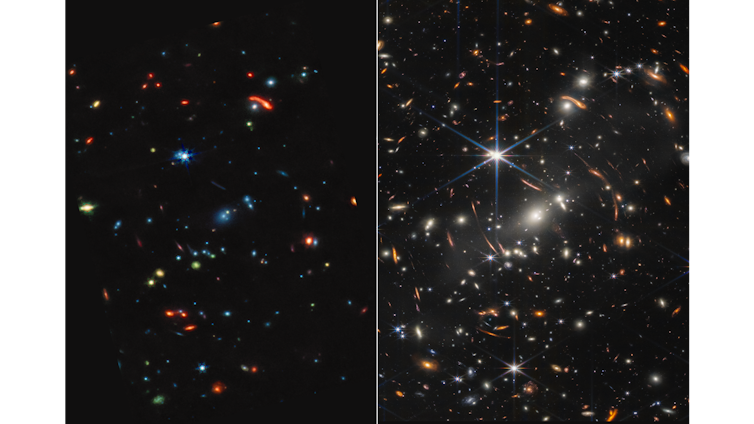

Webb’s first deep-field symbol: The MIRI symbol is at the left and the NIRCam symbol is at the proper.
NASA
As a result of Webb is attempting to locate faint warmth from far flung gadgets, it must stay itself as bloodless as imaginable. That’s why it carries a large solar defend concerning the measurement of a tennis court docket. This five-layer solar defend blocks warmth from the Solar, Earth or even the Moon, serving to Webb keep extremely bloodless: round -370 levels F (-223 levels C).
MIRI must be even chillier. It has its personal particular fridge, referred to as a cryocooler, to stay it chilled to almost -447 levels F (-266 levels C). If Webb had been even slightly heat, its personal warmth would drown out the far-off alerts it’s looking to locate.
Turning house mild into photos
As soon as mild reaches the Webb telescope’s cameras, it hits sensors referred to as detectors. Those detectors don’t seize common footage like a telephone digicam. As an alternative, they convert the incoming infrared mild into virtual information. That information is then despatched again to Earth, the place scientists procedure it into full-color pictures.
The colours we see in Webb’s photos aren’t what the digicam “sees” at once. As a result of infrared mild is invisible, scientists assign colours to other wavelengths to lend a hand us perceive what’s within the symbol. Those processed pictures lend a hand display the construction, age and composition of galaxies, stars and extra.
Through the use of a large replicate to assemble invisible infrared mild and sending it to super-cold cameras, Webb we could us see galaxies that shaped simply after the universe started.
And because interest has no age prohibit – adults, tell us what you’re questioning, too. We gained’t have the ability to solution each and every query, however we will be able to do our easiest.





