Reside and on-demand video constituted an estimated 66% of world web site visitors by way of quantity in 2022, and the highest 10 days for web site visitors in 2024 coincided with are living streaming occasions such because the Jake Paul vs. Mike Tyson boxing fit and protection of the NFL. Streaming permits seamless, on-demand get entry to to video content material, from on-line gaming to brief movies like TikToks, and longer content material reminiscent of motion pictures, podcasts and NFL video games.
The defining side of streaming is its on-demand nature. Believe the worldwide succeed in of a Joe Rogan podcast episode or the are living protection of the SpaceX Staff Dragon spacecraft release – each examples show how streaming connects tens of millions of audience to real-time and on-demand content material international.
I’m a pc scientist whose analysis contains cloud computing, which is the distribution of computing sources reminiscent of video servers around the web.
Netflix claimed that it supported 65 million concurrent streams for the Jake Paul vs. Mike Tyson boxing fit on Nov. 15, 2024, regardless that many customers reported technical problems.
‘Chunks’ of video
In relation to video content material – whether or not it’s a are living circulation or a prerecorded video – there are two main demanding situations to handle. First, video information is huge in measurement, making it time-consuming to transmit from the supply to units reminiscent of TVs, computer systems, capsules and smartphones.
2nd, streaming should be adaptive to house variations in customers’ units and web features. For example, audience with lower-resolution monitors or slower web speeds will have to nonetheless be capable of watch a given video, albeit in decrease high quality, whilst the ones with higher-resolution presentations and quicker connections experience the most efficient imaginable high quality.
To take on those demanding situations, video suppliers put into effect a chain of optimizations. Step one comes to fragmenting movies into smaller items, often known as “chunks.” Those chunks then go through a procedure known as “encoding and compression,” which optimizes the video for various resolutions and bitrates to fit more than a few units and community stipulations.
When a person requests an on-demand video, the machine dynamically selects the proper circulation of chunks in keeping with the features of the person’s instrument, reminiscent of display screen decision and present web velocity. The video participant at the person’s instrument assembles and performs those chunks in collection to create a continuing viewing enjoy.
For customers with slower web connections, the machine delivers lower-quality chunks to make sure clean playback. This is the reason it’s possible you’ll realize a drop in video high quality when your connection velocity is diminished. In a similar fashion, if the video pauses all over playback, it’s typically as a result of your participant is ready to buffer further chunks from the supplier.
Video streams come to customers at other high quality ranges in keeping with the person’s instrument and web connection.
Chetan Jaiswal
Coping with distance and congestion
Handing over video content material on a big scale, whether or not prerecorded or are living, poses an important problem when extrapolated to the immense collection of movies fed on globally. Streaming products and services like YouTube, Hulu and Netflix host huge libraries of on-demand content material, whilst concurrently managing numerous are living streams taking place international.
A apparently easy option to handing over video content material would contain construction a large information heart to retailer the entire movies and similar content material, then streaming them to customers international by way of the web. Alternatively, this technique isn’t appreciated as it comes with vital demanding situations.
One main factor is geographic latency, the place a person’s location relative to the knowledge heart impacts the lengthen they enjoy. For example, if a knowledge heart is positioned in Virginia, a person in Washington, D.C., would enjoy minimum lengthen, whilst a person in Australia would face for much longer delays because of the greater distance and the desire for the knowledge to traverse a couple of interconnected networks. This added trip time slows down content material supply.
Every other downside is community congestion. As extra customers international connect with the central information heart, the interconnecting networks turn into increasingly more busy, leading to irritating delays and video buffering. Moreover, when the similar video is shipped concurrently to a couple of customers, replica information touring over the similar web hyperlinks wastes bandwidth and additional congests the community.
A centralized information heart additionally creates a unmarried level of failure. If the knowledge heart stories an outage, no customers can get entry to their content material, main to an entire provider disruption.
Content material supply networks
To handle those demanding situations, maximum content material suppliers depend on content material supply networks. Those networks distribute content material thru globally scattered issues of presence, which might be clusters of servers that retailer copies of high-demand content material in the neighborhood. This way considerably reduces latency and improves reliability.
Content material supply community suppliers, reminiscent of Akamai and Edgio, put into effect two primary methods for deploying issues of presence.
The primary is the “Enter Deep” way, the place hundreds of smaller point-of-presence nodes are positioned nearer to customers, regularly inside web provider supplier networks. This guarantees minimum latency by way of bringing the content material as shut as imaginable to the tip person.
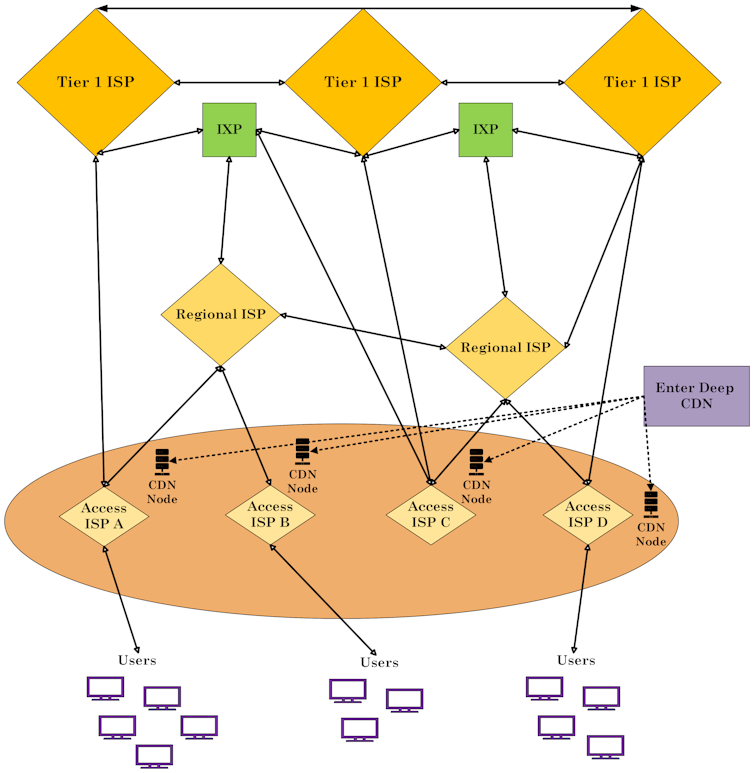
This diagram, with the web spine on the most sensible and customers on the backside, presentations the ‘Enter Deep’ option to hanging content material supply servers ‘deep’ within the community, with regards to customers.
Chetan Jaiswal
The second one technique is “Bring Home,” which comes to deploying masses of bigger point-of-presence clusters at strategic places, usually the place ISPs interconnect: web trade issues. Whilst those clusters are further from customers than within the Input Deep way, they’re better in capability, permitting them to care for increased volumes of site visitors successfully.
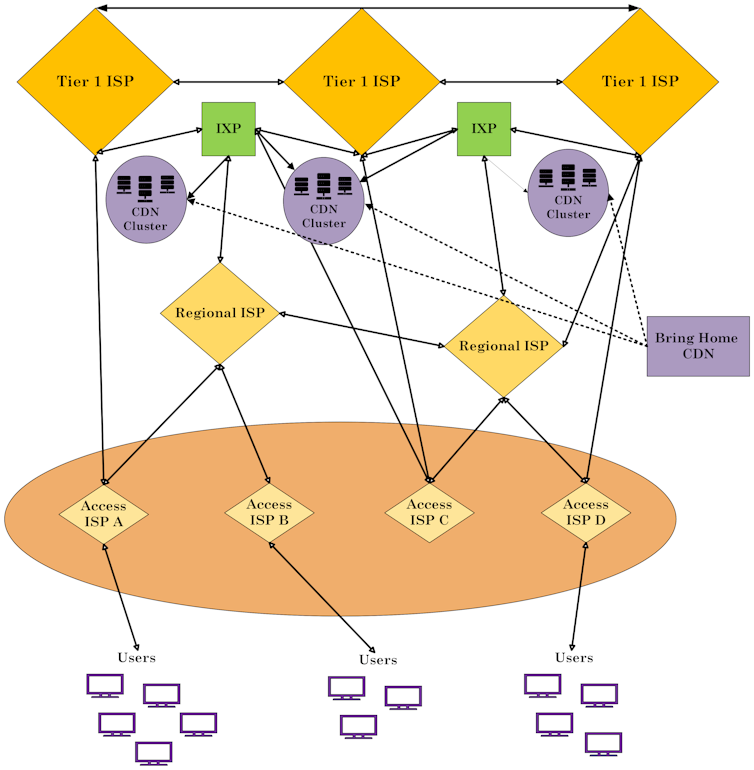
This diagram, with the web spine on the most sensible and customers on the backside, presentations the ‘Bring Home’ option to hanging content material supply servers between spine and regional web provider suppliers.
Chetan Jaiswal
Infrastructure for a hooked up global
Each methods purpose to optimize video streaming by way of lowering delays, minimizing bandwidth waste and making sure a continuing viewing enjoy for customers international.
The speedy enlargement of the web and the surge in video streaming – each are living and on call for – have remodeled how video content material is dropped at customers globally. Alternatively, the demanding situations of dealing with large quantities of video information, lowering geographic latency and accommodating various person units and web speeds require refined answers.
Content material supply networks have emerged as a cornerstone of contemporary streaming, enabling environment friendly and dependable supply of video. This infrastructure helps the rising call for for fine quality video and highlights the cutting edge approaches had to meet the expectancies of a hooked up global.





