Have you learnt the place your consuming water comes from?
In South Florida, consuming water comes from the Everglades, an unlimited panorama of wetlands that has lengthy filtered the water depended on by way of tens of millions of other folks.
However because the Everglades has gotten smaller during the last century, the area’s water provide and water high quality have turn into more and more threatened, together with by way of destructive algal blooms fueled by way of agriculture runoff. Now, the water provide faces some other emerging problem: saltwater intrusion.
Waterways reduce in the course of the Everglades.
South Florida Water Control District/Flickr, CC BY-ND
Protective South Florida’s water hinges on restoring the Everglades. That’s why, 25 years in the past, the government and universities introduced the arena’s biggest ecosystem recovery effort ever tried.
I’m concerned on this paintings as an ecosystem ecologist. The dangers I see recommend proceeding to revive the Everglades is extra a very powerful nowadays than ever.
What came about to the Everglades?
The Florida Everglades is a large mosaic of clean water, sawgrass marshes, cypress domes and tree islands, mangrove forests and seagrass meadows all attached by way of water.
However it’s part its authentic dimension. Within the early 1900s, the U.S. Military Corps of Engineers started putting in canals and levees to regulate flooding within the Everglades, which allowed other folks to construct farms and communities alongside its edges. The Tamiami Path turned into the primary highway around the Everglades in 1928. It attached Tampa to Miami, however the highway and canals bring to a halt or diverted probably the most herbal water go with the flow in South Florida.
Maps display how the Everglades modified over the years. Supply: USGS.
Since then, Florida’s economic system, agriculture and inhabitants have exploded – and with them has come a nutrient air pollution drawback within the Everglades.
The foremost crop, sugarcane, is grown in a area south of Lake Okeechobee overlaying 1,100 sq. miles that’s referred to as the Everglades Agricultural Space. Just about 80 heaps of phosphorus fertilizer from federally backed farm fields runs off into the Everglades wetlands each and every 12 months. And that has turn into a water high quality worry. Consuming water with increased nitrogen is connected to human well being issues, and increased phosphorus and related algal blooms could cause microbes to acquire toxins similar to mercury.
Wholesome wetlands can clear out the ones vitamins and different pollution, cleansing the water.
One of the tactics the Everglades filters water infected with phosphorus.
South Florida Water Control District
Rain falling within the Everglades percolates in the course of the porous limestone and recharges the Biscayne Aquifer, which provides consuming water for 1 in 3 Floridians.
However wetlands want time and area to serve as correctly, and the wear and tear from farm air pollution has harmed that herbal filtering gadget.
By way of the Nineties, Everglades wetlands and the natural world they enhance hit a important tension degree from increased concentrations of phosphorus, a nutrient in fertilizer that washes off farm fields and fuels the expansion of poisonous algal blooms and invasive species that may choke out local plant populations.
The adjustments ended in seagrass die-offs and popular invasion of sawgrass marshes by way of cattail and destructive algal blooms. Degraded wetlands can themselves turn into air pollution resources that may contaminate floor water and groundwater high quality by way of lowering oxygen within the water, which is able to hurt aquatic lifestyles, and freeing chemical compounds and vitamins as they decay.
An unlimited recovery marketing campaign
Congress licensed the Complete Everglades Recovery Plan in 2000 to enhance decreasing phosphorus concentrations by way of recreating huge wetlands spaces to take away extra vitamins and reestablishing extra of the herbal water intensity to strengthen local populations.
That recovery effort is making growth in reconnecting wetlands to herbal water flows by way of rehydrating huge spaces that have been bring to a halt. Phosphorus ranges are decrease in lots of wetlands that now stay hydrated longer, and in those wetlands contemporary water is recharging the aquifer, serving to maintain the consuming water provide.
Alternatively, delays in significantly vital parts of that paintings have left some wetlands in degraded stipulations for longer than anticipated, particularly in areas close to and downstream of the Everglades Agricultural Space, the place phosphorus concentrations stay stubbornly top.
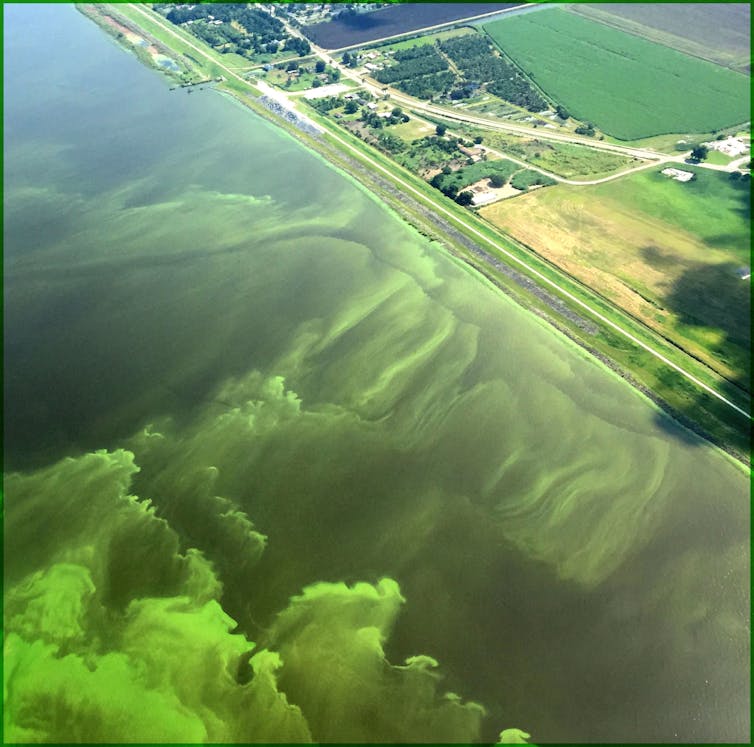

An algal bloom spreads in Florida’s Lake Okeechobee, on the middle of the Everglades.
Nicholas Aumen/USGS
South Florida continues to enjoy destructive algal blooms from phosphorus achieving rivers and the coast, leading to fish kills and the deaths of manatees. Purple tide can close down fishing and stay beach-going vacationers away, harming native economies. This air pollution is estimated to have value Florida’s economic system US$2.7 billion in 2018.
The surprising possibility: Saltwater
An unexpected risk has additionally began to creep into the Everglades: saltwater.
As sea degree rises, saltwater reaches additional inland, each in rivers and underground in the course of the porous limestone underneath South Florida. Saltwater intrusion additionally happens when wells draw down aquifers to offer water for consuming or irrigation. That saltwater is inflicting portions of the Everglades marshes, continuously known as a river of grass, to cave in into open water.
Saltwater intrusion into South Miami and the way Everglades recovery can assist. Supply: Emily Northrop and Rachael Johnson, College of Miami.
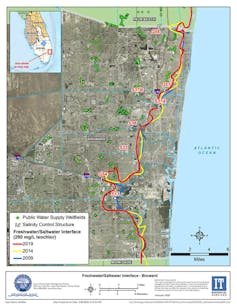
The pink line displays how a ways saltwater had intruded into aquifers underneath Castle Lauderdale as of 2019.
South Florida Water Control District
The lack of those freshwater marshes reduces the capability of the Everglades to take away phosphorus from the water. And that suggests extra vitamins flowing downstream, contaminating aquifers and inflicting destructive algal blooms to shape in coastal waters.
Scientists have realized that marsh vegetation want freshwater pulses throughout the rainy season, from April to November, to keep away from saltwater intrusion.
For instance, saltwater intruded about one mile inland between 2009 and 2019 in portions of the Castle Lauderdale house. Extra contemporary water is had to push the saltwater again out to sea.
Alternatively, the recovery effort used to be by no means meant to battle saltwater intrusion.
Causes for optimism
Regardless of the continued demanding situations, I’m constructive as a result of how scientists, policymakers and communities are running in combination to offer protection to the Everglades and consuming water.
I lead a part of that recovery paintings in the course of the Florida Coastal Everglades Lengthy Time period Ecological Analysis program. The trouble began at Florida World College on Would possibly 1, 2000, the similar 12 months the Everglades recovery plan used to be licensed by way of Congress.
Our analysis used to be used to set the degrees of vitamins allowable to nonetheless offer protection to the area’s water provides, and we have now been running for 25 years to scale back saltwater intrusion and phosphorus air pollution to verify consuming water for South Florida stays each contemporary and blank. We frequently use our analysis to tell water managers and policymakers of the most efficient practices to scale back saltwater intrusion and air pollution.

A roseate spoonbill hunts for dinner in Everglades Nationwide Park.
Nationwide Park Provider, R. Cammauf, by the use of Flickr
As saltwater intrusion continues to threaten South Florida’s freshwater aquifer, Everglades recovery and coverage can be more and more vital.
Everybody within the area can assist.
By way of rehabilitating degraded wetlands, taking into consideration extra contemporary water to go with the flow during the Everglades ecosystems, decreasing using contemporary water on lawns and vegetation, and reusing municipal water for outside wishes, South Florida can stay its consuming water protected for generations of long run citizens and guests. That is one thing that everybody can give a contribution to.

Mangroves alongside Turner River within the Everglades.
Chauncey Davis/Flickr, CC BY
Marjory Stoneman Douglas, Miami’s famend conservationist who helped determine the Everglades Nationwide Park, continuously stated, “The Everglades is a test. If we pass it, we may get to keep the planet.”



